Navigating The Inferno: A Look At Botticelli’s Map Of Hell
Navigating the Inferno: A Look at Botticelli’s Map of Hell
Related Articles: Navigating the Inferno: A Look at Botticelli’s Map of Hell
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Inferno: A Look at Botticelli’s Map of Hell. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Inferno: A Look at Botticelli’s Map of Hell

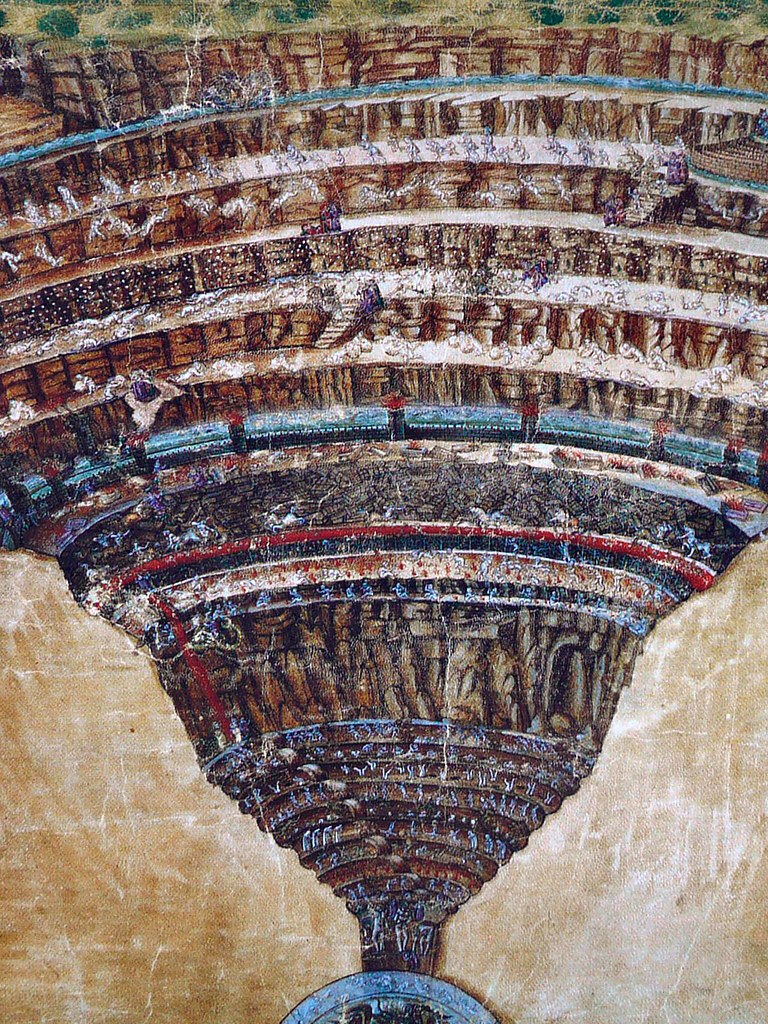
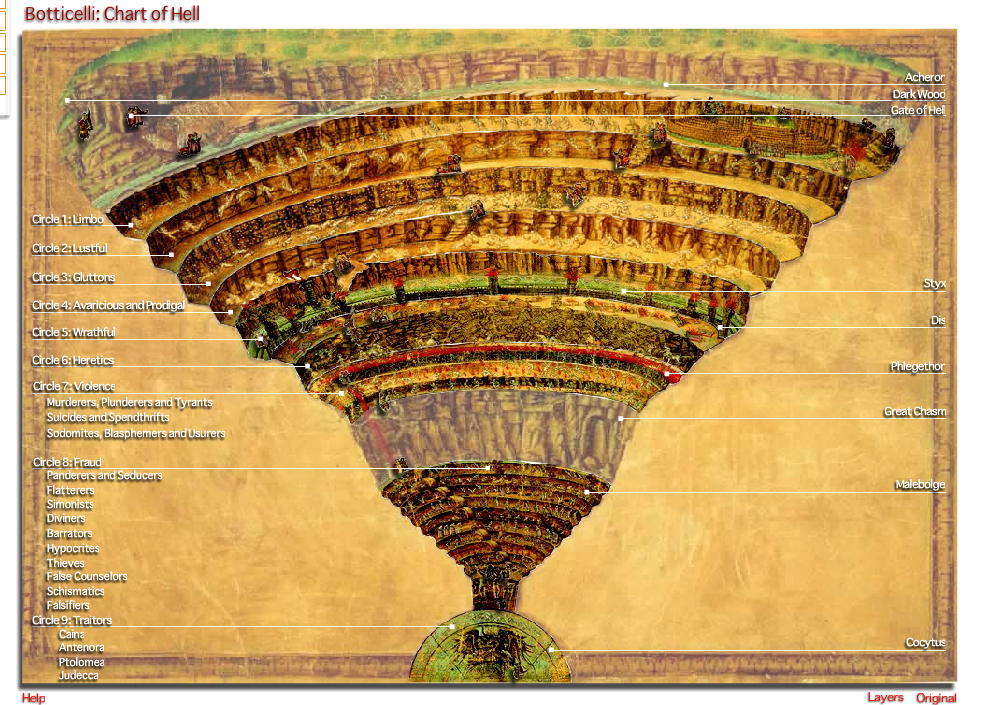
Sandro Botticelli’s "Map of Hell," a meticulously detailed illustration depicting Dante Alighieri’s harrowing journey through the Inferno, transcends its status as a mere visual representation of a literary work. It stands as a testament to the artistic and intellectual fervor of the Italian Renaissance, offering a fascinating glimpse into the societal anxieties and theological beliefs of the period.
The map, created around 1480, is a masterful fusion of art and literature. Botticelli, known for his graceful and ethereal figures in works like "The Birth of Venus," expertly translates Dante’s poetic descriptions into a visually compelling narrative. The map, drawn on parchment, measures approximately 104 centimeters in width and 68 centimeters in height. It features intricate details, including concentric circles representing the nine circles of Hell, each populated with figures and scenes drawn from Dante’s narrative.
Decoding the Circles:
The map’s most striking feature is its clear depiction of the nine circles of Hell, each progressively more severe in its punishment. The first circle, Limbo, is depicted as a vast, shadowy expanse where unbaptized souls reside. The second circle, Lust, is populated by figures entangled in a chaotic whirlwind, while the third circle, Gluttony, shows souls wallowing in a pit of filth.
As the journey descends deeper into the inferno, the punishments become increasingly gruesome. The fourth circle, Greed, depicts souls locked in a perpetual struggle, pushing heavy weights against each other. The fifth circle, Anger, shows souls trapped in a murky swamp, engaged in violent struggles. The sixth circle, Heresy, presents souls trapped in fiery tombs, while the seventh circle, Violence, showcases souls subjected to various forms of physical torture.
The eighth circle, Fraud, is a complex and intricate labyrinth, depicting souls condemned to various forms of deceit and manipulation. Finally, the ninth circle, Treachery, is the deepest and most terrifying, where Satan himself resides, frozen in ice with Judas Iscariot, Brutus, and Cassius, the betrayers of Christ, trapped within his jaws.
Beyond the Visual:
Botticelli’s map is not simply a visual interpretation of Dante’s Inferno. It also reflects the artistic and intellectual trends of the time. The map’s intricate details, its use of perspective, and its realistic depiction of human figures are all hallmarks of the Renaissance period. The map also reflects the intense interest in classical literature and philosophy that characterized the Renaissance. Dante’s Inferno, a work steeped in classical mythology and Christian theology, resonated with the Renaissance’s emphasis on humanism and intellectual inquiry.
A Window into the Past:
Botticelli’s map offers a unique perspective on the societal anxieties and theological beliefs of the Renaissance period. The depiction of Hell as a place of eternal punishment reflects the widespread fear of damnation and the importance of religious piety. The map also highlights the Renaissance fascination with the human condition, its complexities, and its potential for both good and evil.
Beyond the Aesthetics:
The map’s significance extends beyond its artistic merit. It serves as a valuable historical document, offering insights into the intellectual and cultural landscape of the Italian Renaissance. The map’s meticulous details and its adherence to Dante’s narrative provide a window into the minds of the period’s artists and intellectuals. It also underscores the enduring power of Dante’s Inferno, a work that continues to captivate and inspire readers centuries after its creation.
FAQs about Botticelli’s Map of Hell:
1. What is the significance of Botticelli’s Map of Hell?
Botticelli’s Map of Hell is significant for its artistic merit, its historical context, and its insightful portrayal of Dante’s Inferno. It provides a unique window into the Renaissance period’s artistic and intellectual landscape, reflecting societal anxieties, theological beliefs, and the enduring power of Dante’s work.
2. How does the map reflect the artistic trends of the Renaissance?
The map’s intricate details, use of perspective, and realistic depiction of human figures are all hallmarks of the Renaissance period. It also reflects the Renaissance fascination with classical literature and philosophy, which is evident in Dante’s Inferno.
3. What are the key elements of the map?
The map’s key elements include the nine circles of Hell, each depicting a specific sin and punishment, as well as various figures and scenes drawn from Dante’s narrative. The map also features intricate details and realistic depictions of human figures.
4. What is the significance of the nine circles of Hell?
The nine circles of Hell represent the progressive severity of punishment for different sins. They provide a visual and narrative representation of Dante’s journey through the Inferno and the consequences of sin.
5. What is the significance of Satan in the map?
Satan, depicted as a monstrous figure frozen in ice, embodies the ultimate evil and punishment in Dante’s Inferno. His presence signifies the final stage of the journey and the consequences of treachery and betrayal.
Tips for Understanding Botticelli’s Map of Hell:
- Read Dante’s Inferno: The map is best understood in conjunction with Dante’s original text. Reading the poem will provide context and deepen the understanding of the map’s details.
- Research the Renaissance period: Understanding the historical context of the map will enhance its significance and provide insights into its creation.
- Focus on the details: Pay close attention to the map’s intricate details, including the figures, scenes, and symbols. These details offer valuable insights into the map’s meaning and purpose.
- Compare and contrast: Compare Botticelli’s map with other depictions of Hell from the Renaissance period. This comparison will highlight the unique aspects of Botticelli’s work.
Conclusion:
Botticelli’s Map of Hell is a remarkable artistic and historical artifact. It offers a captivating glimpse into the Italian Renaissance, its artistic and intellectual trends, and its profound engagement with Dante’s Inferno. The map serves as a testament to the power of art and literature to transcend time and offer insights into the human condition, its complexities, and its enduring fascination with the mysteries of the afterlife. The map’s intricate details, its realistic depictions, and its adherence to Dante’s narrative continue to captivate and inspire, reminding us of the enduring power of imagination and the timeless allure of the human quest for meaning and understanding.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Inferno: A Look at Botticelli’s Map of Hell. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Navigating The Digital Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide To AT&T’s Service Map For Internet
- Navigating The Keystone Resort Ski Map: A Comprehensive Guide To Exploring The Mountain
- Navigating The Waters: Understanding Nautical Mile Maps
- Navigating The Rails: A Comprehensive Guide To The RTD Train Map
- Navigating Baltimore County: A Guide To The Zoning Map
- A Comprehensive Guide To Parris Island, South Carolina: Navigating The Cradle Of Marines
- Navigating The Waters Of Smith Lake, Alabama: A Comprehensive Guide
- Navigating Kingsland, Texas: A Comprehensive Guide To The City’s Map
Leave a Reply