Navigating The German Political Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide To The Country’s Administrative Divisions
Navigating the German Political Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Country’s Administrative Divisions
Related Articles: Navigating the German Political Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Country’s Administrative Divisions
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the German Political Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Country’s Administrative Divisions. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the German Political Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Country’s Administrative Divisions
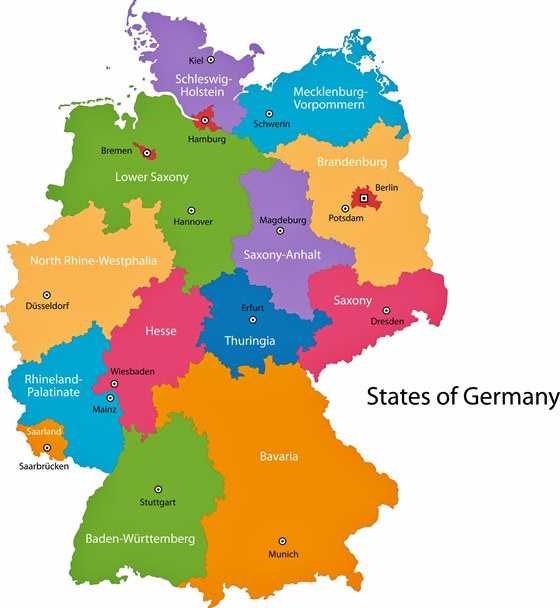
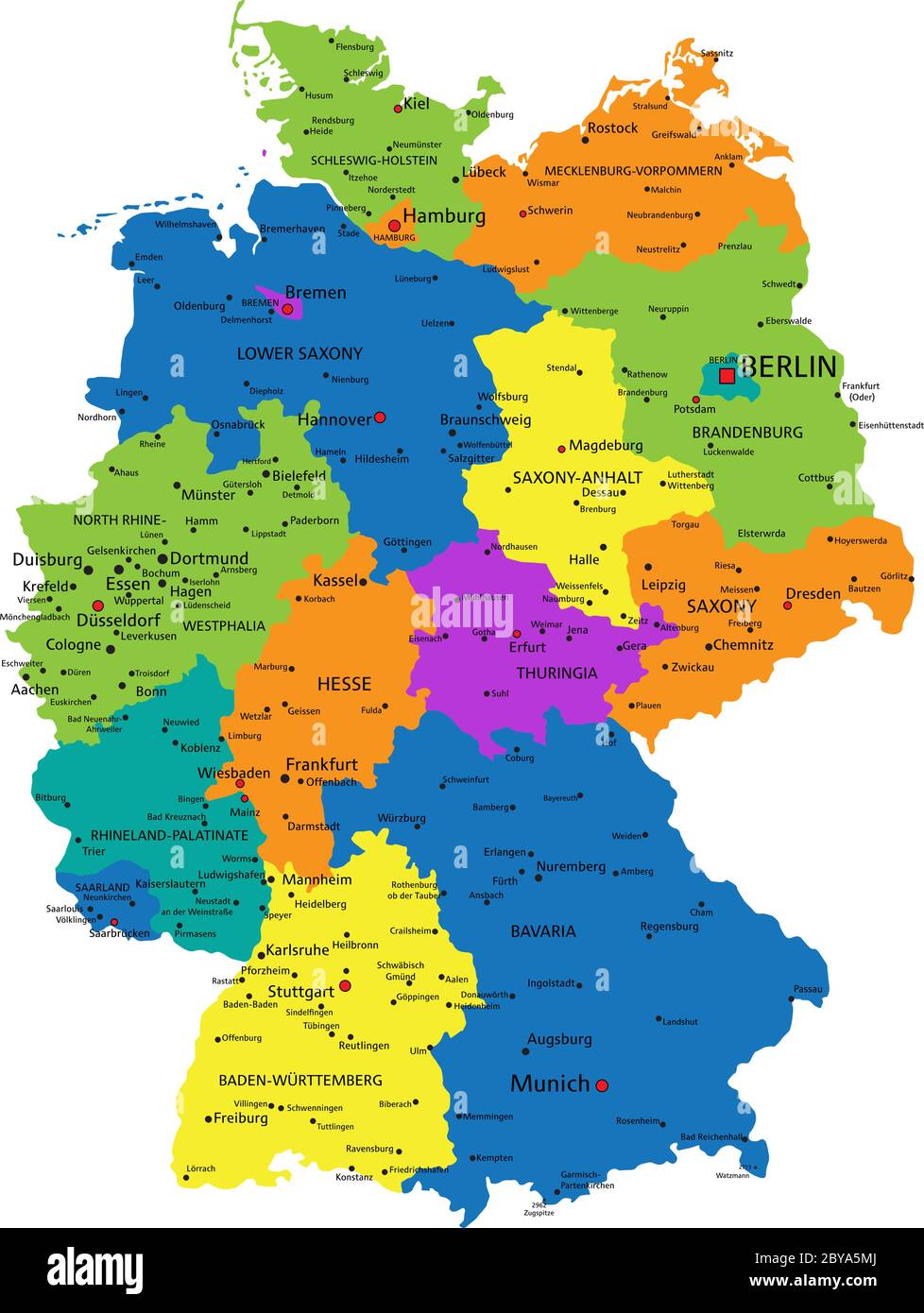
Germany, a nation renowned for its rich history, cultural vibrancy, and economic prowess, possesses a complex yet well-defined political structure. This structure is visually represented by its political map, a valuable tool for understanding the country’s administrative divisions and their interrelationships. By dissecting the map, we gain insights into the intricate network of governance that shapes Germany’s political landscape.
Understanding the Layers of Governance:
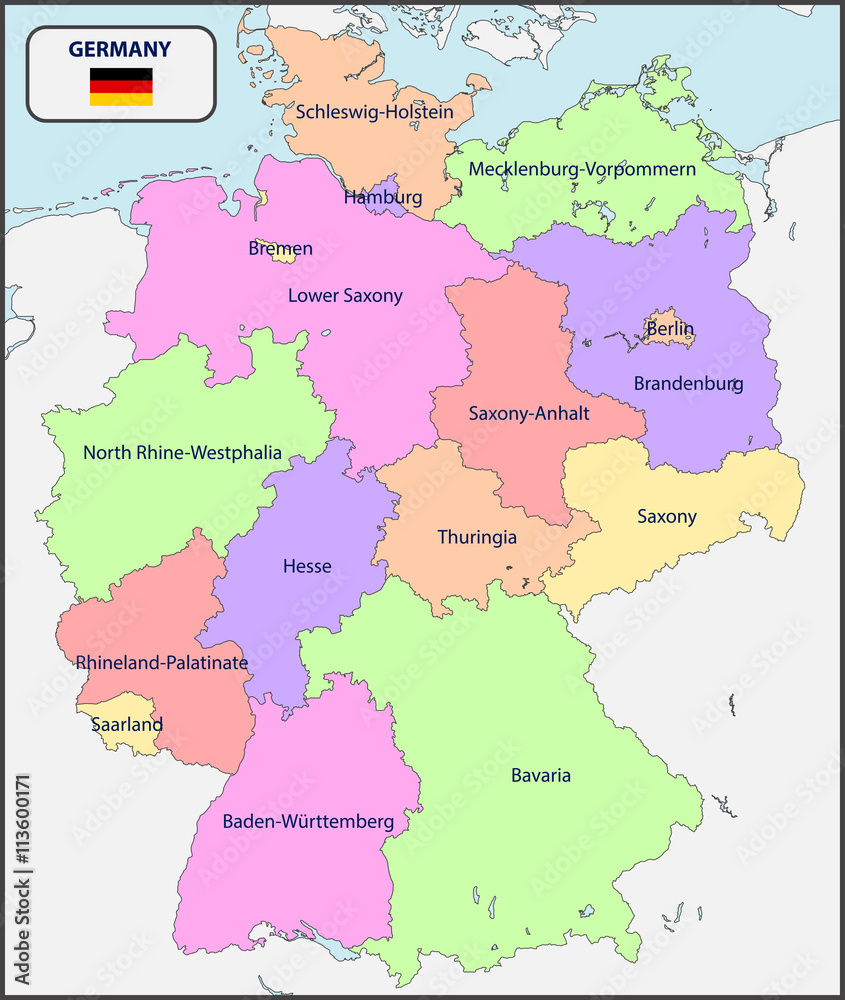
At the heart of Germany’s political map lies a federal system, where power is shared between the national government and 16 constituent states, known as Länder. This division of power is a defining feature of German governance, ensuring a balance between central authority and regional autonomy.
The Federal Level:
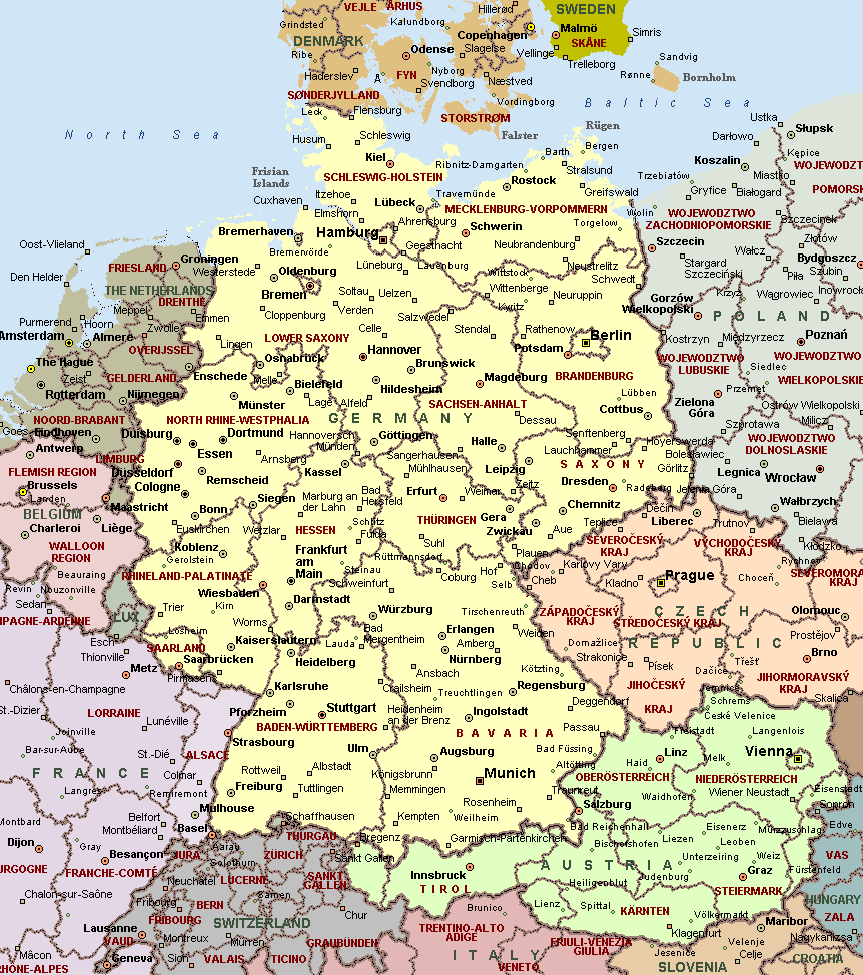
The federal government, headquartered in Berlin, is responsible for matters of national concern, including defense, foreign policy, and economic policy. This level of government comprises the Bundestag, the lower house of parliament, and the Bundesrat, the upper house representing the Länder.
The Länder Level:
Each Land possesses its own constitution, parliament (Landtag), and government (Landesregierung). They hold authority over matters such as education, culture, and public order. This decentralized system allows for tailored policies to address the unique needs and characteristics of each region.
The Sub-State Level:
Beyond the Länder, Germany’s political map further subdivides into smaller administrative units. These include:
- Bezirke: Large administrative districts found in some Länder, primarily in the south and east. They are responsible for coordinating services and overseeing local authorities.
- Kreise: Counties or districts, which are the most common sub-state administrative unit. They handle tasks such as social welfare, public health, and environmental protection.
- Gemeinden: Municipalities, the smallest administrative units, encompassing towns, cities, and villages. They are responsible for local services like waste collection, public transport, and community development.
Exploring the Map’s Significance:
The political map of Germany serves as a visual representation of the country’s administrative framework, offering a comprehensive overview of its governance structure. It highlights the interplay between federal and regional authorities, showcasing the balance of power and the distribution of responsibilities.
Benefits of Understanding the Map:
- Navigating Policy and Governance: The map aids in understanding the different levels of government and their respective roles in shaping policies and providing services to citizens.
- Identifying Regional Differences: By examining the map, one can discern the unique political and administrative characteristics of each Land, highlighting regional variations in governance and policy implementation.
- Understanding Political Dynamics: The map provides a framework for analyzing political trends and understanding the interplay between different levels of government in shaping national and regional politics.
- Promoting Regional Development: By recognizing the distinct needs and priorities of each Land, the map facilitates targeted regional development initiatives and fosters a sense of regional identity.
FAQs about Germany’s Political Map:
Q: What are the major political parties in Germany?
A: The German political landscape is characterized by a multi-party system. The two dominant parties are the Christian Democratic Union (CDU) and the Social Democratic Party (SPD). Other significant parties include the Free Democratic Party (FDP), the Green Party (Bündnis 90/Die Grünen), and the Left Party (Die Linke).
Q: How does the German federal system work?
A: The German federal system operates on the principle of shared sovereignty. The federal government has exclusive jurisdiction over certain areas, while the Länder have authority over others. In areas of concurrent jurisdiction, both levels of government can legislate.
Q: What is the role of the Bundesrat in German politics?
A: The Bundesrat, representing the Länder, serves as the upper house of parliament. It has a significant role in shaping legislation, particularly in areas where the Länder hold primary responsibility.
Q: How are elections conducted in Germany?
A: Germany employs a mixed electoral system, combining proportional representation with direct election of individual candidates. This system ensures both national representation and local accountability.
Q: What are the main challenges facing German governance?
A: Germany faces various challenges, including:
- Demographic Change: An aging population and low birth rates pose challenges to social security systems and economic growth.
- Economic Globalization: The rise of global competition and technological advancements necessitate adaptation and innovation.
- Immigration and Integration: Germany is a destination for migrants, creating challenges in integration and social cohesion.
- Climate Change: Addressing climate change requires ambitious policies and investments in sustainable development.
Tips for Navigating Germany’s Political Map:
- Focus on Key Administrative Units: Start by understanding the major divisions of the country, including the Länder and their respective capitals.
- Explore Regional Variations: Examine the political map to identify unique characteristics and challenges of each Land.
- Consult Online Resources: Utilize online maps and resources to gain a deeper understanding of the administrative structure and political dynamics.
- Engage in Informed Discussion: Participate in discussions and debates about German politics, using your knowledge of the map to contribute to informed dialogue.
Conclusion:
Germany’s political map serves as a valuable tool for comprehending the country’s complex administrative structure and its diverse political landscape. By understanding the interplay between federal and regional authorities, the distribution of power, and the unique characteristics of each Land, one gains a deeper appreciation for the intricate network of governance that shapes Germany’s political reality. The map provides a foundation for navigating the country’s political landscape, fostering informed discussion, and promoting a deeper understanding of the dynamics that shape German society.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the German Political Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Country’s Administrative Divisions. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Navigating The Digital Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide To AT&T’s Service Map For Internet
- Navigating The Keystone Resort Ski Map: A Comprehensive Guide To Exploring The Mountain
- Navigating The Waters: Understanding Nautical Mile Maps
- Navigating The Rails: A Comprehensive Guide To The RTD Train Map
- Navigating Baltimore County: A Guide To The Zoning Map
- A Comprehensive Guide To Parris Island, South Carolina: Navigating The Cradle Of Marines
- Navigating The Waters Of Smith Lake, Alabama: A Comprehensive Guide
- Navigating Kingsland, Texas: A Comprehensive Guide To The City’s Map
Leave a Reply