Mapping The Silent Threat: Understanding Hantavirus Distribution And Its Implications
Mapping the Silent Threat: Understanding Hantavirus Distribution and Its Implications
Related Articles: Mapping the Silent Threat: Understanding Hantavirus Distribution and Its Implications
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Mapping the Silent Threat: Understanding Hantavirus Distribution and Its Implications. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping the Silent Threat: Understanding Hantavirus Distribution and Its Implications
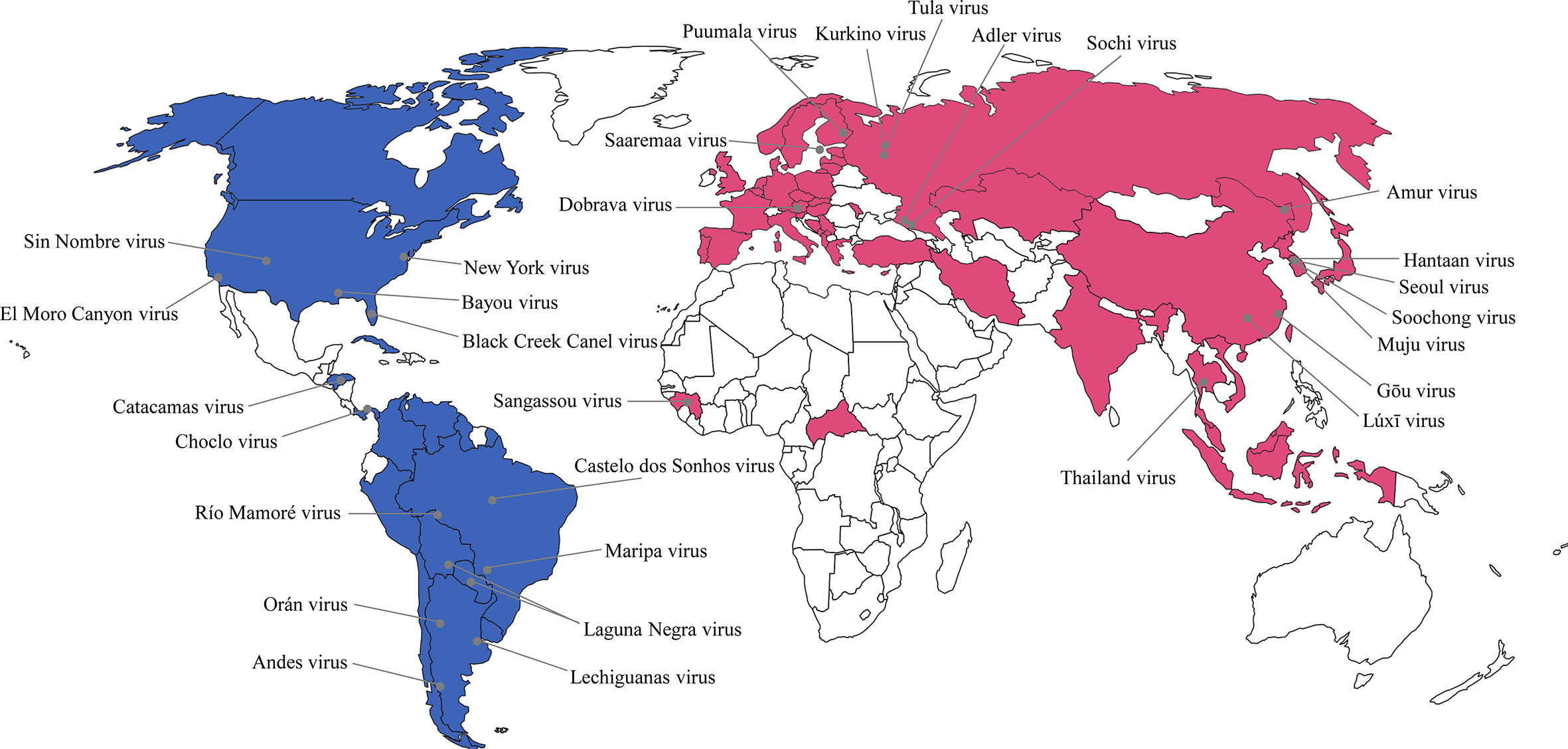
Hantaviruses, a group of RNA viruses carried by rodents, pose a significant public health threat globally. While often associated with remote regions, these viruses are present across continents, affecting both human and animal populations. Understanding the geographical distribution of hantaviruses is crucial for preventing disease outbreaks, implementing effective control measures, and safeguarding public health.
The Global Landscape of Hantavirus Distribution:
Hantavirus distribution is influenced by a complex interplay of factors, including rodent populations, climate, and human activities. A comprehensive map of hantavirus prevalence provides a visual representation of this complex reality, offering insights into:
- Endemic Regions: Identifying areas where hantaviruses are consistently present, allowing for targeted surveillance and prevention programs.
- Emerging Threats: Tracking the emergence of new hantavirus strains and their spread into previously unaffected regions.
- Risk Assessment: Evaluating the potential for disease transmission in specific locations, aiding in the development of risk mitigation strategies.
- Research and Development: Guiding research efforts towards understanding the factors driving hantavirus distribution and developing effective treatments and vaccines.
Hantavirus Map: A Vital Tool for Public Health
The development of accurate and detailed hantavirus maps requires collaborative efforts from researchers, public health officials, and local communities. Data collection methods include:
- Surveillance of rodent populations: Monitoring rodent populations for the presence of hantaviruses through trapping, serological testing, and genetic analysis.
- Human case reporting: Collecting data on confirmed and suspected cases of hantavirus pulmonary syndrome (HPS) or hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS).
- Environmental monitoring: Assessing the presence of hantaviruses in soil, water, and other environmental samples.
Interpreting the Map: Understanding the Significance of Geographic Distribution
Hantavirus maps are not static representations; they reflect the dynamic nature of these viruses and the ongoing changes in their distribution. Factors influencing shifts in hantavirus prevalence include:
- Climate change: Altered rainfall patterns, temperature fluctuations, and habitat changes can impact rodent populations and hantavirus transmission.
- Human activities: Deforestation, urbanization, and agricultural practices can disrupt rodent ecosystems, potentially increasing the risk of human exposure.
- Travel and trade: The movement of goods and people can facilitate the spread of hantaviruses to new regions.
Beyond the Map: Addressing the Challenge of Hantavirus Prevention
While the map provides valuable information, it is only one piece of the puzzle. Effective hantavirus prevention requires a multi-pronged approach, encompassing:
- Rodent control: Implementing measures to reduce rodent populations, such as sealing entry points in homes and buildings, removing food sources, and using safe and effective rodent control methods.
- Public awareness: Educating the public about hantavirus transmission, symptoms, and preventive measures, emphasizing the importance of avoiding contact with rodents and their droppings.
- Early diagnosis and treatment: Recognizing the signs and symptoms of HPS and HFRS, seeking prompt medical attention, and administering appropriate antiviral therapies.
- Research and development: Investing in research to develop vaccines and more effective antiviral treatments, as well as to improve our understanding of hantavirus ecology and transmission.
Frequently Asked Questions about Hantavirus Distribution
Q: What are the most common types of hantaviruses?
A: Several hantavirus species are responsible for human disease, including Sin Nombre virus (SNV) in North America, Seoul virus (SEOV) in Asia, and Hantaan virus (HTNV) in Asia and Europe.
Q: Are there any specific regions where hantaviruses are more prevalent?
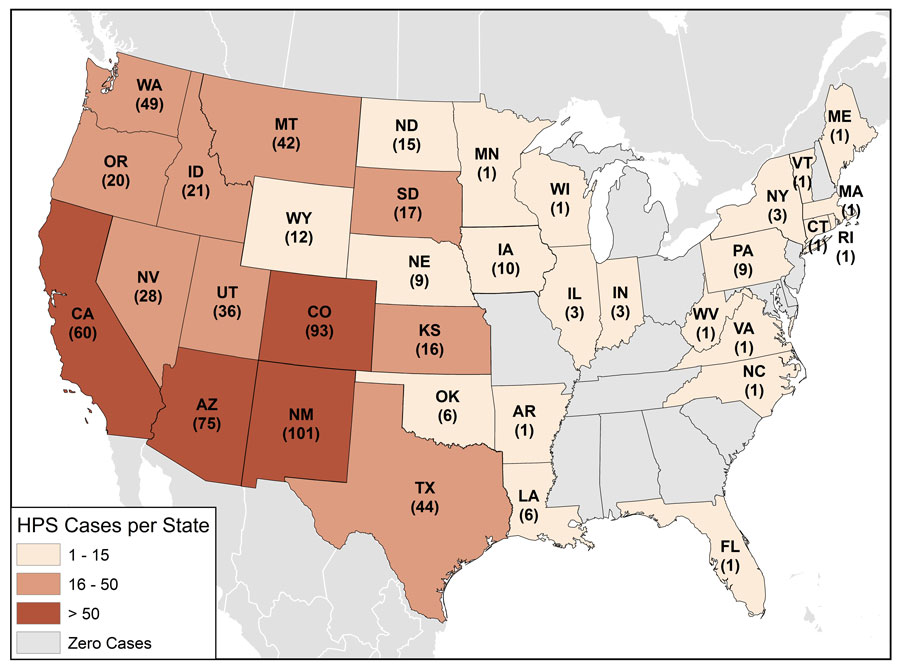
A: Hantaviruses are found worldwide, but certain regions have higher prevalence rates. For example, SNV is common in the southwestern United States, while HTNV is prevalent in East Asia.
Q: Can hantaviruses be transmitted from person to person?
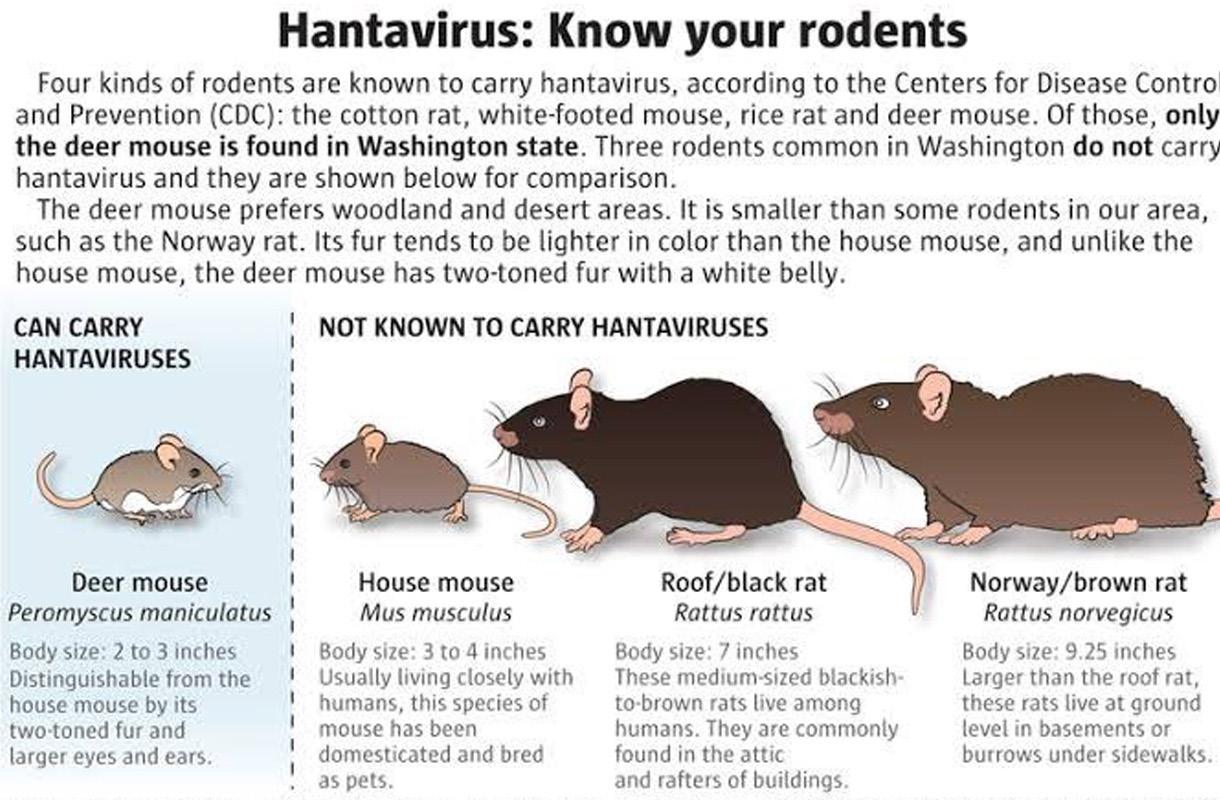
A: Hantaviruses are not typically transmitted directly from person to person. The primary mode of transmission is through contact with infected rodent droppings, urine, or saliva.
Q: What are the symptoms of hantavirus infection?
A: Symptoms of HPS and HFRS can vary but often include fever, muscle aches, fatigue, headache, and respiratory distress. In severe cases, HPS can lead to respiratory failure.
Q: Is there a cure for hantavirus infection?
A: There is no specific cure for hantavirus infection, but supportive care can help manage symptoms and improve outcomes. Antiviral medications may be used in some cases.
Tips for Preventing Hantavirus Infection:
- Avoid contact with rodents and their droppings: Seal up holes and cracks in your home, store food in rodent-proof containers, and use traps or other methods to control rodent populations.
- Wear gloves and a mask when cleaning areas potentially contaminated with rodent droppings: Dispose of contaminated materials safely.
- Wash hands thoroughly after handling rodents or cleaning areas where they may have been present: Use soap and water for at least 20 seconds.
- Be aware of the risks when camping or hiking: Avoid areas where rodents are known to be present, and use tents and sleeping bags that are rodent-proof.
Conclusion: A Collaborative Approach for a Shared Future
Understanding the global distribution of hantaviruses is crucial for safeguarding public health. By utilizing accurate and comprehensive maps, we can identify areas at risk, implement targeted prevention measures, and facilitate research efforts to develop effective treatments and vaccines. Through ongoing surveillance, public awareness, and collaborative efforts, we can mitigate the threat of hantaviruses and protect human health worldwide.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping the Silent Threat: Understanding Hantavirus Distribution and Its Implications. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Navigating The Digital Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide To AT&T’s Service Map For Internet
- Navigating The Keystone Resort Ski Map: A Comprehensive Guide To Exploring The Mountain
- Navigating The Waters: Understanding Nautical Mile Maps
- Navigating The Rails: A Comprehensive Guide To The RTD Train Map
- Navigating Baltimore County: A Guide To The Zoning Map
- A Comprehensive Guide To Parris Island, South Carolina: Navigating The Cradle Of Marines
- Navigating The Waters Of Smith Lake, Alabama: A Comprehensive Guide
- Navigating Kingsland, Texas: A Comprehensive Guide To The City’s Map
Leave a Reply