Navigating The Competitive Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide To Perceptual Mapping
Navigating the Competitive Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Perceptual Mapping
Related Articles: Navigating the Competitive Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Perceptual Mapping
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Competitive Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Perceptual Mapping. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating the Competitive Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Perceptual Mapping
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the Competitive Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Perceptual Mapping
- 3.1 Defining the Terrain: Understanding Perceptual Maps
- 3.2 Crafting the Map: A Step-by-Step Approach
- 3.3 Applications of Perceptual Mapping: Unveiling Competitive Advantage
- 3.4 The Power of Visualization: Benefits of Perceptual Mapping
- 3.5 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 3.6 Tips for Effective Perceptual Mapping
- 3.7 Conclusion: Navigating the Market with Confidence
- 4 Closure
Navigating the Competitive Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Perceptual Mapping

In the dynamic world of business, understanding the competitive landscape is paramount. This involves not only identifying competitors but also grasping their positioning in the minds of consumers. Here, perceptual mapping emerges as a powerful tool, providing a visual representation of how different products or brands are perceived by their target audience. This article delves into the intricacies of perceptual mapping, exploring its construction, applications, and benefits, offering a comprehensive guide for businesses seeking to gain a competitive edge.
Defining the Terrain: Understanding Perceptual Maps
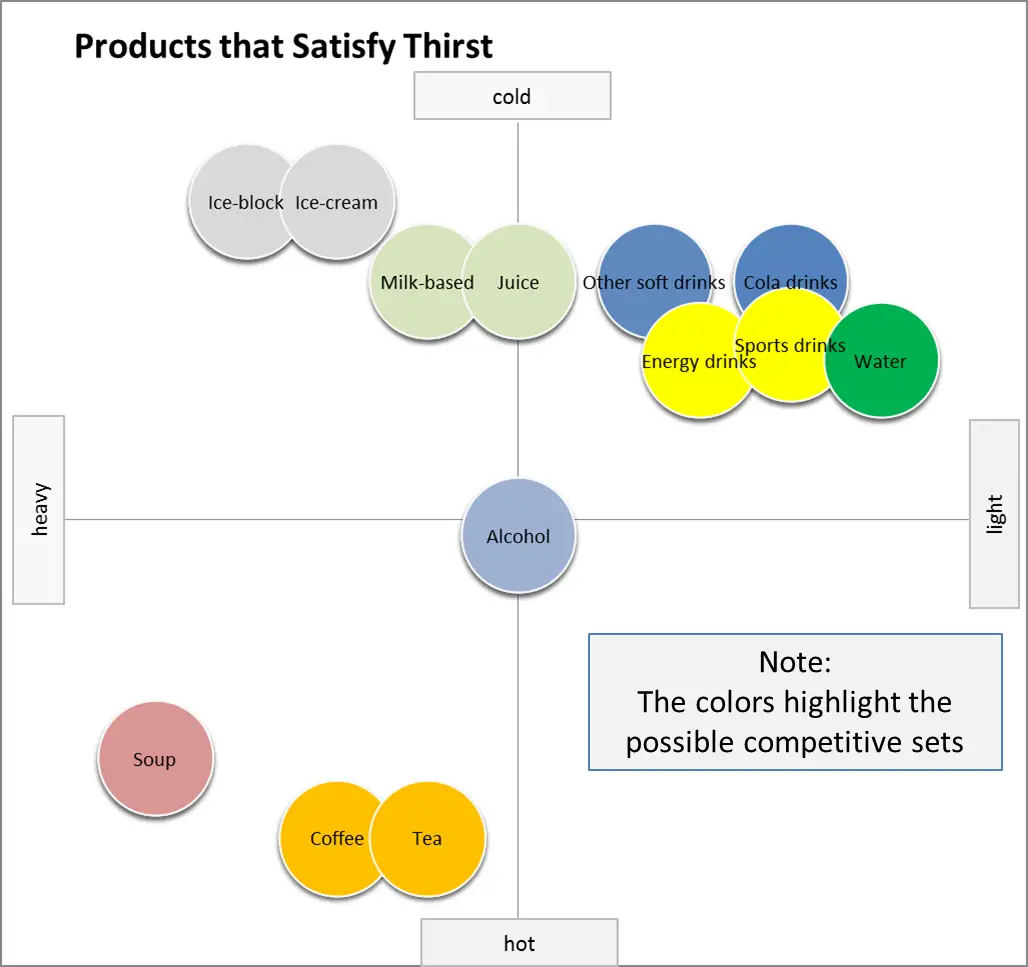
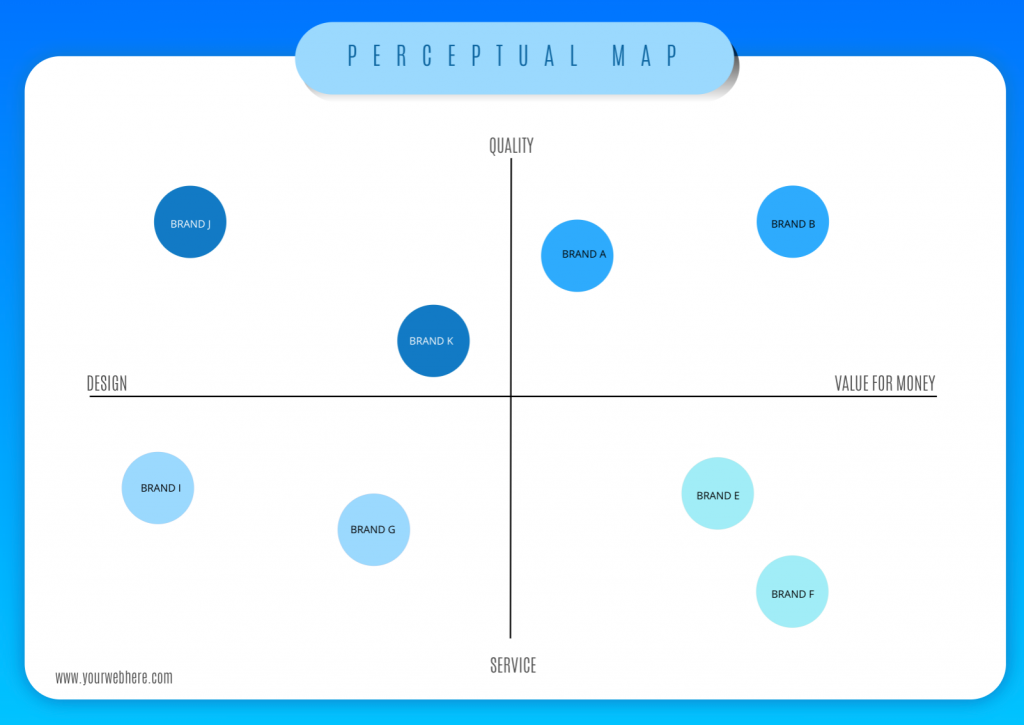
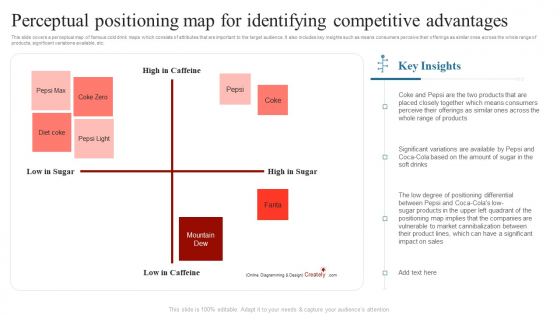
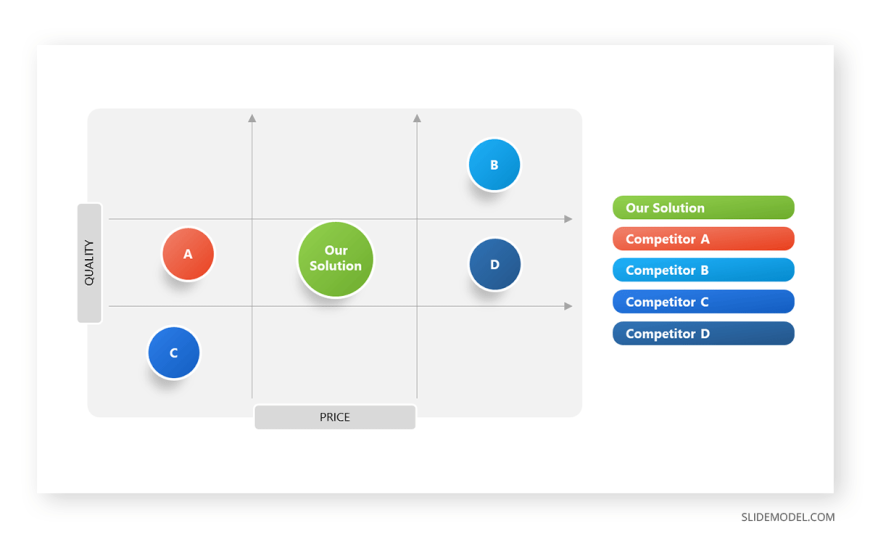
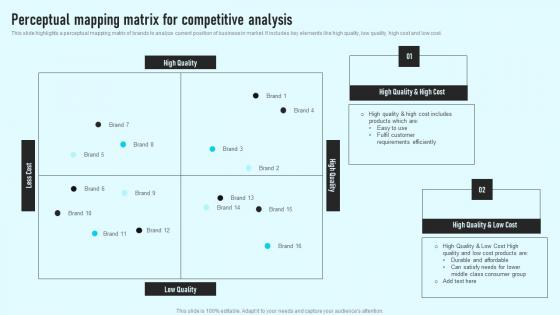
A perceptual map, at its core, is a visual representation of consumer perceptions regarding competing products or brands within a specific market. It plots these entities on a two-dimensional graph, using key attributes or dimensions relevant to the target audience. These attributes can range from price and quality to features and benefits, depending on the industry and the specific market under analysis.
Imagine a map where instead of geographical locations, we see the positions of various brands based on how consumers perceive their offerings. For instance, a map for the automobile industry might use "Price" and "Fuel Efficiency" as axes, with brands like Toyota positioned in a "Fuel-Efficient" quadrant and BMW in a "Luxury" quadrant.
Crafting the Map: A Step-by-Step Approach
Creating a perceptual map involves a systematic process, ensuring the resulting visualization accurately reflects consumer perceptions:
-
Defining the Target Market: Identify the specific customer segment whose perceptions are being analyzed. This ensures the map remains relevant and actionable.
-
Selecting Relevant Attributes: Choose attributes that are crucial for the target market when making purchasing decisions. These attributes should be quantifiable and distinct, allowing for clear differentiation between brands.
-
Data Collection: Gather data on consumer perceptions regarding each brand’s performance on the chosen attributes. This data can be obtained through surveys, focus groups, market research, or existing data analysis.
-
Creating the Map: Plot each brand on the graph based on its perceived performance on the chosen attributes. This can be done using a simple scatterplot or more sophisticated techniques like multidimensional scaling.
-
Analyzing the Map: Once the map is created, analyze the positions of different brands and identify key insights. This includes understanding clusters, competitive gaps, and potential opportunities for differentiation.
Applications of Perceptual Mapping: Unveiling Competitive Advantage
Perceptual maps find applications across various business functions, offering valuable insights for strategic decision-making:
-
Product Development: By understanding the gaps in the market, companies can identify opportunities for developing new products or features that cater to unmet consumer needs.
-
Marketing Strategy: Perceptual maps help refine marketing messages and target specific customer segments. Brands can reposition themselves within the market by highlighting their unique strengths and emphasizing their competitive advantages.
-
Pricing Strategy: The map reveals how price points influence consumer perceptions. This information can inform pricing strategies, ensuring products are priced competitively while maintaining the desired brand image.
-
Competitive Analysis: Perceptual maps provide a comprehensive understanding of the competitive landscape. By analyzing the positions of competitors, companies can identify their strengths and weaknesses, informing strategic decisions.
-
Brand Management: Perceptual maps help track brand positioning over time, allowing businesses to monitor their performance and make necessary adjustments to maintain their desired image.
The Power of Visualization: Benefits of Perceptual Mapping
Perceptual mapping provides numerous benefits for businesses seeking to optimize their strategies:
-
Clear Visual Representation: Maps offer a simple and intuitive way to visualize complex data, making it easier for stakeholders to understand consumer perceptions and market dynamics.
-
Identification of Gaps: Perceptual maps highlight areas where competitors are lacking, revealing opportunities for brands to differentiate themselves and capture market share.
-
Strategic Decision-Making: The insights derived from maps inform key business decisions, from product development and pricing to marketing and brand management.
-
Improved Competitiveness: By understanding their own positioning and that of competitors, businesses can develop strategies to enhance their competitiveness and achieve sustainable success.
-
Enhanced Customer Understanding: Perceptual maps provide a deeper understanding of consumer preferences, allowing companies to tailor their offerings to meet specific needs and desires.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are the limitations of perceptual mapping?
A: Perceptual maps are based on consumer perceptions, which can be subjective and influenced by various factors. Additionally, maps are typically limited to two or three dimensions, potentially neglecting other important attributes.
Q: How can I ensure the accuracy of my perceptual map?
A: Use reliable data sources, employ multiple data collection methods, and involve experts in the field to validate the results. Regularly update the map to reflect evolving consumer perceptions.
Q: Can perceptual mapping be used for non-product-based markets?
A: Yes, perceptual maps can be applied to various markets, including services, political campaigns, and even non-profit organizations. The key is to select relevant attributes that accurately reflect the target audience’s perceptions.
Q: What are some popular software tools for creating perceptual maps?
A: Various software tools can assist in creating perceptual maps, including SPSS, R, and Microsoft Excel. Many online platforms also offer specialized mapping tools.
Tips for Effective Perceptual Mapping
-
Focus on Key Attributes: Choose attributes that are truly important for the target market, avoiding unnecessary complexity.
-
Use Clear and Concise Language: Ensure that the attributes and labels on the map are easily understood by all stakeholders.
-
Regularly Update the Map: As consumer perceptions evolve, update the map to reflect these changes and maintain its relevance.
-
Combine with Other Data Sources: Complement the map with other data sources, such as sales figures or market share data, for a more comprehensive understanding.
Conclusion: Navigating the Market with Confidence
Perceptual mapping provides a powerful tool for understanding consumer perceptions and navigating the competitive landscape. By visualizing how different products or brands are perceived, businesses can gain valuable insights to inform strategic decisions, optimize marketing efforts, and ultimately achieve sustainable success. The process of creating and analyzing perceptual maps requires a systematic approach and a deep understanding of the target market, but the rewards in terms of market intelligence and strategic advantage are substantial. By embracing this tool, businesses can navigate the complexities of the market with confidence and achieve their desired outcomes.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Competitive Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Perceptual Mapping. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Navigating The Digital Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide To AT&T’s Service Map For Internet
- Navigating The Keystone Resort Ski Map: A Comprehensive Guide To Exploring The Mountain
- Navigating The Waters: Understanding Nautical Mile Maps
- Navigating The Rails: A Comprehensive Guide To The RTD Train Map
- Navigating Baltimore County: A Guide To The Zoning Map
- A Comprehensive Guide To Parris Island, South Carolina: Navigating The Cradle Of Marines
- Navigating The Waters Of Smith Lake, Alabama: A Comprehensive Guide
- Navigating Kingsland, Texas: A Comprehensive Guide To The City’s Map
Leave a Reply