Deciphering The Landscape: Understanding Map Elevation Lines
Deciphering the Landscape: Understanding Map Elevation Lines
Related Articles: Deciphering the Landscape: Understanding Map Elevation Lines
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Deciphering the Landscape: Understanding Map Elevation Lines. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Deciphering the Landscape: Understanding Map Elevation Lines
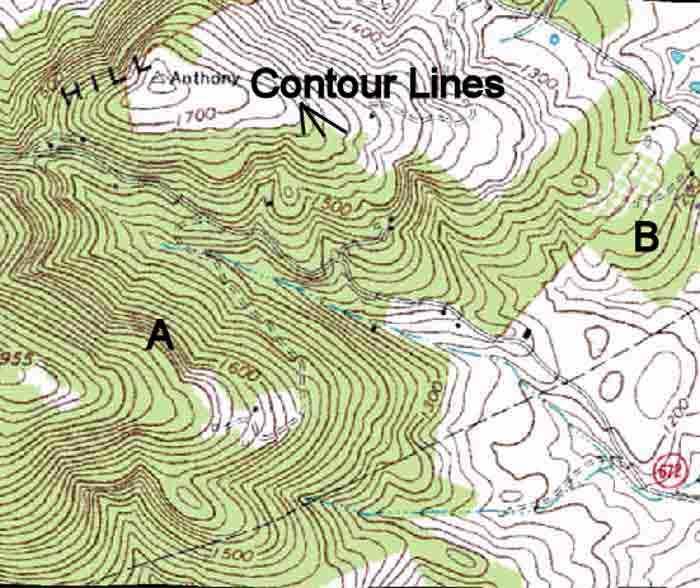
Maps are powerful tools that provide a visual representation of the world around us. While they depict the distribution of land and water, they also offer crucial insights into the terrain’s topography, a critical element for navigating, planning, and understanding the environment. Elevation lines, often referred to as contour lines, play a vital role in conveying this topographic information, transforming flat maps into three-dimensional representations of the Earth’s surface.
The Language of Contour Lines:
Contour lines are imaginary lines that connect points of equal elevation on a map. They essentially trace the shape of the land by depicting the rise and fall of the terrain. Imagine a landscape with a series of hills and valleys. Contour lines would follow the contours of these features, creating a visual representation of their shape and relative height.
Understanding the Fundamentals:
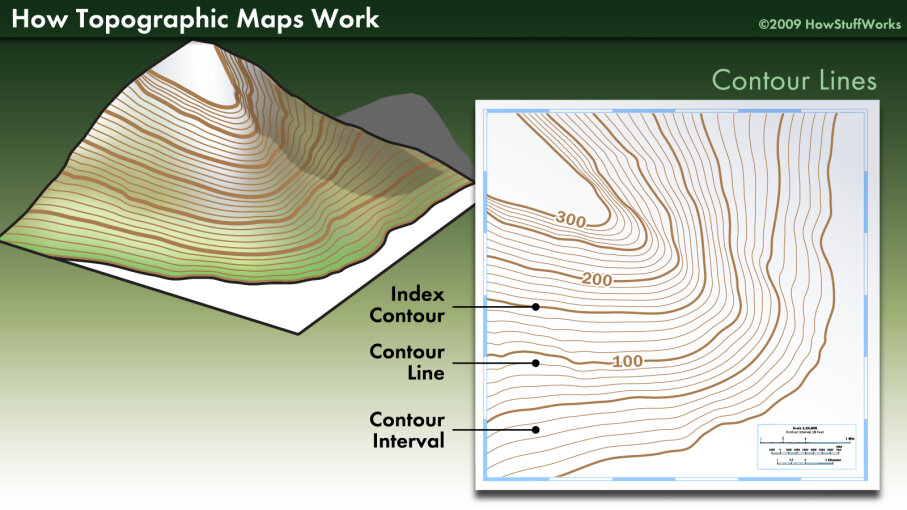
- Elevation: Each contour line represents a specific elevation, measured in feet or meters above sea level. This value is typically indicated on the map, usually near the bottom or top margin.
- Contour Interval: The difference in elevation between adjacent contour lines is known as the contour interval. This value remains constant throughout the map, ensuring consistency in the representation of elevation changes.
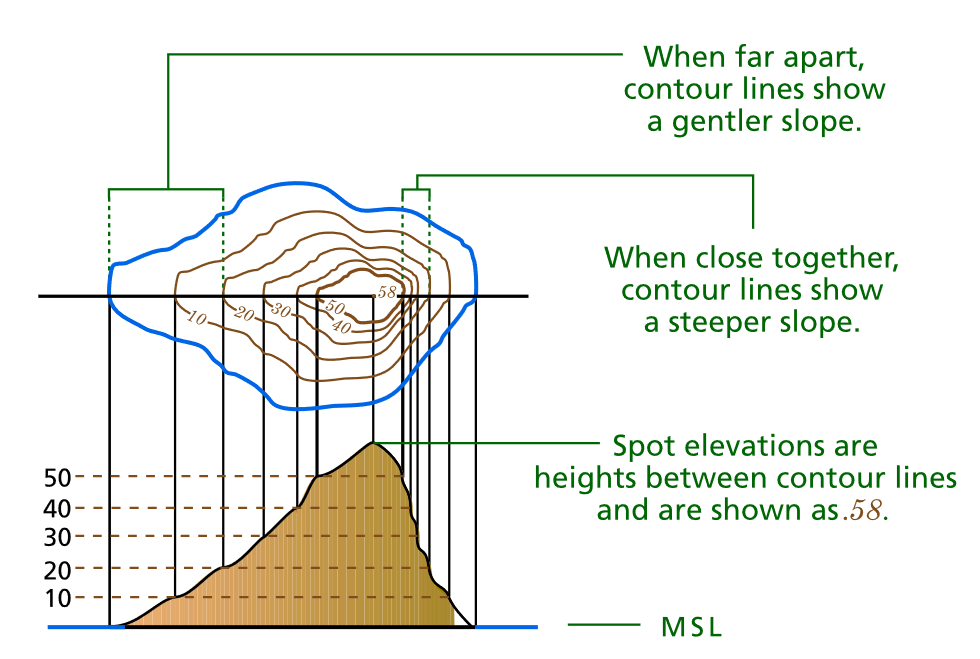
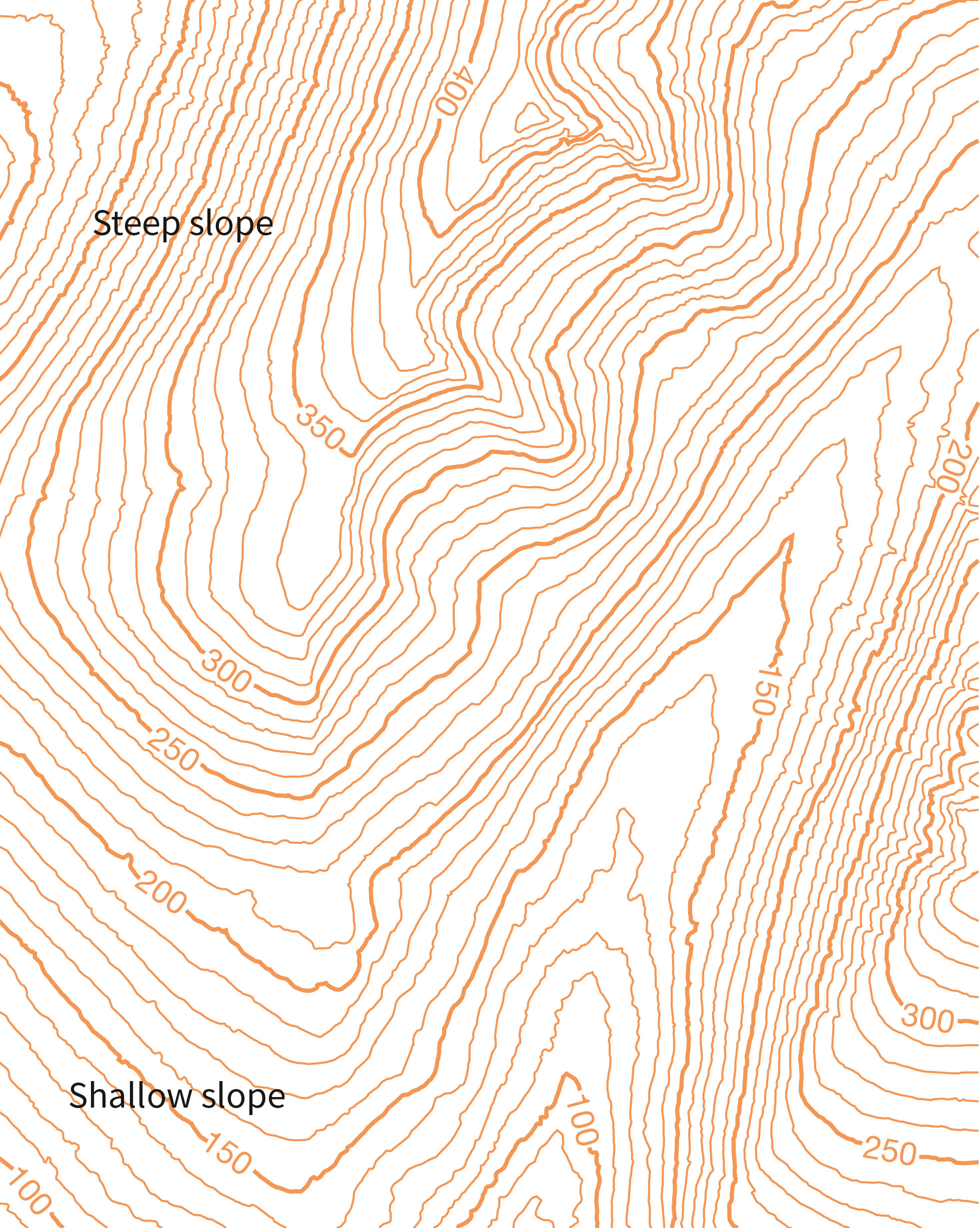
- Close Spacing: Closely spaced contour lines indicate a steep slope, as the terrain rises or falls rapidly over a short distance.
- Wide Spacing: Conversely, widely spaced contour lines suggest a gentle slope, signifying a gradual change in elevation.
Interpreting the Landscape:
Contour lines provide a wealth of information about the terrain:
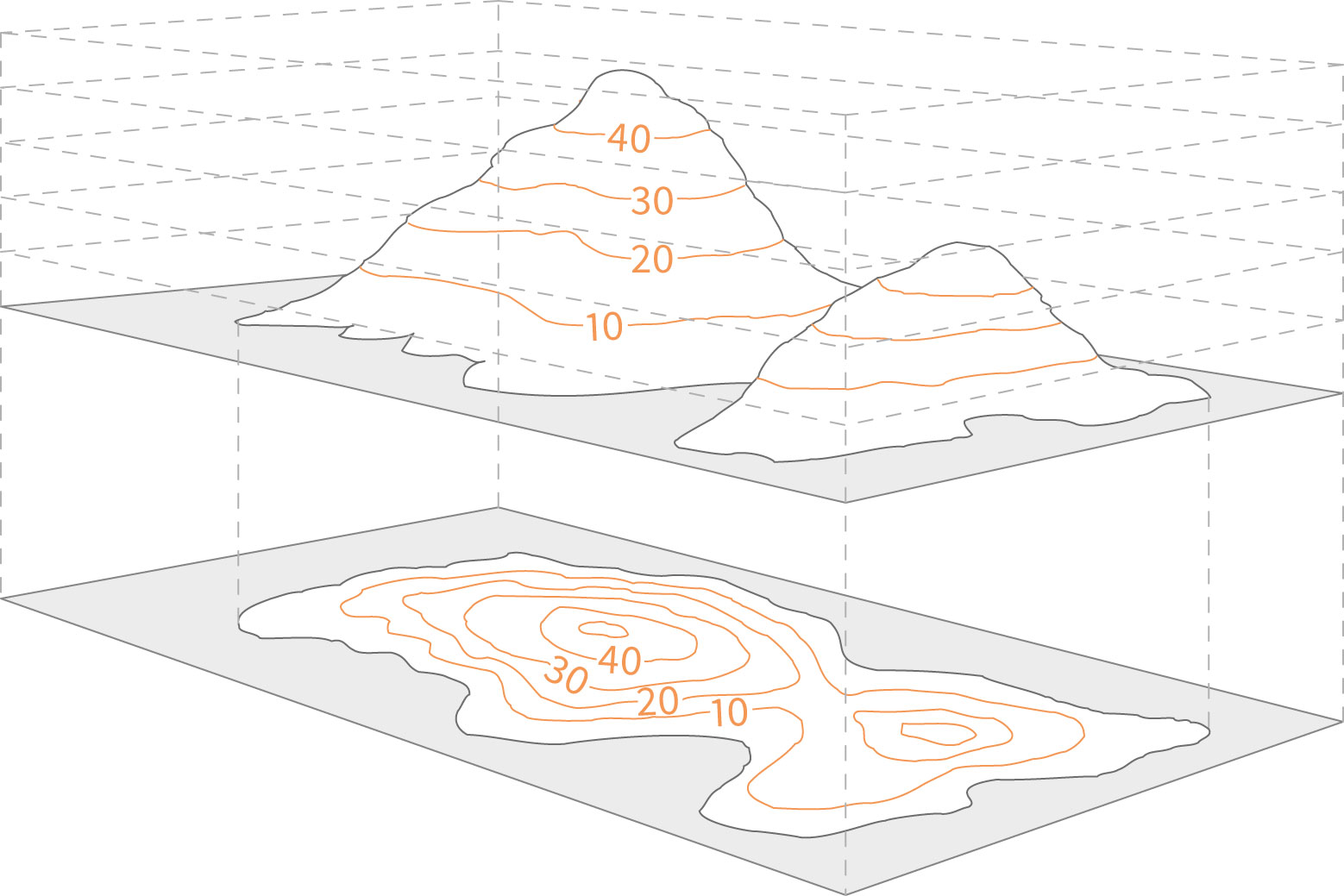
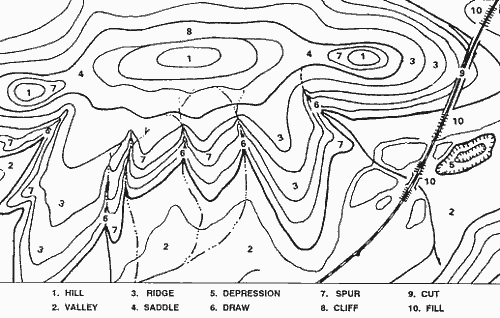
- Hills and Valleys: Closed loops of contour lines represent hills, with the highest elevation found in the center of the loop. Conversely, valleys are depicted by contour lines that point uphill, forming a "V" shape where they converge.
- Ridges and Depressions: Ridges, which are elongated high points, are represented by contour lines that form a series of "U" shapes. Depressions, or low points, are indicated by contour lines that form a series of "U" shapes pointing uphill.
- Slope Direction: The direction of the slope can be determined by observing the direction in which the contour lines bend. Lines bending towards the higher elevation indicate a downward slope, while lines bending towards the lower elevation suggest an upward slope.
Beyond the Basics: Additional Information:
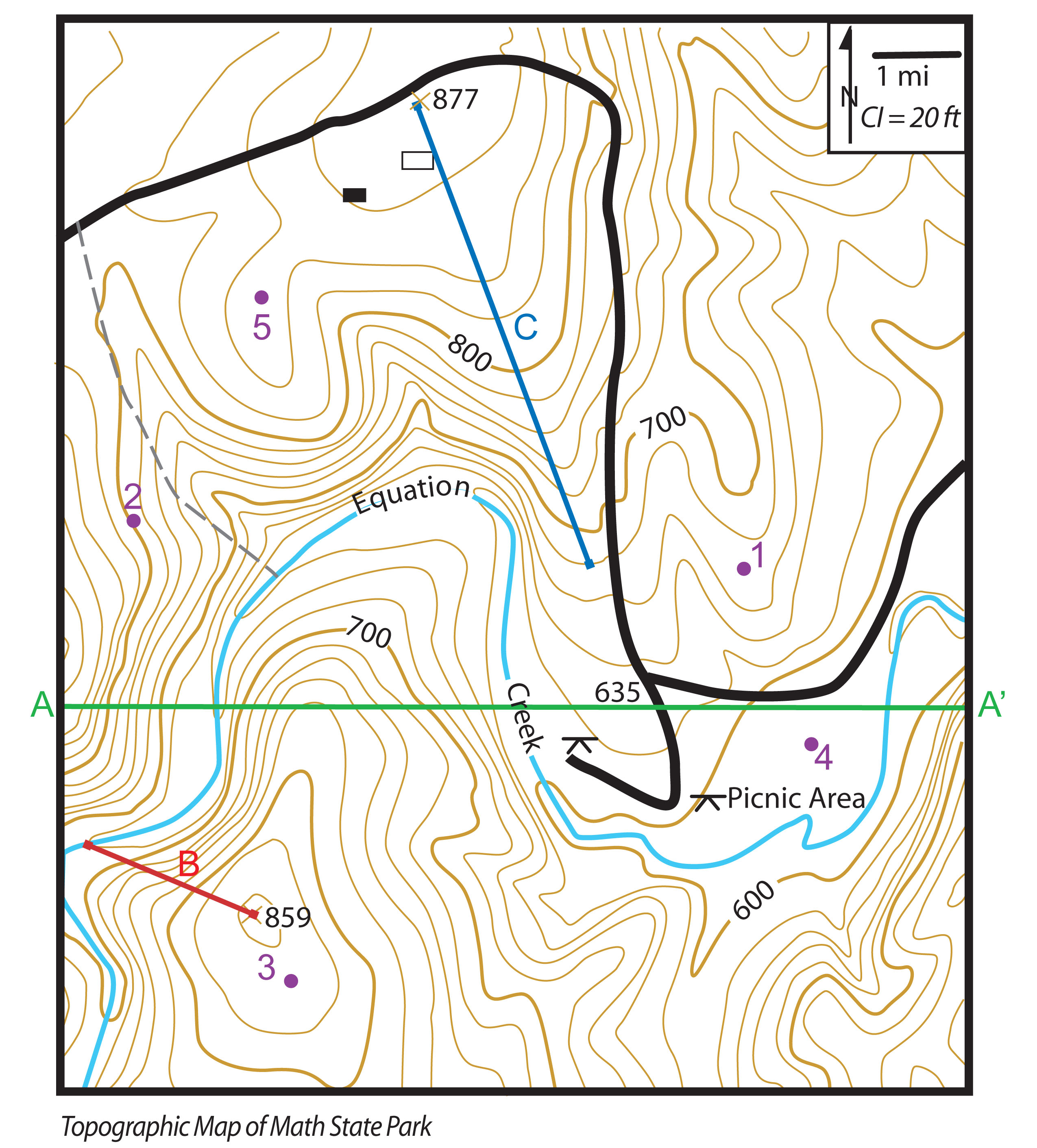
- Spot Elevations: Specific points on the map may be labeled with their exact elevation, offering precise information about particular locations.
- Index Contours: Every fifth contour line is often thicker or darker than the others, serving as index contours. They are usually labeled with their elevation, making it easier to read the map.
- Benchmarks: Permanent reference points, often marked by a triangle or a cross, are located on the ground and their elevations are precisely determined. These benchmarks provide a reliable source for verifying the accuracy of the map.
The Importance of Contour Lines:
Contour lines are essential tools for a wide range of applications:
- Navigation: Hikers, climbers, and outdoor enthusiasts rely on contour lines to navigate challenging terrains, plan routes, and assess the difficulty of trails.
- Land Management: Contour lines are used for land planning, surveying, and resource management, aiding in identifying suitable areas for construction, agriculture, or conservation efforts.
- Environmental Studies: Geographers, hydrologists, and environmental scientists utilize contour lines to analyze the distribution of water resources, understand erosion patterns, and assess potential flood risks.
- Military Applications: Military personnel use contour lines to plan maneuvers, determine optimal firing positions, and assess the tactical advantages of various terrain features.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What is the difference between contour lines and elevation lines?
Contour lines and elevation lines are essentially the same thing. They are both used to represent the elevation of the terrain on a map. The term "contour lines" is more commonly used, while "elevation lines" may be used interchangeably.
2. How do I determine the contour interval of a map?
The contour interval is usually indicated on the map itself, often near the bottom or top margin. If it is not clearly stated, you can calculate it by examining the elevation values of two adjacent contour lines.
3. Can I use contour lines to determine the steepness of a slope?
Yes, you can determine the steepness of a slope by observing the spacing of contour lines. Closely spaced lines indicate a steep slope, while widely spaced lines suggest a gentle slope.
4. How do I identify a hill on a map using contour lines?
Hills are represented by closed loops of contour lines. The highest elevation of the hill is located in the center of the loop.
5. How do I identify a valley on a map using contour lines?
Valleys are depicted by contour lines that point uphill, forming a "V" shape where they converge.
Tips for Using Contour Lines:
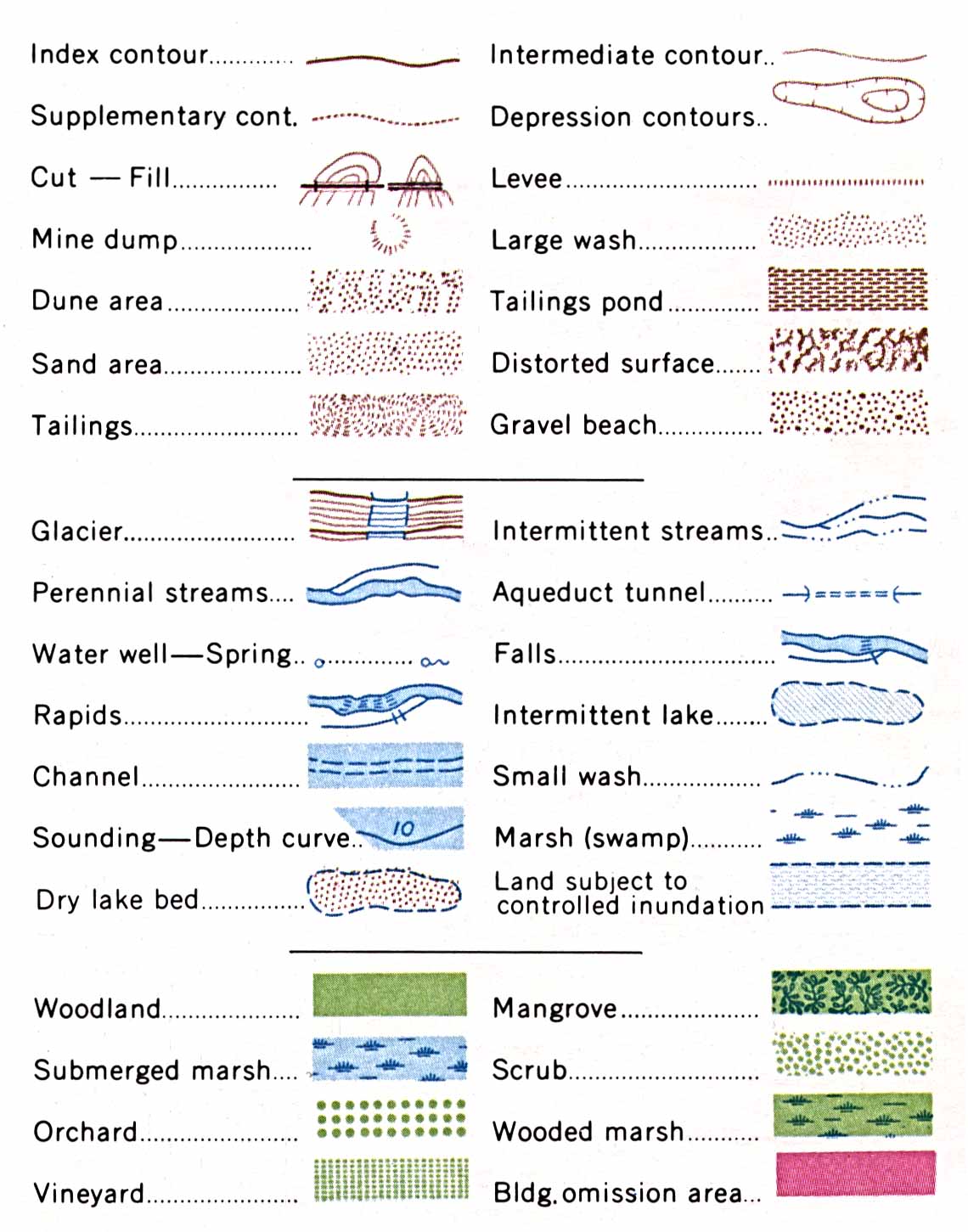
- Study the Map Legend: Familiarize yourself with the map’s contour interval and any other symbols or markings that may be used.
- Look for Patterns: Pay attention to the spacing and direction of contour lines to understand the shape and elevation of the terrain.
- Use a Pencil: Trace the contour lines with a pencil to better visualize the terrain’s features.
- Practice: The more you practice interpreting contour lines, the more comfortable you will become with understanding the information they convey.
Conclusion:
Contour lines are fundamental tools for understanding and interpreting the Earth’s topography. They transform flat maps into three-dimensional representations of the landscape, providing valuable information for navigation, planning, and environmental analysis. By mastering the language of contour lines, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of the terrain and its complexities, unlocking a new level of appreciation for the world around them. Whether navigating challenging trails, planning construction projects, or conducting environmental studies, contour lines remain indispensable tools for exploring and understanding the Earth’s diverse and ever-changing surface.

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Deciphering the Landscape: Understanding Map Elevation Lines. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Navigating The Digital Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide To AT&T’s Service Map For Internet
- Navigating The Keystone Resort Ski Map: A Comprehensive Guide To Exploring The Mountain
- Navigating The Waters: Understanding Nautical Mile Maps
- Navigating The Rails: A Comprehensive Guide To The RTD Train Map
- Navigating Baltimore County: A Guide To The Zoning Map
- A Comprehensive Guide To Parris Island, South Carolina: Navigating The Cradle Of Marines
- Navigating The Waters Of Smith Lake, Alabama: A Comprehensive Guide
- Navigating Kingsland, Texas: A Comprehensive Guide To The City’s Map
Leave a Reply