Python 3’s Map Function: A Powerful Tool For Transforming Data
Python 3’s Map Function: A Powerful Tool for Transforming Data
Related Articles: Python 3’s Map Function: A Powerful Tool for Transforming Data
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Python 3’s Map Function: A Powerful Tool for Transforming Data. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Python 3’s Map Function: A Powerful Tool for Transforming Data
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Python 3’s Map Function: A Powerful Tool for Transforming Data
- 3.1 Understanding the Fundamentals of map
- 3.2 The Advantages of Using map
- 3.3 Beyond Basic Usage: Exploring Advanced Applications
- 3.4 Understanding the Importance of map in Python
- 3.5 Frequently Asked Questions about Python’s map
- 3.6 Tips for Effectively Utilizing map
- 3.7 Conclusion: Embracing the Power of map
- 4 Closure
Python 3’s Map Function: A Powerful Tool for Transforming Data

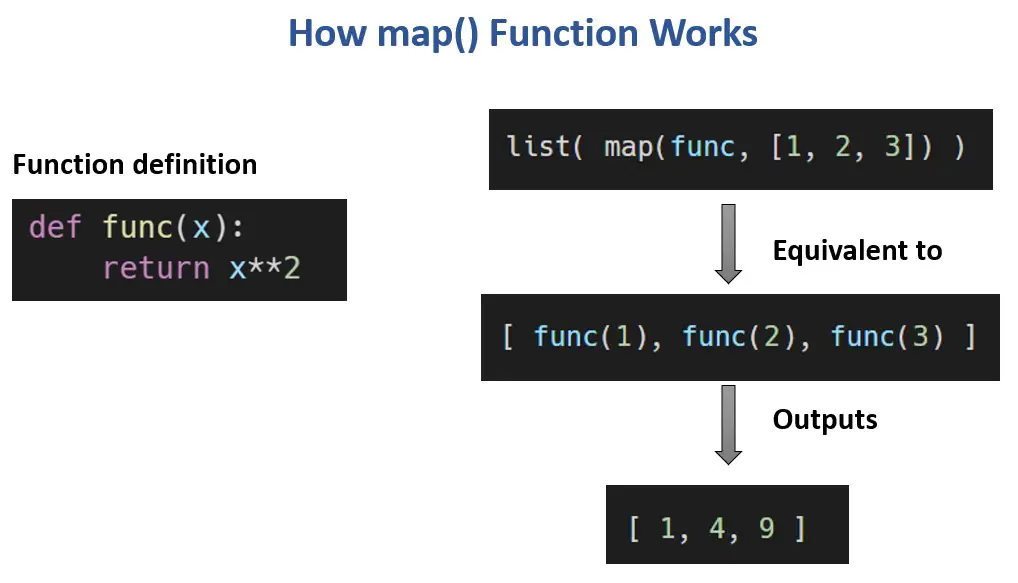
Python’s map function is a versatile tool for applying a given function to every element within an iterable, such as a list, tuple, or string. This powerful function streamlines data processing and manipulation, making code more concise and efficient. Understanding map empowers developers to write elegant and performant Python code, particularly when working with large datasets.
Understanding the Fundamentals of map
At its core, map takes two arguments: a function and an iterable. The function defines the operation to be applied to each element of the iterable. The map function then iterates through the iterable, applying the function to each element and generating a new iterable containing the results.
Let’s illustrate this with a simple example:
def square(x):
return x * x
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
squared_numbers = map(square, numbers)
print(list(squared_numbers)) # Output: [1, 4, 9, 16, 25]In this example, the square function multiplies its input by itself. map applies this function to each element in the numbers list, resulting in a new iterable (squared_numbers) containing the squares of each number.
The Advantages of Using map
Employing map offers several significant advantages:
-
Conciseness:
mapallows for compact and readable code, eliminating the need for explicit loops to process each element individually. -
Efficiency: By leveraging the power of Python’s built-in functions,
mapoften provides performance benefits, especially when dealing with large datasets. -
Flexibility:
mapcan accept any function, including user-defined functions, built-in functions, and lambda functions. This flexibility allows for a wide range of data transformation possibilities. -
Readability: The declarative nature of
mapenhances code readability, making it easier to understand the intended data transformation.
Beyond Basic Usage: Exploring Advanced Applications
While the basic example demonstrates the core functionality of map, its true power lies in its ability to handle complex transformations and scenarios.
-
Multiple Iterables:
mapcan accept multiple iterables as arguments, applying the function to corresponding elements from each iterable. This enables parallel transformations across multiple data sources.
def add(x, y):
return x + y
numbers1 = [1, 2, 3]
numbers2 = [4, 5, 6]
summed_numbers = map(add, numbers1, numbers2)
print(list(summed_numbers)) # Output: [5, 7, 9]-
Lambda Functions:
mapseamlessly integrates with lambda functions, providing a concise way to define anonymous functions for specific transformations.
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
doubled_numbers = map(lambda x: x * 2, numbers)
print(list(doubled_numbers)) # Output: [2, 4, 6, 8, 10]-
Custom Data Structures:
mapcan be used with custom data structures, allowing for transformations tailored to specific data types and objects.
class Person:
def __init__(self, name, age):
self.name = name
self.age = age
people = [Person("Alice", 25), Person("Bob", 30), Person("Charlie", 28)]
def get_name(person):
return person.name
names = map(get_name, people)
print(list(names)) # Output: ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie']Understanding the Importance of map in Python
map is a cornerstone of functional programming in Python, promoting a style that emphasizes data transformation and immutability. By abstracting away the details of iteration and function application, map enables developers to focus on the logic of their transformations, leading to more concise and readable code.
Frequently Asked Questions about Python’s map
Q: Can map handle iterables of different lengths?
A: No, map stops iterating when the shortest iterable is exhausted. If the iterables have different lengths, the resulting iterable will only contain elements processed before the shortest iterable is fully consumed.
Q: What is the difference between map and list comprehensions?
A: Both map and list comprehensions can perform similar data transformations. However, list comprehensions offer greater flexibility in terms of conditional logic and nested structures. map is generally preferred for simple transformations, while list comprehensions are more suitable for complex scenarios.
Q: Is map always faster than explicit loops?
A: While map often provides performance benefits, its speed can vary depending on the specific function and the size of the iterable. For small datasets, the overhead associated with map might be negligible. However, for large datasets, the performance gain can be significant.
Tips for Effectively Utilizing map
-
Choose
mapfor simple transformations: If the transformation logic is straightforward and can be expressed as a single function,mapis an excellent choice. -
Consider list comprehensions for complex scenarios: For transformations involving conditional logic, nested structures, or multiple operations, list comprehensions offer greater flexibility and control.
-
Use
mapwith lambda functions: Lambda functions provide a concise way to define anonymous functions, makingmapeven more expressive. -
Be mindful of iterable lengths: If working with multiple iterables, ensure they have the same length to avoid unexpected results.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of map
Python’s map function is a powerful tool for transforming data efficiently and concisely. Its ability to apply a function to each element of an iterable streamlines data processing, promotes readability, and encourages a functional programming style. By understanding the core concepts and nuances of map, developers can leverage its capabilities to write more efficient and elegant Python code.
![]()





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Python 3’s Map Function: A Powerful Tool for Transforming Data. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Navigating The Digital Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide To AT&T’s Service Map For Internet
- Navigating The Keystone Resort Ski Map: A Comprehensive Guide To Exploring The Mountain
- Navigating The Waters: Understanding Nautical Mile Maps
- Navigating The Rails: A Comprehensive Guide To The RTD Train Map
- Navigating Baltimore County: A Guide To The Zoning Map
- A Comprehensive Guide To Parris Island, South Carolina: Navigating The Cradle Of Marines
- Navigating The Waters Of Smith Lake, Alabama: A Comprehensive Guide
- Navigating Kingsland, Texas: A Comprehensive Guide To The City’s Map
Leave a Reply