Navigating The Air We Breathe: Understanding The US Air Pollution Map
Navigating the Air We Breathe: Understanding the US Air Pollution Map
Related Articles: Navigating the Air We Breathe: Understanding the US Air Pollution Map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Air We Breathe: Understanding the US Air Pollution Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Air We Breathe: Understanding the US Air Pollution Map
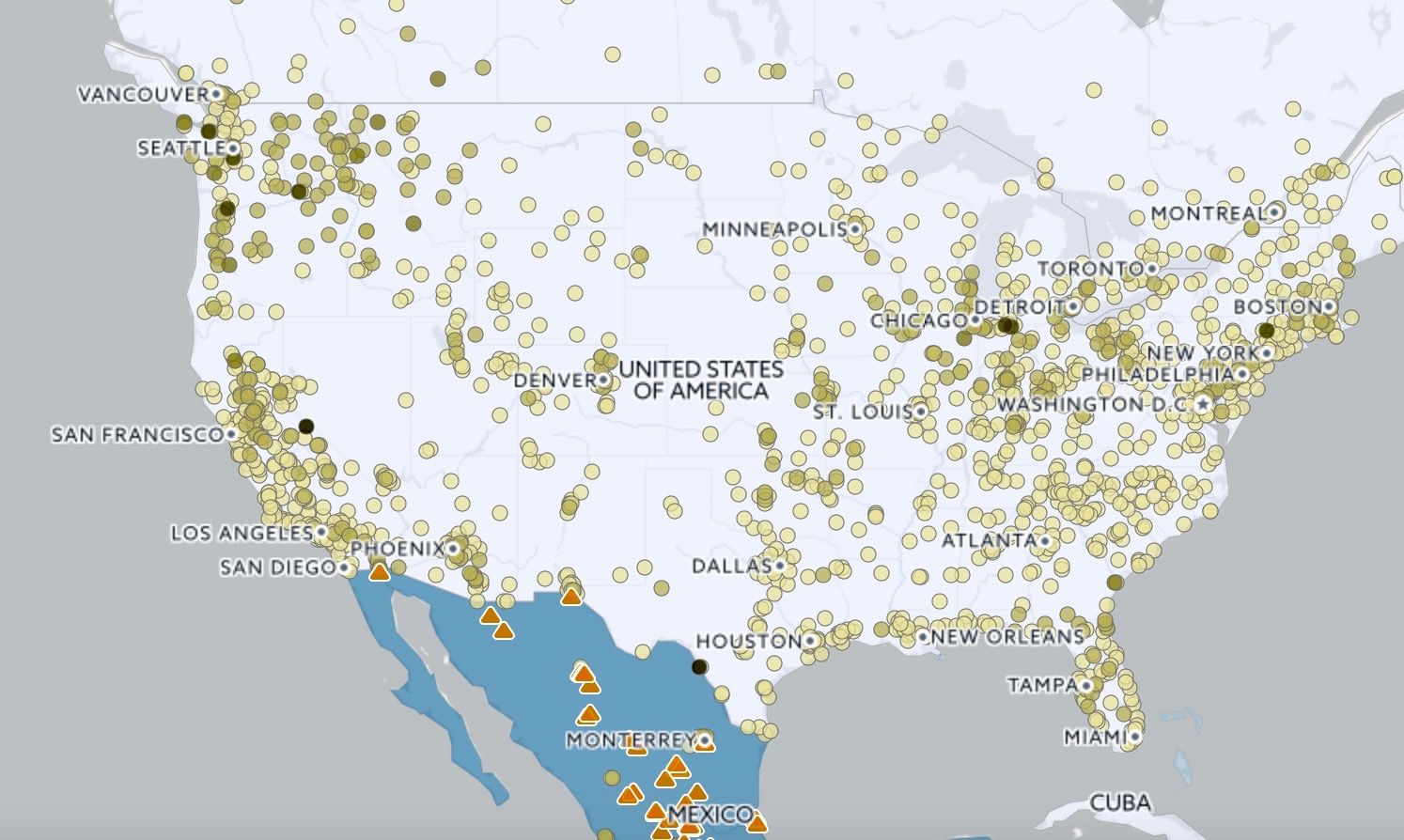
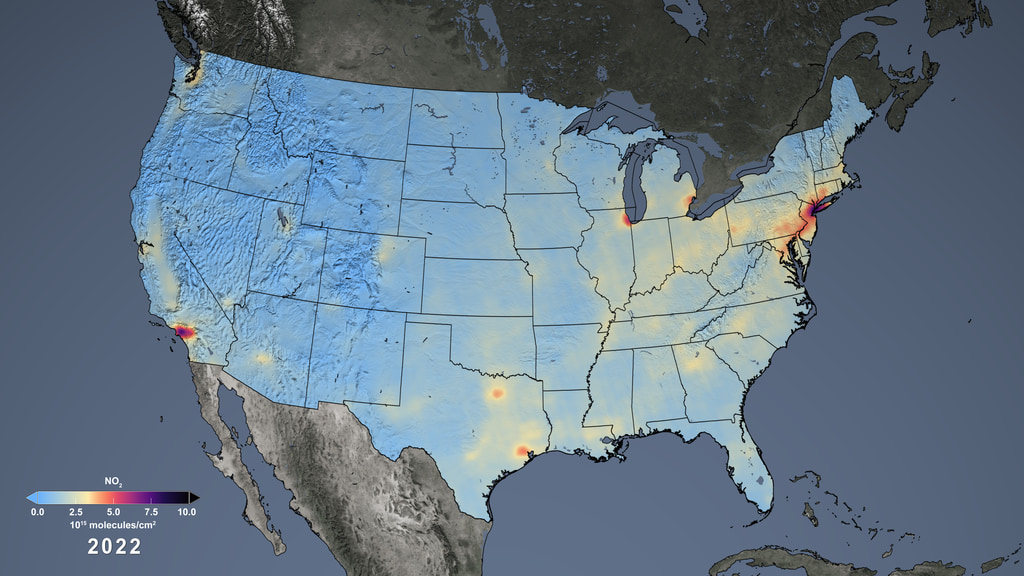
The United States Air Pollution Map is a vital tool for understanding the quality of the air we breathe. This interactive resource, developed and maintained by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), provides a comprehensive visual representation of air pollution levels across the nation. Its data, collected from a network of monitoring stations, empowers individuals, communities, and policymakers to make informed decisions about public health, environmental protection, and sustainable development.
Deciphering the Map: A Visual Guide to Air Quality
The US Air Pollution Map displays air quality data for various pollutants, including:
- Ozone (O3): A harmful gas formed by chemical reactions involving volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and nitrogen oxides (NOx) in the presence of sunlight. It can damage the lungs and contribute to respiratory problems.
- Particulate Matter (PM2.5 and PM10): Microscopic particles suspended in the air, categorized by their size. PM2.5, smaller than 2.5 micrometers in diameter, can penetrate deep into the lungs and contribute to heart and lung diseases.
- Carbon Monoxide (CO): A colorless, odorless gas produced by incomplete combustion of fossil fuels. It can reduce oxygen-carrying capacity in the blood and lead to cardiovascular problems.
- Sulfur Dioxide (SO2): A gas released primarily from burning fossil fuels, particularly coal. It contributes to acid rain and respiratory issues.
- Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2): A reddish-brown gas formed during the combustion of fossil fuels. It can damage the lungs and exacerbate respiratory conditions.
The map utilizes color-coded scales to represent air quality levels for each pollutant. These scales are based on the Air Quality Index (AQI), a standardized measure that ranges from 0 to 500. A higher AQI value indicates poorer air quality and increased health risks.
Beyond the Data: Unveiling the Significance of the US Air Pollution Map
The US Air Pollution Map serves as a powerful tool for:
- Public Awareness and Education: It empowers individuals to understand the air quality in their communities and take proactive steps to protect their health.
- Community Engagement: It encourages community members to participate in efforts to improve air quality, such as reducing emissions from vehicles and industrial sources.
- Policymaking and Regulation: It provides valuable data for policymakers to develop and implement effective air quality regulations, setting standards for emissions and monitoring compliance.
- Research and Monitoring: It serves as a vital resource for scientists and researchers studying air pollution patterns, trends, and impacts.
- Environmental Management: It helps organizations and businesses identify areas with high pollution levels and implement strategies to reduce their environmental footprint.
FAQs: Exploring the Nuances of Air Pollution Mapping
1. How is the air quality data collected?
Air quality data is collected from a network of monitoring stations strategically located across the country. These stations continuously measure pollutants using sophisticated instruments and transmit the data to the EPA.
2. How frequently is the air quality data updated?
The air quality data is updated in real-time, providing the most current information on air pollution levels. The EPA website and mobile app display the latest data and forecasts.
3. What are the health risks associated with air pollution?
Air pollution can have a significant impact on human health, contributing to respiratory problems, cardiovascular diseases, cancer, and other health issues. Vulnerable populations, such as children, the elderly, and individuals with pre-existing conditions, are particularly susceptible to the harmful effects of air pollution.
4. What steps can individuals take to reduce their exposure to air pollution?
Individuals can reduce their exposure to air pollution by:
- Minimizing driving: Walking, cycling, or using public transportation whenever possible.
- Avoiding outdoor activities during periods of high pollution: Checking air quality forecasts and limiting outdoor activities during times when pollution levels are elevated.
- Using air purifiers indoors: Filtering indoor air to reduce the presence of pollutants.
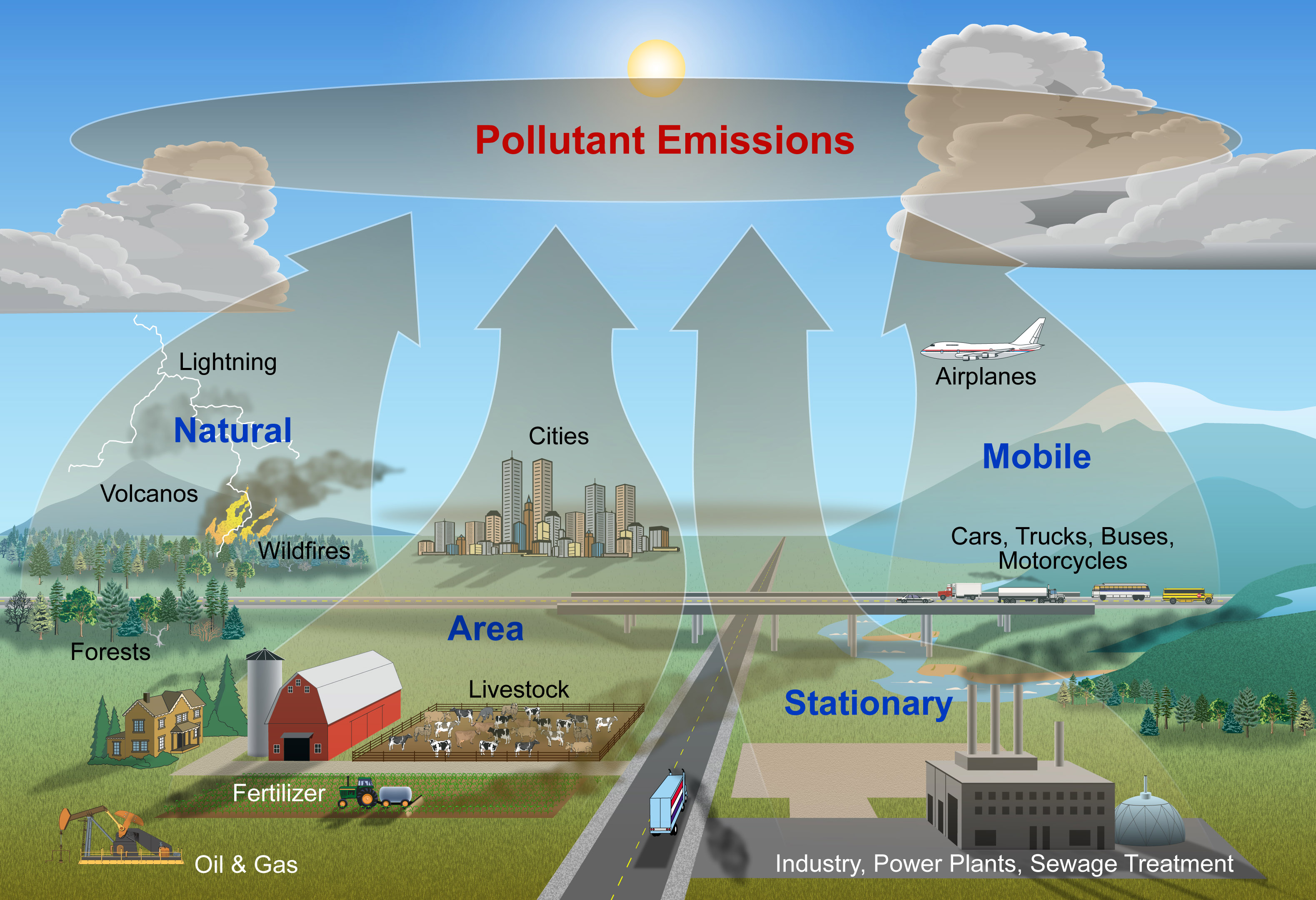
5. What are the sources of air pollution?
Air pollution originates from various sources, including:
- Transportation: Vehicles, particularly gasoline-powered cars and trucks, are a significant contributor to air pollution.
- Industrial activities: Manufacturing processes, power plants, and other industrial facilities release pollutants into the air.
- Residential sources: Home heating, cooking, and lawn care equipment can also emit pollutants.
- Natural sources: Wildfires, volcanic eruptions, and dust storms can contribute to air pollution.
Tips for Utilizing the US Air Pollution Map Effectively
- Understand the AQI scale: Familiarize yourself with the AQI levels and their corresponding health risks.
- Check the air quality forecast: Use the map and its associated forecasts to plan outdoor activities and minimize exposure to high pollution levels.
- Share information with others: Encourage friends, family, and colleagues to use the map and stay informed about air quality.
- Support efforts to reduce air pollution: Advocate for policies and initiatives aimed at reducing emissions from various sources.
Conclusion: A Call to Action for Cleaner Air
The US Air Pollution Map is a crucial tool for understanding and addressing the challenges posed by air pollution. By providing accessible and comprehensive data, it empowers individuals, communities, and policymakers to take action to protect public health and environmental sustainability. Utilizing the map effectively requires a commitment to staying informed, reducing our individual impact, and advocating for cleaner air for all.
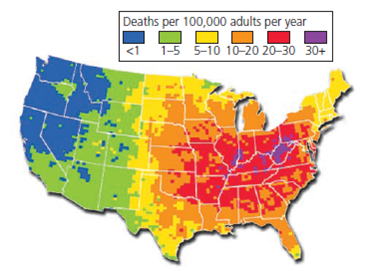
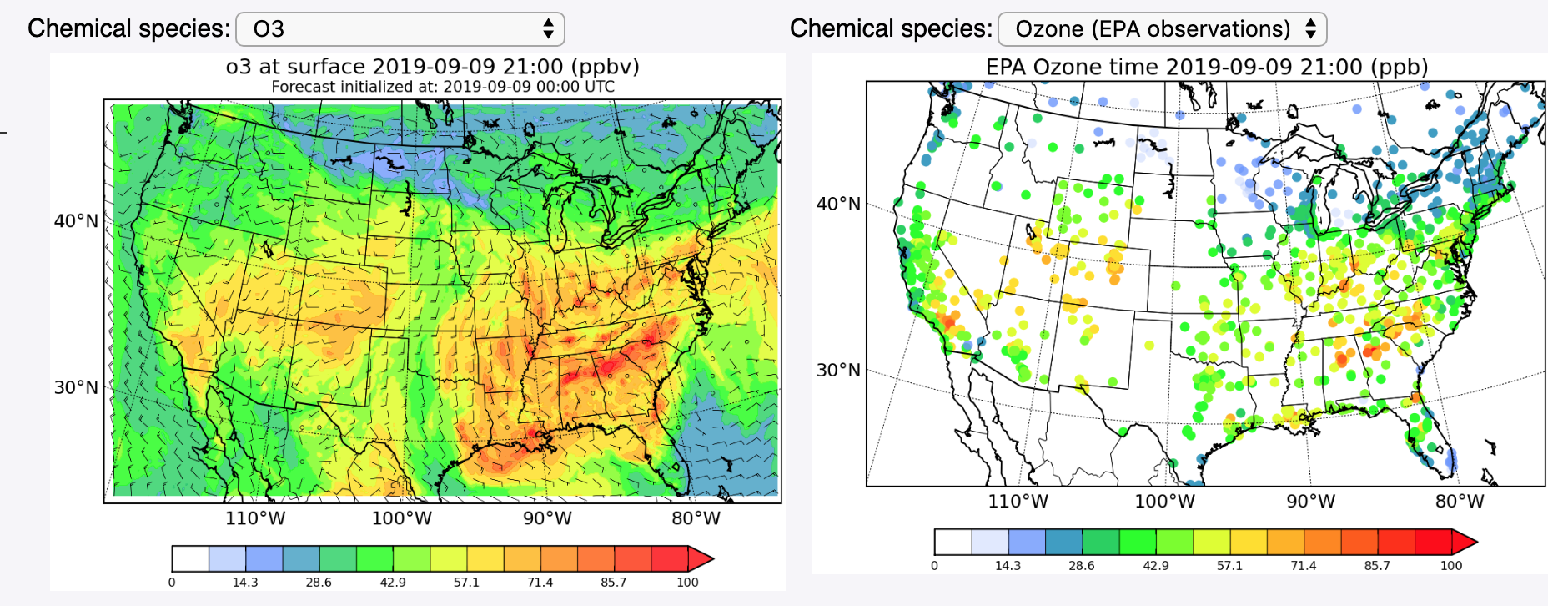
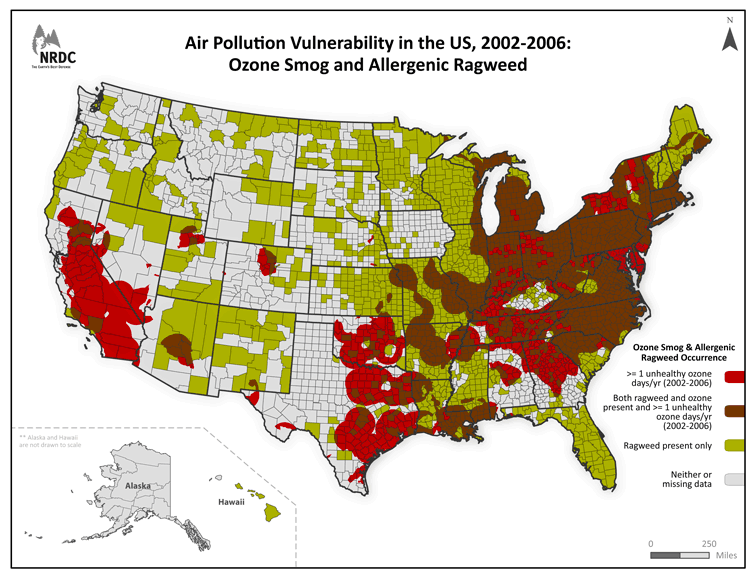



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Air We Breathe: Understanding the US Air Pollution Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Navigating The Digital Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide To AT&T’s Service Map For Internet
- Navigating The Keystone Resort Ski Map: A Comprehensive Guide To Exploring The Mountain
- Navigating The Waters: Understanding Nautical Mile Maps
- Navigating The Rails: A Comprehensive Guide To The RTD Train Map
- Navigating Baltimore County: A Guide To The Zoning Map
- A Comprehensive Guide To Parris Island, South Carolina: Navigating The Cradle Of Marines
- Navigating The Waters Of Smith Lake, Alabama: A Comprehensive Guide
- Navigating Kingsland, Texas: A Comprehensive Guide To The City’s Map
Leave a Reply