Pennsylvania’s Mountainous Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide
Pennsylvania’s Mountainous Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Pennsylvania’s Mountainous Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Pennsylvania’s Mountainous Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Pennsylvania’s Mountainous Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide
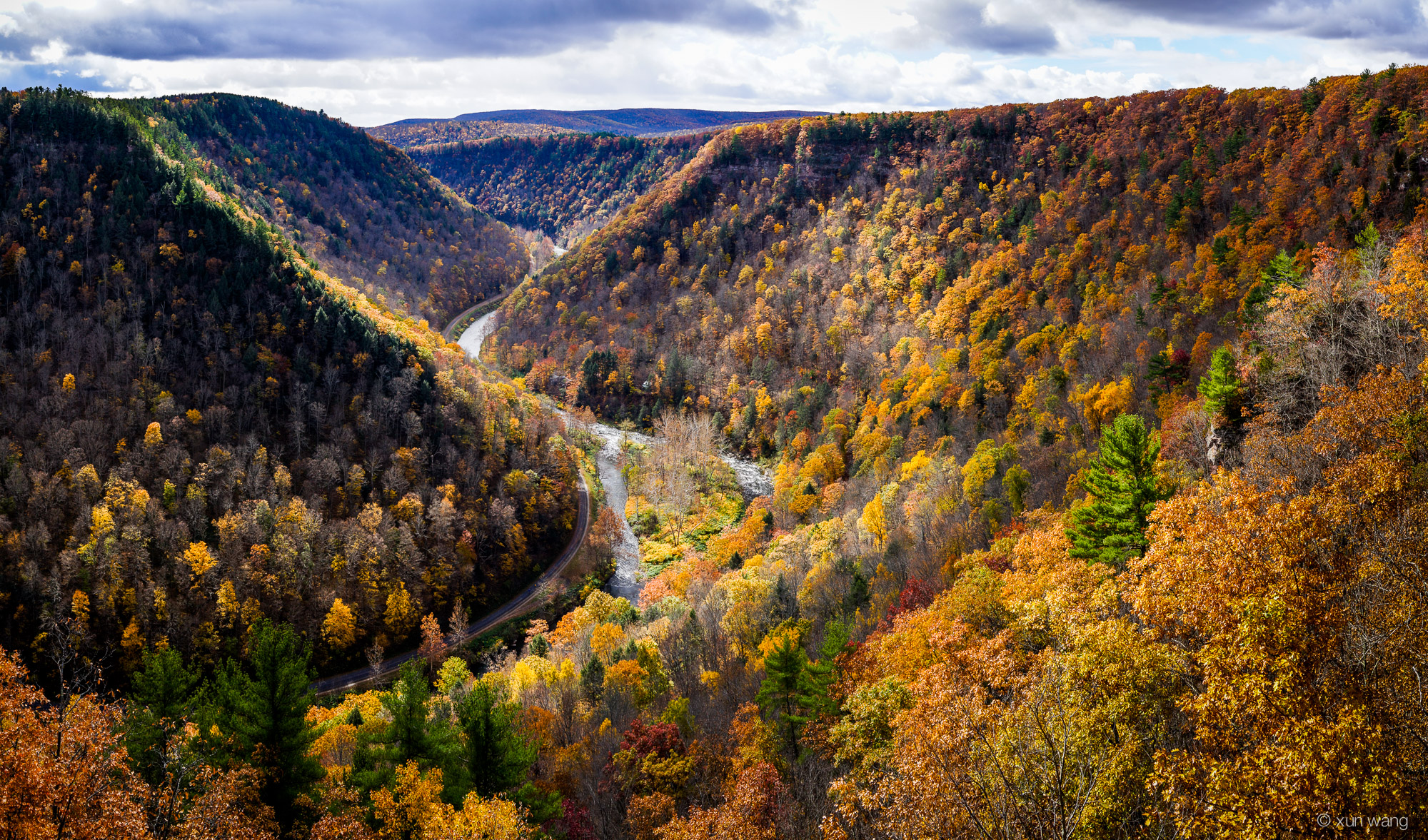

Pennsylvania, often referred to as the Keystone State, is renowned for its diverse geography, encompassing rolling hills, fertile valleys, and, notably, a significant mountainous region. This mountainous landscape, a defining feature of the state, plays a vital role in its ecology, economy, and cultural identity. Understanding the distribution and characteristics of these mountains is crucial for appreciating the state’s natural beauty and its impact on various aspects of life.
The Appalachian Backbone: A Defining Feature
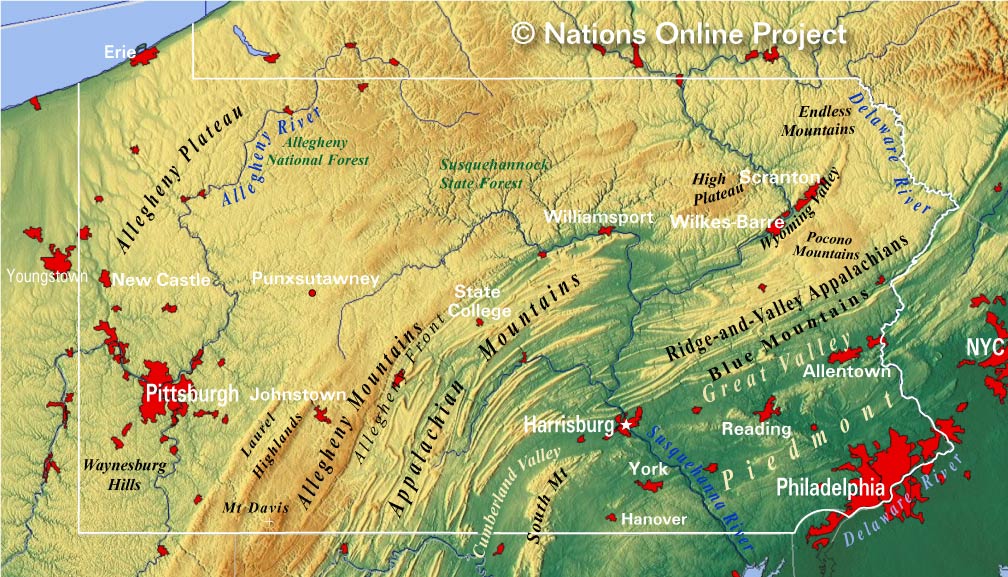
Pennsylvania’s mountains are part of the vast Appalachian Mountain system, a chain stretching from the Canadian Maritimes to Alabama. Within the state, the Appalachians are divided into two distinct physiographic provinces: the Allegheny Plateau and the Ridge and Valley Province.
-
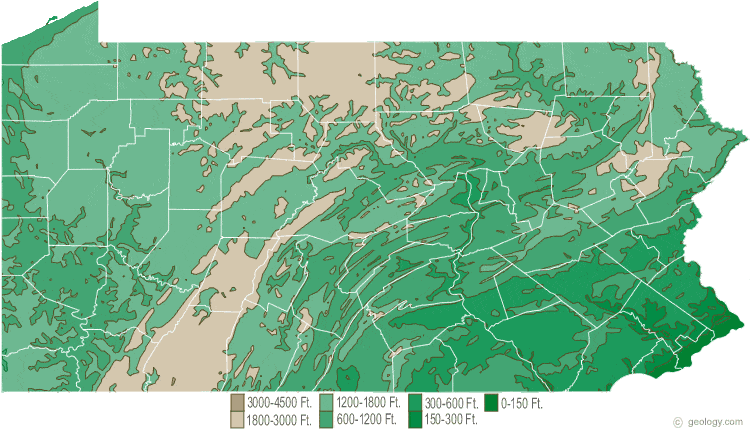
The Allegheny Plateau: This region, covering the western and north-central parts of Pennsylvania, is characterized by relatively flat, elevated plateaus dissected by deep valleys and rivers. The plateau’s elevation ranges from 1,500 to 2,500 feet, with its highest point being the summit of Mount Davis at 3,213 feet. The Allegheny Plateau is heavily forested and home to diverse wildlife, including black bears, deer, and various bird species. Its geological composition primarily consists of sandstone, shale, and coal.
-
The Ridge and Valley Province: This region, located east of the Allegheny Plateau, is distinguished by a series of parallel ridges and valleys formed by folding and faulting of sedimentary rocks. The ridges are often capped by resistant sandstone, while the valleys are carved by streams and rivers. This region is known for its scenic beauty, with rolling hills and panoramic views. Prominent features include the Blue Mountain, a major ridge running along the eastern edge of the state, and the Susquehanna River Valley, a significant agricultural area.
Significant Mountain Ranges and Peaks
Within these physiographic provinces, several notable mountain ranges and peaks contribute to Pennsylvania’s unique landscape.
-
Allegheny Mountains: These mountains, part of the Allegheny Plateau, extend through western Pennsylvania and into neighboring states. They are known for their rugged terrain, dense forests, and abundant natural resources.
-
Pocono Mountains: Situated in northeastern Pennsylvania, the Poconos are a popular tourist destination. These mountains are characterized by rolling hills, scenic lakes, and numerous recreational opportunities. Their elevation ranges from 1,000 to 2,000 feet, with the highest peak being Mount Toby at 1,926 feet.
-
Blue Mountain: This prominent ridge, forming the eastern boundary of the Ridge and Valley Province, stretches for over 100 miles across Pennsylvania. Its elevation ranges from 1,500 to 2,000 feet, with its highest point being Blue Mountain at 2,148 feet. The Blue Mountain is a popular hiking and scenic driving destination.
-
Laurel Highlands: This region, located in southwestern Pennsylvania, is known for its rugged beauty and its role in the history of the state. It is home to numerous state parks, historic sites, and recreational opportunities. The Laurel Highlands are characterized by steep slopes, deep valleys, and numerous waterfalls.
The Importance of Pennsylvania’s Mountains
Pennsylvania’s mountains play a crucial role in the state’s ecology, economy, and cultural identity.
-
Ecological Significance: The mountains provide habitat for a wide variety of plant and animal life, including endangered and threatened species. They also play a vital role in regulating water flow and maintaining air quality.
-
Economic Importance: The mountains are a significant source of natural resources, including timber, coal, and natural gas. They also support tourism, recreation, and agriculture.
-
Cultural Significance: The mountains have played a significant role in the history and culture of Pennsylvania. They have inspired artists, writers, and musicians, and they continue to attract visitors from around the world.
Mountains of Pennsylvania Map: A Tool for Understanding
A map of Pennsylvania’s mountains is an invaluable tool for understanding the state’s geography and its various features. It can help identify specific mountain ranges, peaks, and valleys, providing context for their location and characteristics. Furthermore, the map can highlight the distribution of natural resources, recreational opportunities, and cultural landmarks within the mountainous regions.
FAQs about Mountains of Pennsylvania Map
Q: What is the highest mountain in Pennsylvania?
A: The highest mountain in Pennsylvania is Mount Davis, located in the Allegheny Plateau, with an elevation of 3,213 feet.
Q: What are the major mountain ranges in Pennsylvania?
A: The major mountain ranges in Pennsylvania include the Allegheny Mountains, Pocono Mountains, Blue Mountain, and Laurel Highlands.
Q: What are some popular hiking trails in the Pennsylvania mountains?
A: Popular hiking trails in the Pennsylvania mountains include the Appalachian Trail, the Mid-Atlantic Trail, and the Pennsylvania Highlands Trail.
Q: What are some popular tourist destinations in the Pennsylvania mountains?
A: Popular tourist destinations in the Pennsylvania mountains include the Pocono Mountains, the Laurel Highlands, and the Delaware Water Gap National Recreation Area.
Q: How do I find a map of Pennsylvania’s mountains?
A: Maps of Pennsylvania’s mountains can be found online, at libraries, and at outdoor recreation stores.
Tips for Using a Mountains of Pennsylvania Map
- Identify key features: Focus on identifying major mountain ranges, peaks, and valleys.
- Consider elevation: Use the map to understand the elevation of different areas and plan accordingly.
- Explore recreational opportunities: Use the map to locate hiking trails, camping sites, and other recreational activities.
- Research historical landmarks: The map can help you find historic sites and learn about the region’s past.
Conclusion
Pennsylvania’s mountains are a defining feature of the state, contributing significantly to its natural beauty, economic prosperity, and cultural identity. Understanding the distribution and characteristics of these mountains is essential for appreciating their importance and exploring the diverse opportunities they offer. A map of Pennsylvania’s mountains serves as a valuable tool for navigating this rugged and beautiful landscape, providing insights into its geography, resources, and cultural heritage.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Pennsylvania’s Mountainous Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Navigating The Digital Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide To AT&T’s Service Map For Internet
- Navigating The Keystone Resort Ski Map: A Comprehensive Guide To Exploring The Mountain
- Navigating The Waters: Understanding Nautical Mile Maps
- Navigating The Rails: A Comprehensive Guide To The RTD Train Map
- Navigating Baltimore County: A Guide To The Zoning Map
- A Comprehensive Guide To Parris Island, South Carolina: Navigating The Cradle Of Marines
- Navigating The Waters Of Smith Lake, Alabama: A Comprehensive Guide
- Navigating Kingsland, Texas: A Comprehensive Guide To The City’s Map
Leave a Reply