California: A Land Of Diverse Landscapes Revealed Through Physical Maps
California: A Land of Diverse Landscapes Revealed through Physical Maps
Related Articles: California: A Land of Diverse Landscapes Revealed through Physical Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to California: A Land of Diverse Landscapes Revealed through Physical Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
California: A Land of Diverse Landscapes Revealed through Physical Maps
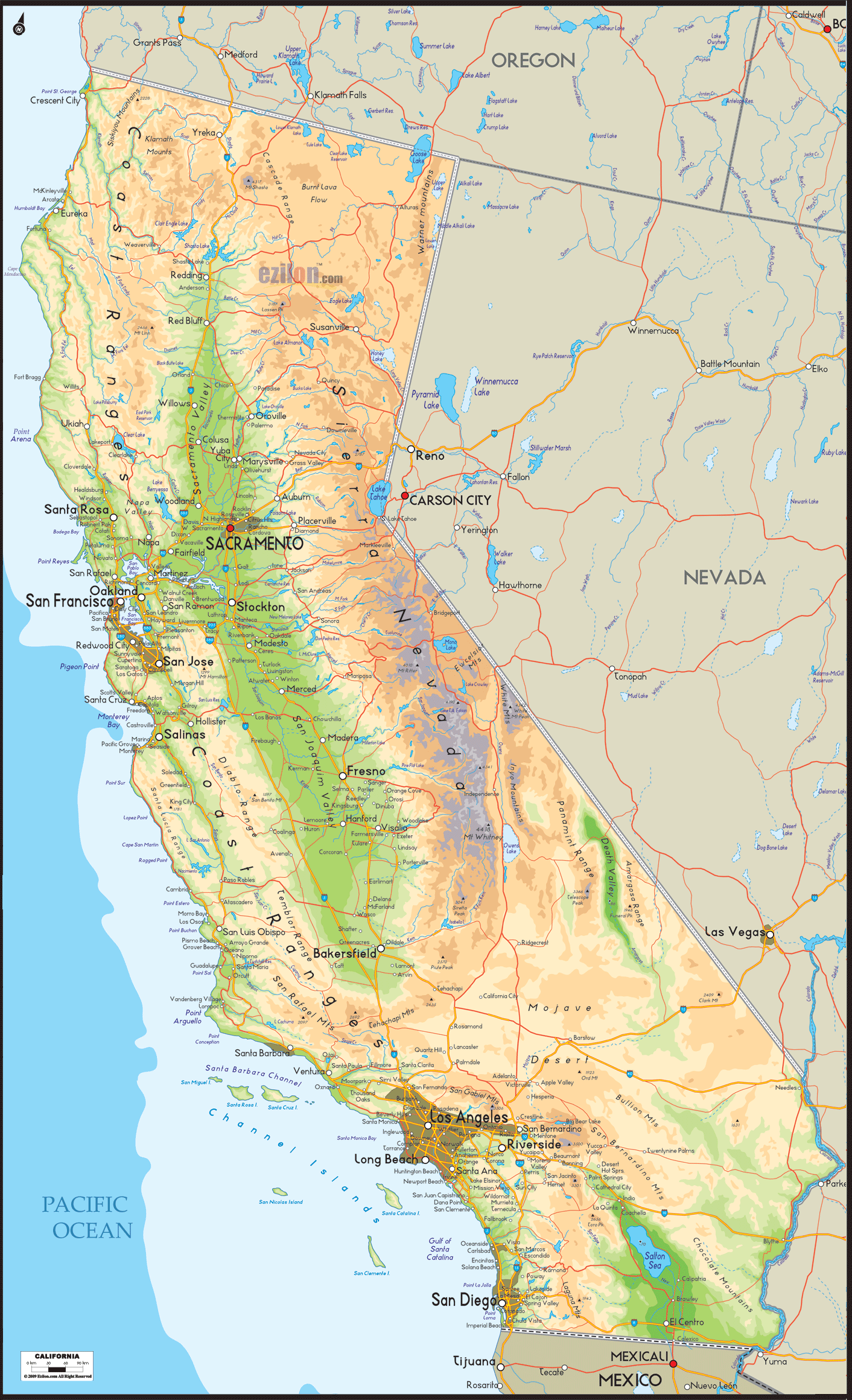
California, a state renowned for its diverse landscapes, vibrant culture, and technological prowess, presents a captivating study in physical geography. Its varied terrain, shaped over millennia by tectonic forces, volcanic activity, and climatic fluctuations, offers a rich tapestry of mountains, valleys, deserts, and coastlines. Understanding the physical characteristics of California is crucial for comprehending its unique ecological systems, its economic activities, and the challenges it faces in a rapidly changing world. Physical maps, with their detailed depiction of elevation, landforms, and waterways, provide an invaluable tool for exploring this intricate landscape.
A Tapestry of Terrain:
California’s physical geography is defined by its dramatic topography, ranging from the soaring heights of the Sierra Nevada to the sun-baked expanse of the Mojave Desert. The state is divided into six physiographic provinces, each with distinct geological and ecological characteristics:
-
The Coast Ranges: This province stretches along the Pacific coast, forming a series of low-lying mountains and valleys. The Coast Ranges are characterized by their rugged terrain, dense forests, and fertile agricultural lands.
-
The Sierra Nevada: This majestic mountain range, home to towering peaks like Mount Whitney, the highest point in the contiguous United States, runs along the eastern edge of California. The Sierra Nevada is a source of vital water resources, providing irrigation for agriculture and drinking water for millions of residents.
-
The Cascade Range: This volcanic mountain range extends northward from the Sierra Nevada, marking the eastern boundary of the Central Valley. Mount Shasta, a prominent stratovolcano, is a defining feature of this region.
-
The Central Valley: A vast, fertile plain lying between the Coast Ranges and the Sierra Nevada, the Central Valley is the heart of California’s agricultural industry. Its rich soils, abundant water resources, and temperate climate make it ideal for growing a wide variety of crops.
-
The Mojave Desert: This arid region, located in southeastern California, is characterized by its extreme temperatures, sparse vegetation, and unique geological formations. The Mojave Desert is home to a diverse array of desert flora and fauna, adapted to survive in harsh conditions.
-
The Colorado Desert: This desert region, located in the southeastern corner of California, is characterized by its low elevation, scorching temperatures, and vast sand dunes. The Colorado Desert is home to the Salton Sea, a large, shallow lake formed by accidental flooding.
The Shaping Forces:
California’s physical geography is a product of complex geological processes that have unfolded over millions of years. The state sits at the boundary of the Pacific and North American tectonic plates, making it a region of intense seismic activity. The San Andreas Fault, a major transform fault, runs along the western edge of the state, causing earthquakes and shaping the landscape.
Volcanic activity has also played a significant role in shaping California’s terrain. The Cascade Range, with its numerous volcanoes, is a testament to the state’s volcanic past. Volcanic eruptions have deposited ash and lava flows, creating fertile soils and unique geological features.
Climate, too, has been a major factor in shaping California’s landscape. The state experiences a wide range of climates, from the Mediterranean climate of the coast to the arid climate of the deserts. These climatic variations have led to the development of distinct plant and animal communities, each adapted to its specific environment.
The Significance of Physical Maps:
Physical maps provide a valuable tool for understanding and appreciating the complexities of California’s physical geography. They offer a clear visual representation of the state’s topography, including its mountains, valleys, deserts, and coastlines. This visual representation allows users to:
-
Gain a comprehensive understanding of the state’s diverse landscapes: Physical maps highlight the dramatic variations in elevation, landforms, and waterways, providing a clear picture of California’s varied terrain.
-
Identify key geological features: The maps depict major fault lines, volcanoes, and other geological formations, offering insights into the forces that have shaped the state’s landscape.
-
Understand the distribution of natural resources: Physical maps illustrate the location of water resources, forests, minerals, and other natural resources, providing a basis for resource management and conservation efforts.
-
Analyze the impact of physical geography on human activities: The maps reveal how the state’s topography influences transportation, agriculture, urban development, and other human activities.
-
Explore the relationships between physical geography and climate: Physical maps can be used to study the influence of elevation, landforms, and water bodies on climate patterns, providing insights into the state’s diverse climates.
FAQs about Physical Maps of California:
1. What are the key features depicted on a physical map of California?
A physical map of California typically showcases the state’s elevation, major landforms, rivers, lakes, and coastal features. It uses contour lines to indicate elevation changes, creating a three-dimensional representation of the terrain.
2. How can a physical map help me understand California’s climate?
Physical maps can help you visualize how elevation, proximity to the coast, and other geographic features influence climate patterns. For example, you can see how the Sierra Nevada acts as a rain shadow, creating a drier climate on its eastern slopes.
3. What are some important geological features to look for on a physical map of California?
Key geological features to identify on a physical map include the San Andreas Fault, the Sierra Nevada, the Cascade Range, and the Mojave Desert. These features represent the state’s tectonic activity, volcanic history, and arid landscapes.
4. How can physical maps be used in resource management and conservation efforts?
Physical maps provide valuable information about the distribution of water resources, forests, minerals, and other natural resources. This information can be used to develop sustainable management plans and conservation strategies.
5. What are some of the challenges faced by California due to its physical geography?
California’s physical geography poses several challenges, including earthquakes, wildfires, droughts, and coastal erosion. Physical maps can help us understand the spatial distribution of these hazards and develop strategies to mitigate their impacts.
Tips for Using Physical Maps of California:
-
Pay attention to elevation: The contour lines on a physical map indicate changes in elevation, providing insights into the state’s mountainous terrain and valleys.
-
Identify major landforms: Look for the Sierra Nevada, the Coast Ranges, the Central Valley, and the deserts to understand the state’s diverse landscapes.
-
Trace the flow of rivers and streams: This will help you understand the distribution of water resources and their importance for agriculture and human settlements.
-
Locate major fault lines: The San Andreas Fault is a prominent feature on a physical map, highlighting the state’s seismic activity.
-
Consider the relationship between physical geography and climate: Observe how elevation, landforms, and proximity to the coast influence climate patterns across the state.
Conclusion:
Physical maps offer a powerful tool for understanding the complex physical geography of California. By visualizing the state’s elevation, landforms, waterways, and geological features, these maps provide insights into the forces that have shaped the landscape, the distribution of natural resources, and the challenges faced by California in the face of a changing environment. Whether you are a student of geography, a nature enthusiast, or simply interested in the diverse landscapes of California, a physical map can serve as an invaluable guide to exploring this remarkable state.








Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into California: A Land of Diverse Landscapes Revealed through Physical Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Navigating The Digital Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide To AT&T’s Service Map For Internet
- Navigating The Keystone Resort Ski Map: A Comprehensive Guide To Exploring The Mountain
- Navigating The Waters: Understanding Nautical Mile Maps
- Navigating The Rails: A Comprehensive Guide To The RTD Train Map
- Navigating Baltimore County: A Guide To The Zoning Map
- A Comprehensive Guide To Parris Island, South Carolina: Navigating The Cradle Of Marines
- Navigating The Waters Of Smith Lake, Alabama: A Comprehensive Guide
- Navigating Kingsland, Texas: A Comprehensive Guide To The City’s Map
Leave a Reply