A Tapestry Of Terrain: Exploring The Landforms Of Africa
A Tapestry of Terrain: Exploring the Landforms of Africa
Related Articles: A Tapestry of Terrain: Exploring the Landforms of Africa
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Tapestry of Terrain: Exploring the Landforms of Africa. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Tapestry of Terrain: Exploring the Landforms of Africa
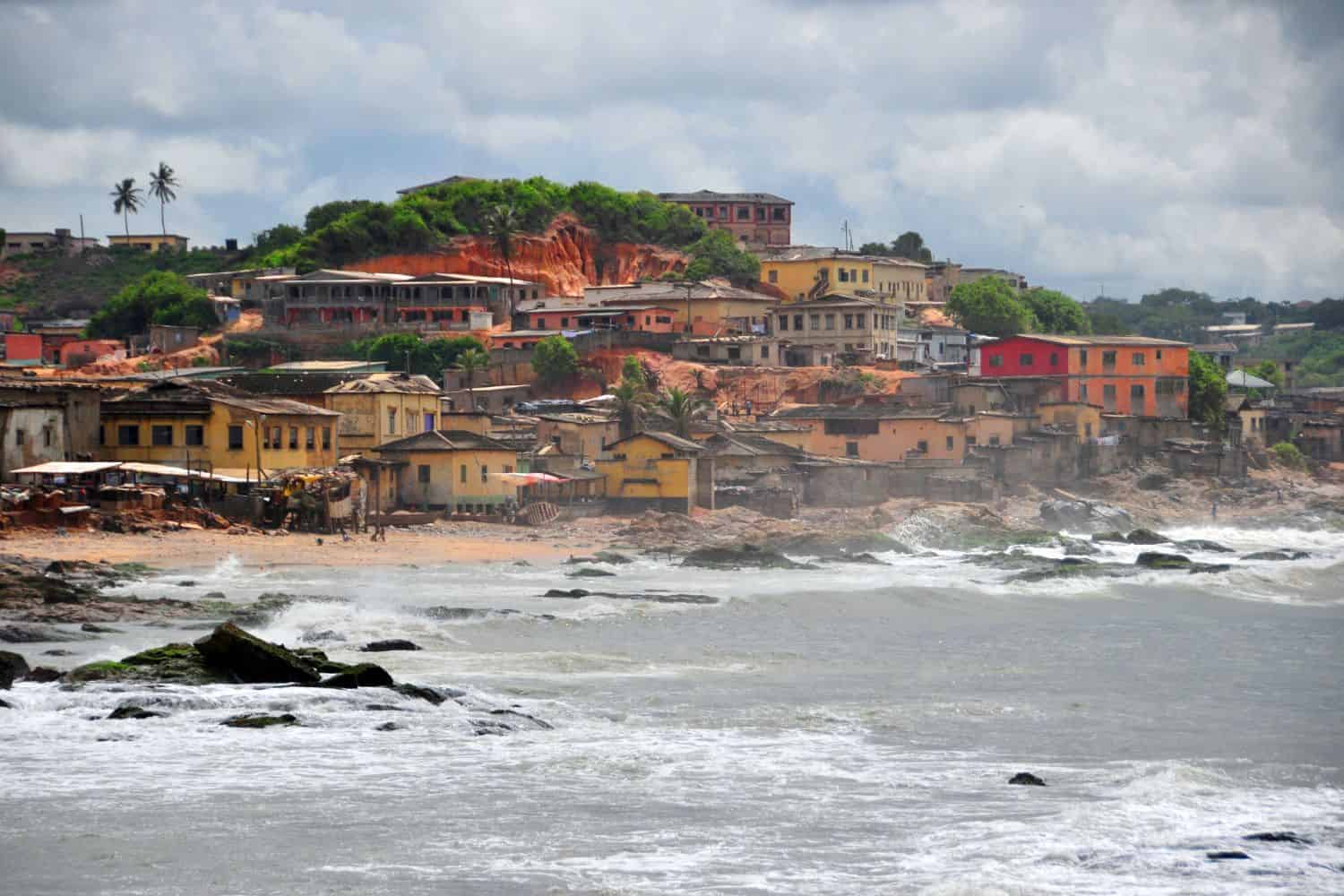

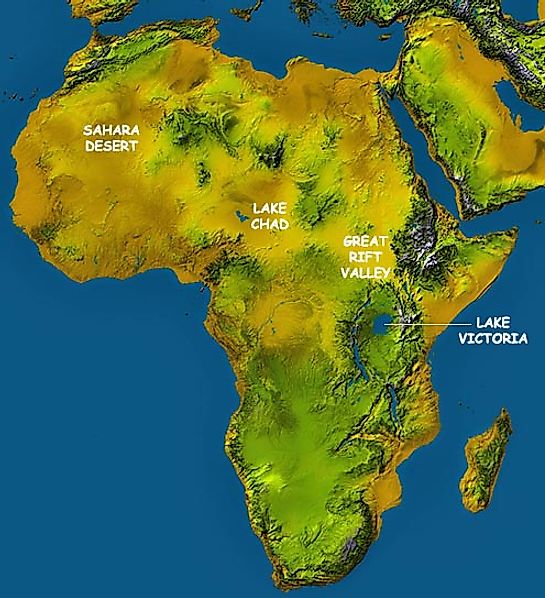
Africa, the second-largest continent, boasts a remarkably diverse landscape, a testament to its complex geological history and dynamic natural processes. From towering mountains to expansive deserts, from fertile valleys to vast plateaus, the continent’s landforms tell a story of ancient forces shaping its present-day geography. Understanding these landforms is crucial for comprehending Africa’s unique ecosystems, cultural diversity, and economic potential.
A Geographical Mosaic
Africa’s landforms can be broadly categorized into:
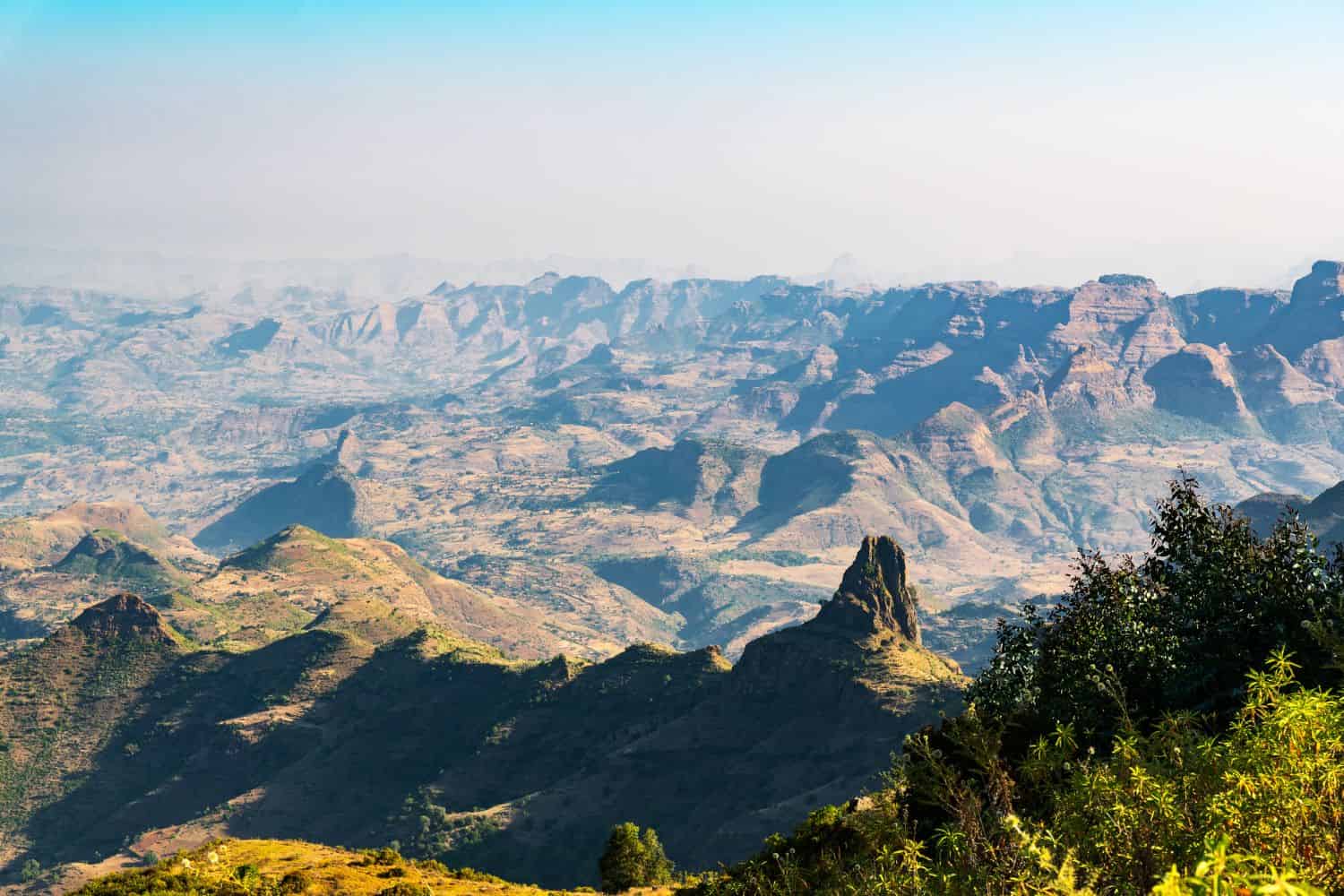
- Mountains: The continent’s most prominent mountain ranges are concentrated along its eastern and northwestern edges. The Atlas Mountains in North Africa form a dramatic arc, reaching heights of over 4,000 meters, while the East African Rift Valley hosts a chain of volcanoes and the iconic Mount Kilimanjaro, Africa’s highest peak.
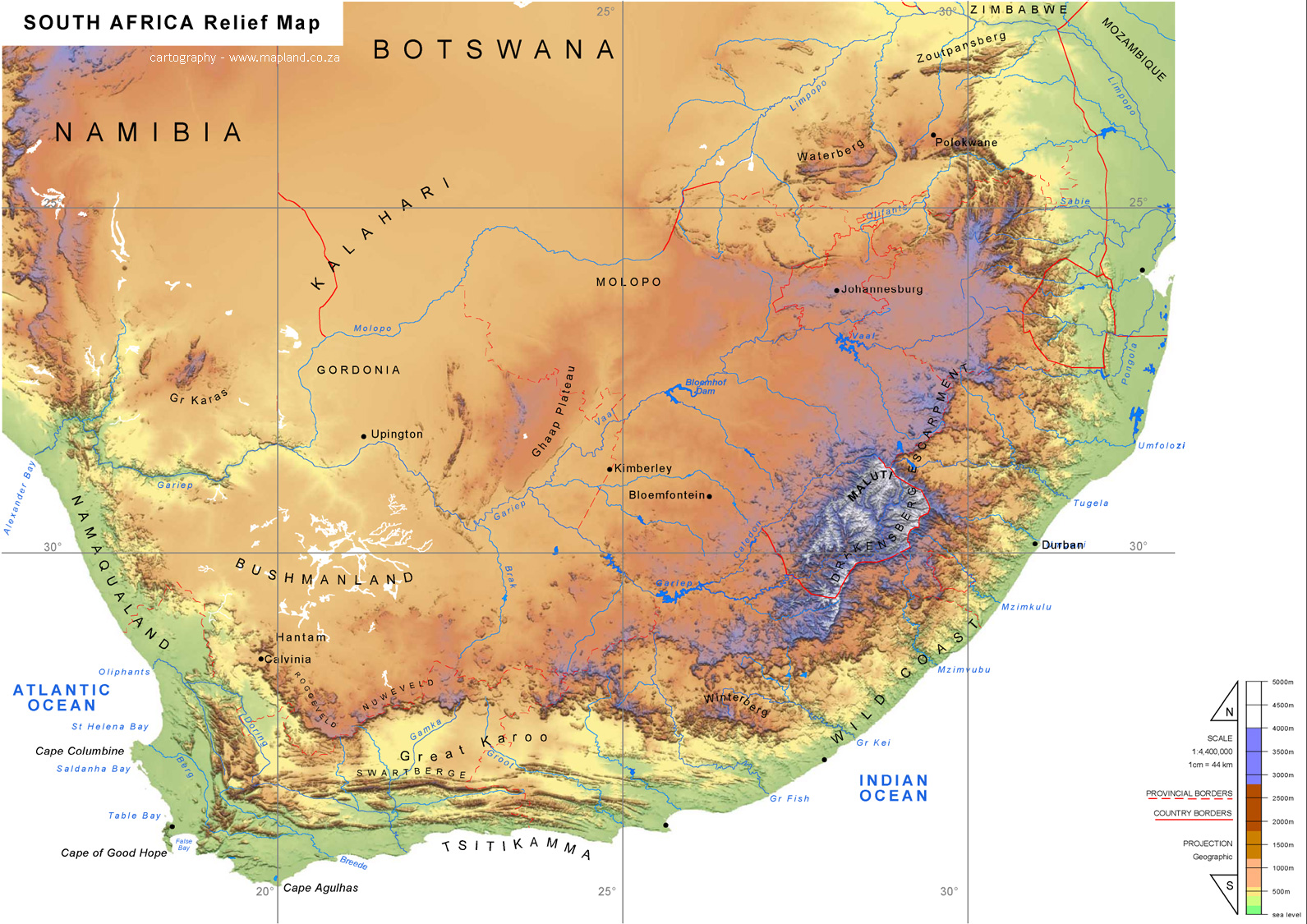
- Plateaus: Vast plateaus, elevated plains with relatively flat surfaces, dominate much of Africa. The Ethiopian Highlands, known for their volcanic origins and coffee production, are a prime example. The Southern African Plateau, characterized by its extensive grasslands and savannas, is another prominent plateau.
- Deserts: Africa is home to the world’s largest hot desert, the Sahara, stretching across North Africa. Other notable deserts include the Namib Desert along the southwestern coast and the Kalahari Desert in the south. These arid regions are shaped by wind erosion and sparse rainfall.
- Rivers and Lakes: Africa’s major rivers, such as the Nile, Congo, and Niger, are crucial for transportation, agriculture, and biodiversity. The continent also boasts several large lakes, including Lake Victoria, the largest lake in Africa by surface area, and Lake Tanganyika, the second deepest lake in the world.
- Coastal Zones: The continent’s extensive coastline is characterized by diverse features, including sandy beaches, rocky cliffs, mangrove swamps, and coral reefs. The Mediterranean Sea, the Red Sea, and the Indian Ocean all contribute to Africa’s coastline.
The Importance of Landforms
Africa’s diverse landforms play a critical role in shaping its environment, society, and economy:
- Biodiversity: The continent’s varied landscapes support a rich tapestry of flora and fauna. Mountains provide refuge for unique species, while the savannas are home to iconic wildlife like lions, elephants, and giraffes.
- Climate Regulation: Mountains influence rainfall patterns, creating distinct microclimates. Plateaus moderate temperatures, while deserts contribute to the global climate system through their influence on atmospheric circulation.
- Resource Distribution: Landforms influence the distribution of natural resources, including water, minerals, and fertile soil. Mountains often contain valuable mineral deposits, while rivers provide water for agriculture and hydroelectric power generation.
- Cultural Diversity: Africa’s landforms have influenced its cultural landscapes, with different communities adapting their lifestyles and traditions to the specific challenges and opportunities of their environment.
- Economic Development: Landforms play a crucial role in shaping economic activities, from agriculture and tourism to mining and energy production. Understanding the characteristics of different landforms is essential for sustainable development and resource management.
FAQs: Understanding the Landforms of Africa
1. What are the major mountain ranges in Africa?
Africa’s major mountain ranges include the Atlas Mountains in North Africa, the East African Rift Valley, and the Drakensberg Mountains in South Africa.
2. What is the significance of the East African Rift Valley?
The East African Rift Valley is a geologically active region where the Earth’s tectonic plates are pulling apart. This process has created a series of volcanoes, fault lines, and dramatic landscapes, including the iconic Mount Kilimanjaro.
3. What are the factors that contribute to the formation of deserts in Africa?
Deserts in Africa are formed by a combination of factors, including low rainfall, high temperatures, and wind erosion. The Sahara Desert, for example, is influenced by the dry air masses that descend from the north, while the Namib Desert is shaped by the cold Benguela Current, which creates a dry, coastal environment.
4. How do rivers and lakes contribute to the development of Africa?
Rivers and lakes are crucial for transportation, agriculture, and biodiversity in Africa. They provide water for drinking, irrigation, and hydroelectric power generation, and they support a wide range of aquatic life.
5. What are the challenges and opportunities associated with Africa’s landforms?
Africa’s landforms present both challenges and opportunities. For example, mountains can be difficult to access, but they also offer potential for tourism and mineral extraction. Deserts are challenging environments to live in, but they also offer opportunities for renewable energy development.
Tips for Exploring the Landforms of Africa
- Use a detailed map: A physical map of Africa is essential for understanding the continent’s diverse landforms.
- Read about the geological history: Researching the geological history of Africa can provide valuable insights into the formation of its landforms.
- Visit different regions: Travel to different parts of Africa to experience the continent’s diverse landscapes firsthand.
- Support conservation efforts: Contribute to organizations working to protect Africa’s unique ecosystems and biodiversity.
Conclusion
Africa’s landforms are a testament to the continent’s complex geological history and dynamic natural processes. From towering mountains to expansive deserts, from fertile valleys to vast plateaus, the continent’s diverse landscape is a source of both beauty and challenges. Understanding the characteristics and significance of Africa’s landforms is essential for appreciating its unique ecosystems, cultural diversity, and economic potential. By embracing the knowledge and insights gained from studying Africa’s landforms, we can foster a deeper understanding and appreciation of this remarkable continent.
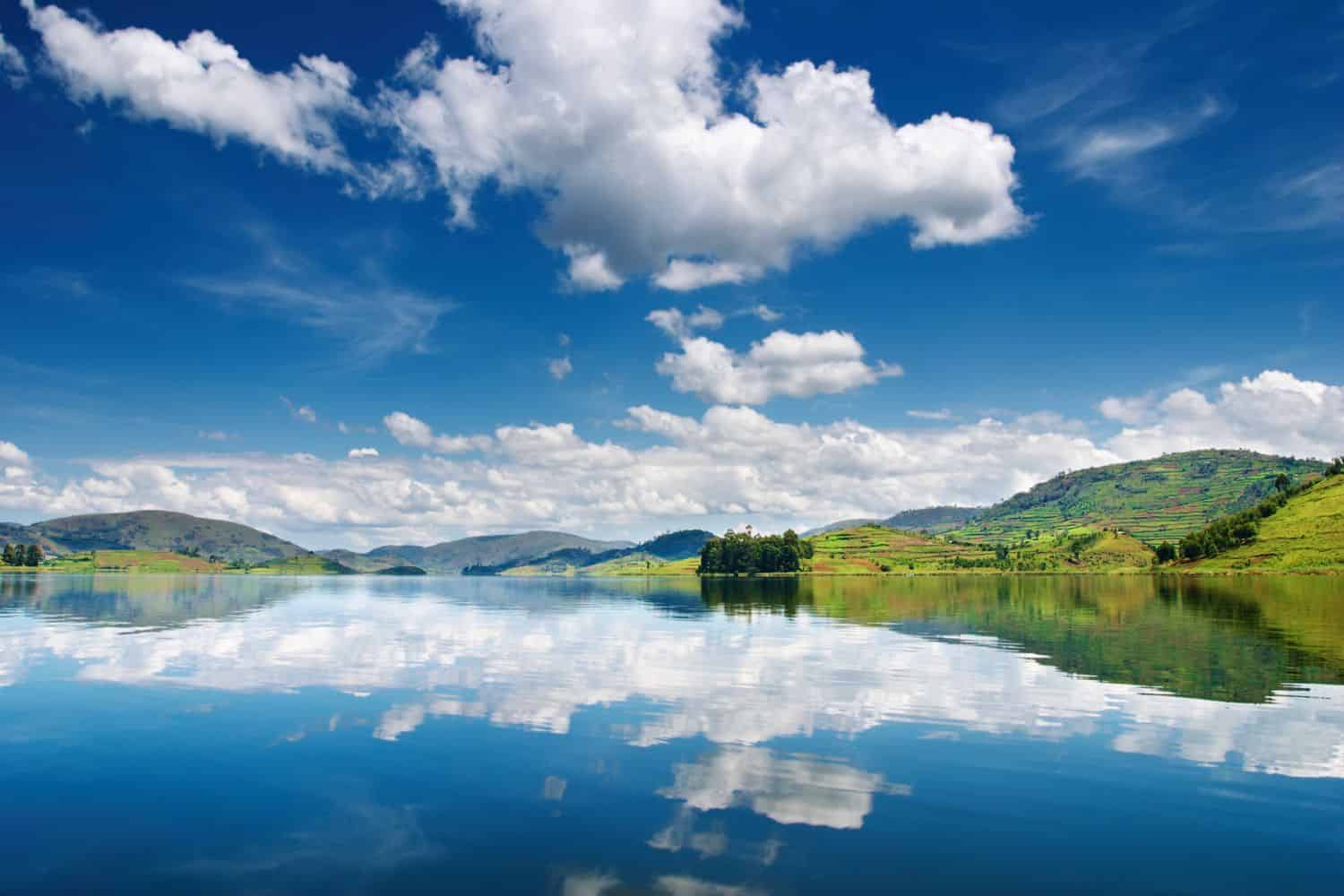






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Tapestry of Terrain: Exploring the Landforms of Africa. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Navigating The Digital Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide To AT&T’s Service Map For Internet
- Navigating The Keystone Resort Ski Map: A Comprehensive Guide To Exploring The Mountain
- Navigating The Waters: Understanding Nautical Mile Maps
- Navigating The Rails: A Comprehensive Guide To The RTD Train Map
- Navigating Baltimore County: A Guide To The Zoning Map
- A Comprehensive Guide To Parris Island, South Carolina: Navigating The Cradle Of Marines
- Navigating The Waters Of Smith Lake, Alabama: A Comprehensive Guide
- Navigating Kingsland, Texas: A Comprehensive Guide To The City’s Map
Leave a Reply