The Earth’s Diverse Topography: A Journey Through World Map Terrain
The Earth’s Diverse Topography: A Journey Through World Map Terrain
Related Articles: The Earth’s Diverse Topography: A Journey Through World Map Terrain
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Earth’s Diverse Topography: A Journey Through World Map Terrain. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Earth’s Diverse Topography: A Journey Through World Map Terrain
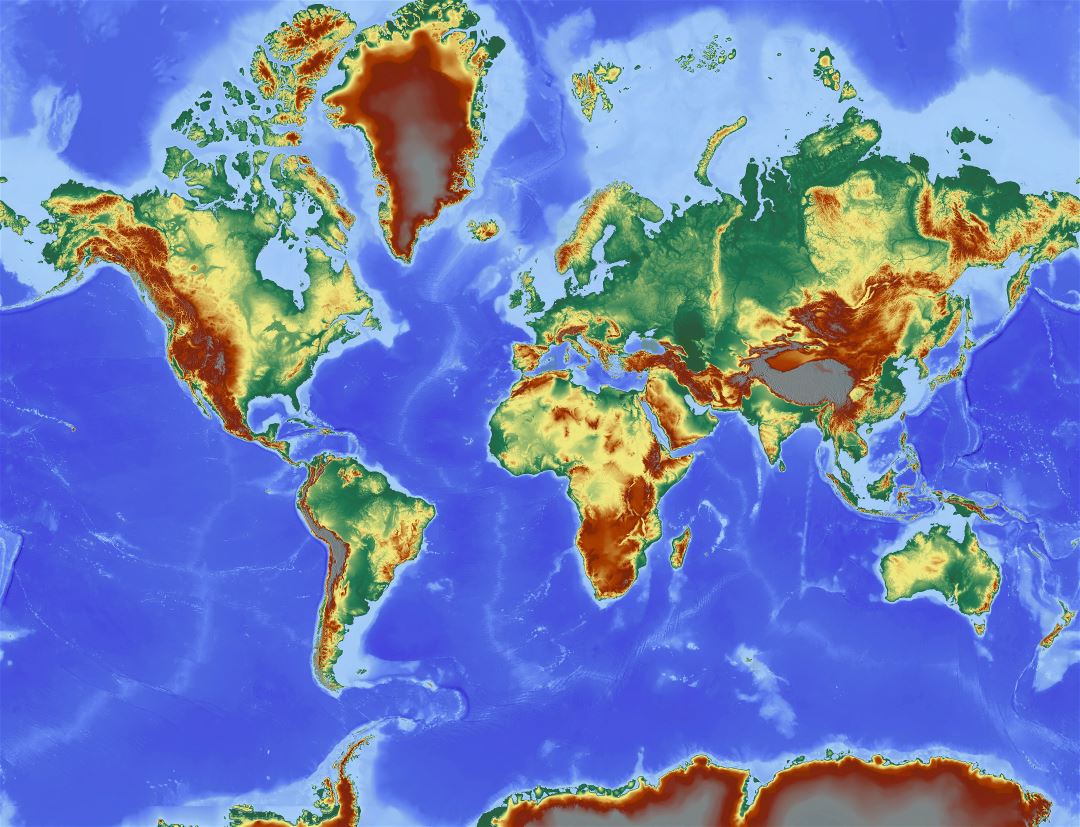
The Earth’s surface is far from uniform. It is a tapestry of diverse landforms, each with its unique characteristics, formed over millions of years by the interplay of tectonic forces, erosion, and climate. This dynamic interplay has sculpted the planet’s landscape into a mesmerizing array of mountains, valleys, plateaus, deserts, and coastlines, collectively known as the Earth’s terrain. Understanding these diverse features is crucial for comprehending the planet’s history, its present-day ecosystems, and its future.
Tectonic Plates: The Foundation of Earth’s Terrain
The Earth’s crust is not a solid, monolithic shell. It is instead comprised of massive, rigid plates known as tectonic plates. These plates are constantly moving, driven by convection currents within the Earth’s mantle. The interactions between these plates at their boundaries are responsible for the formation of many of the Earth’s most dramatic landforms.
Convergent Boundaries: Mountains and Trenches
When two tectonic plates collide, the denser plate subducts beneath the less dense plate. This process, known as subduction, generates intense heat and pressure, leading to the formation of volcanic arcs and deep ocean trenches. The collision of continental plates, however, creates massive mountain ranges like the Himalayas, formed by the ongoing collision of the Indian and Eurasian plates.
Divergent Boundaries: Rifts and Mid-Ocean Ridges
At divergent boundaries, tectonic plates move apart, creating rifts and mid-ocean ridges. As the plates separate, molten rock from the mantle rises to the surface, solidifying to form new crust. This process, known as seafloor spreading, is responsible for the creation of new ocean floor and the expansion of ocean basins.
Transform Boundaries: Earthquakes and Faults
At transform boundaries, tectonic plates slide past each other horizontally. This movement is often accompanied by intense seismic activity, resulting in earthquakes and fault lines. The San Andreas Fault in California, for example, is a transform boundary where the Pacific Plate slides past the North American Plate.
Erosion: Shaping the Landscape
While tectonic forces are responsible for the initial formation of many landforms, erosion plays a crucial role in shaping and modifying them. Wind, water, and ice are the primary agents of erosion. Wind can carve out canyons and deserts, while water can create rivers, valleys, and deltas. Glaciers, powerful agents of erosion, carve out valleys, fjords, and cirques.
Climate and Terrain: A Complex Relationship
Climate exerts a significant influence on terrain development. Precipitation, temperature, and wind patterns all contribute to the erosion and deposition of materials, shaping the landscape. Deserts, for example, are characterized by arid conditions and wind erosion, resulting in vast, flat plains and sand dunes. Tropical regions, on the other hand, experience high rainfall and lush vegetation, leading to the formation of dense forests and fertile valleys.
The Importance of Understanding World Map Terrain
Understanding world map terrain is crucial for a multitude of reasons:
- Resource Management: Terrain plays a vital role in determining the distribution of natural resources, such as water, minerals, and fertile land. Understanding terrain patterns is essential for managing these resources effectively.
- Infrastructure Development: Terrain considerations are essential for planning and constructing infrastructure, including roads, bridges, and buildings. Steep slopes, for example, pose challenges for road construction, while flat plains are ideal for building cities.
- Disaster Mitigation: Terrain can influence the severity and impact of natural disasters, such as earthquakes, floods, and landslides. Understanding terrain features can help in developing effective disaster mitigation strategies.
- Climate Change: Terrain plays a crucial role in influencing climate patterns. Mountains, for example, act as barriers to air flow, influencing precipitation patterns. Understanding terrain can help in predicting the impacts of climate change on different regions.
- Biodiversity: Terrain diversity supports a wide range of ecosystems and species. Understanding terrain patterns is crucial for conserving biodiversity and managing protected areas.
FAQs about World Map Terrain
Q: What is the highest point on Earth?
A: The highest point on Earth is Mount Everest, located in the Himalayas, with a summit elevation of 8,848.86 meters (29,031.7 feet) above sea level.
Q: What is the deepest point on Earth?
A: The deepest point on Earth is the Challenger Deep, located in the Mariana Trench in the Pacific Ocean, with a depth of approximately 10,924 meters (35,838 feet).
Q: What are the major types of terrain?
A: The major types of terrain include mountains, valleys, plateaus, plains, deserts, and coastlines. Each type has its unique characteristics and is formed by different geological processes.
Q: How does terrain affect climate?
A: Terrain can significantly influence climate patterns. Mountains, for example, can create rain shadows on their leeward sides, leading to drier conditions. Coastal areas, on the other hand, experience milder temperatures due to the moderating influence of the ocean.
Q: How does terrain affect biodiversity?
A: Terrain diversity supports a wide range of ecosystems and species. Mountains, for example, are home to unique alpine ecosystems, while coastal areas are characterized by diverse marine life.
Tips for Understanding World Map Terrain
- Use online maps and atlases: Interactive maps and atlases can provide detailed information about terrain features, elevations, and landforms.
- Explore topographic maps: Topographic maps use contour lines to represent elevation changes, providing a detailed view of the terrain.
- Read about geological history: Understanding the geological history of a region can help explain the formation of its terrain features.
- Observe the landscape: Pay attention to the shapes, slopes, and patterns of the terrain when you travel or explore.
- Learn about different landforms: Familiarize yourself with the characteristics and formation processes of different landforms, such as mountains, valleys, and deserts.
Conclusion
World map terrain is a testament to the Earth’s dynamic and ever-changing nature. Understanding this diverse topography is not just a matter of intellectual curiosity. It is essential for navigating the planet, managing its resources, mitigating natural disasters, and understanding the complex interplay between climate and ecosystems. By appreciating the intricate beauty and significance of world map terrain, we gain a deeper understanding of our planet and its remarkable ability to evolve and adapt over time.

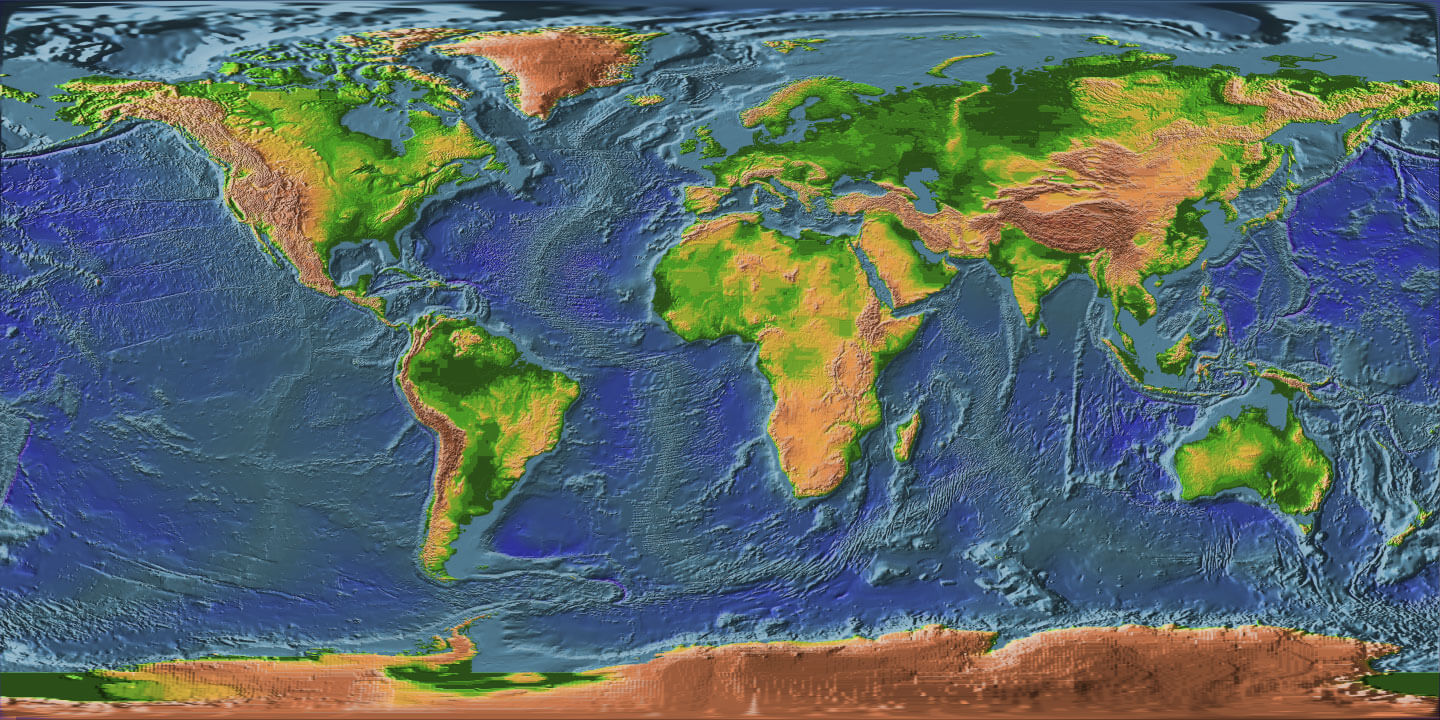
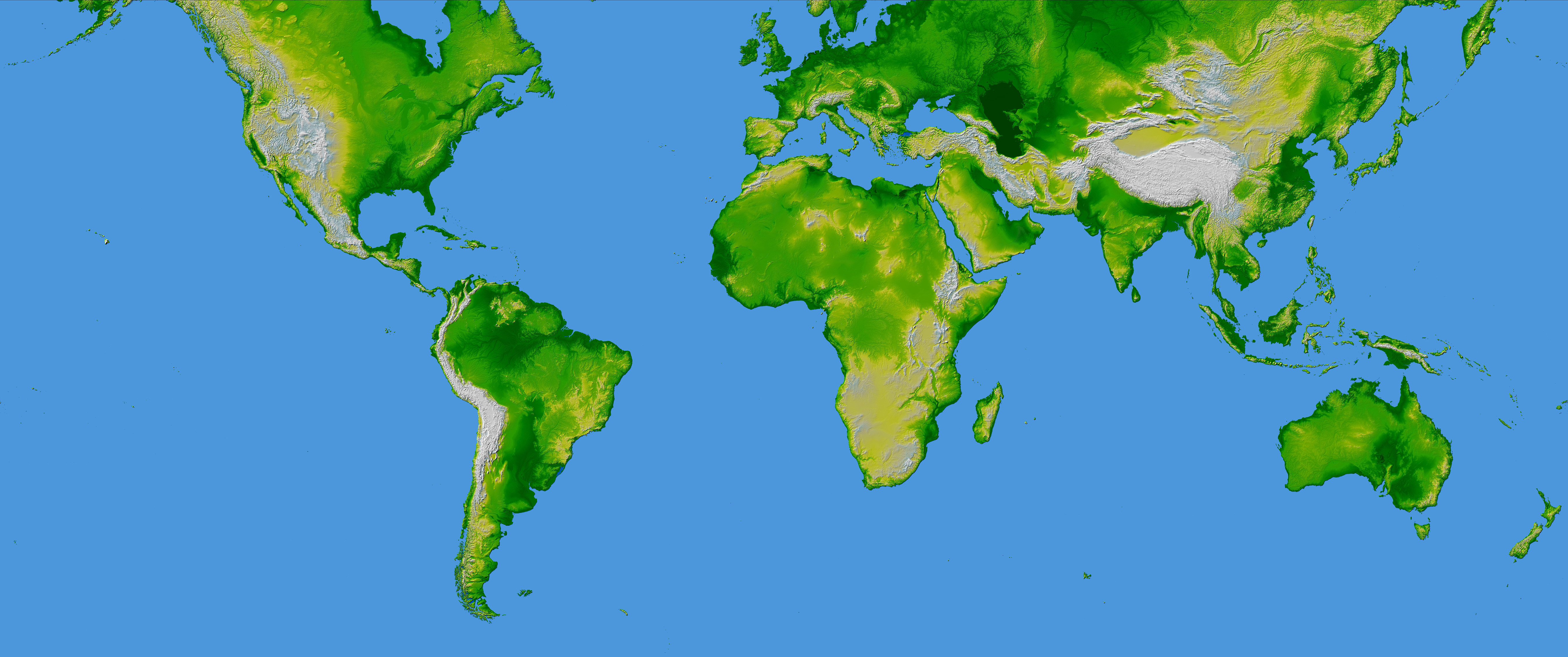
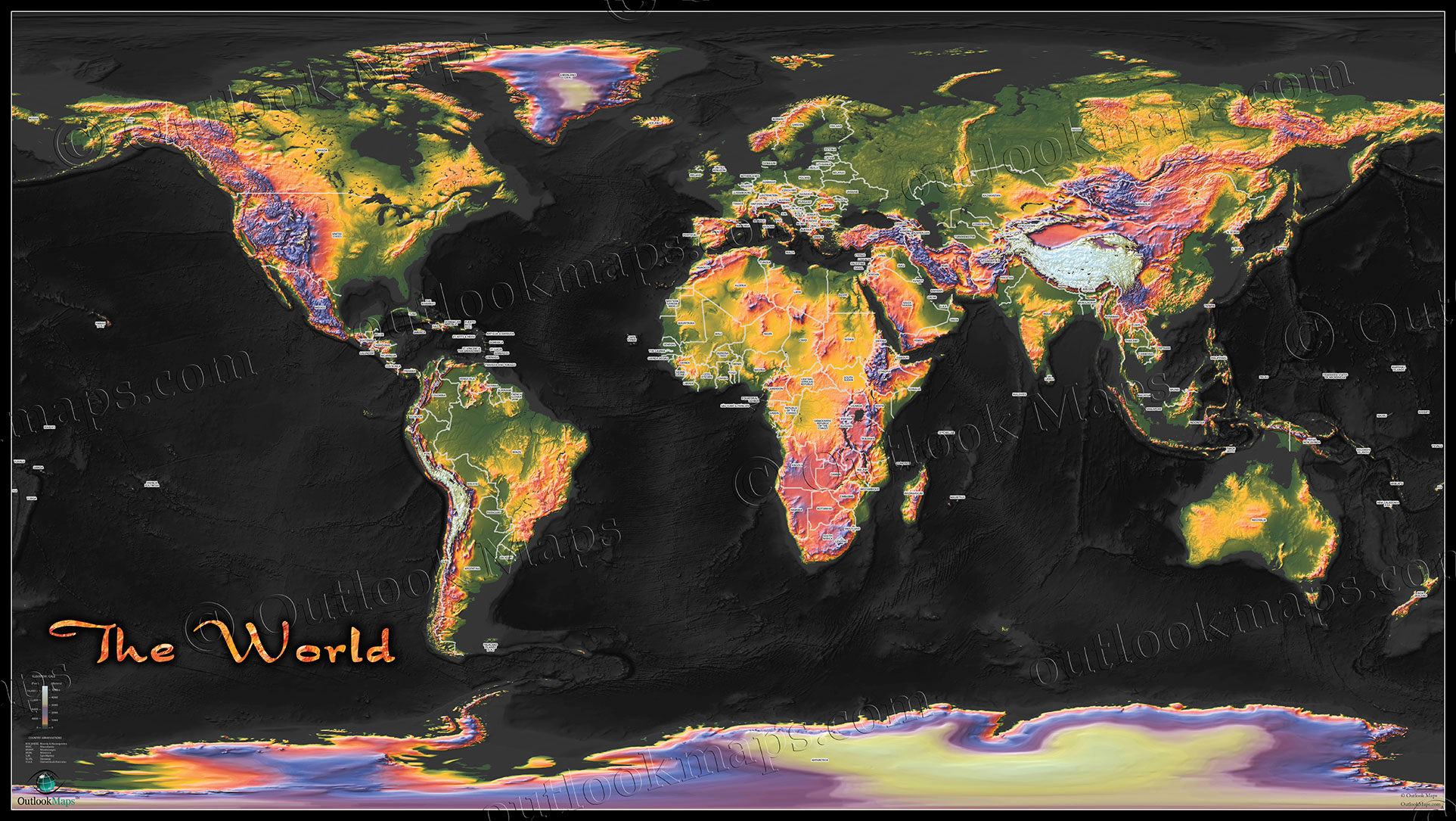
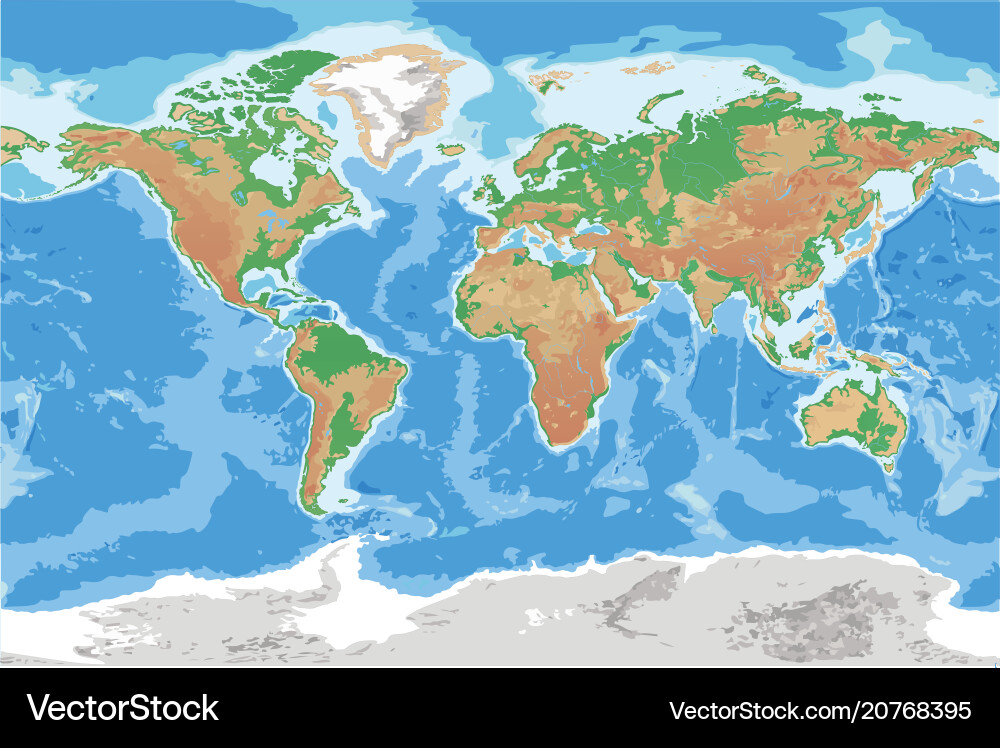

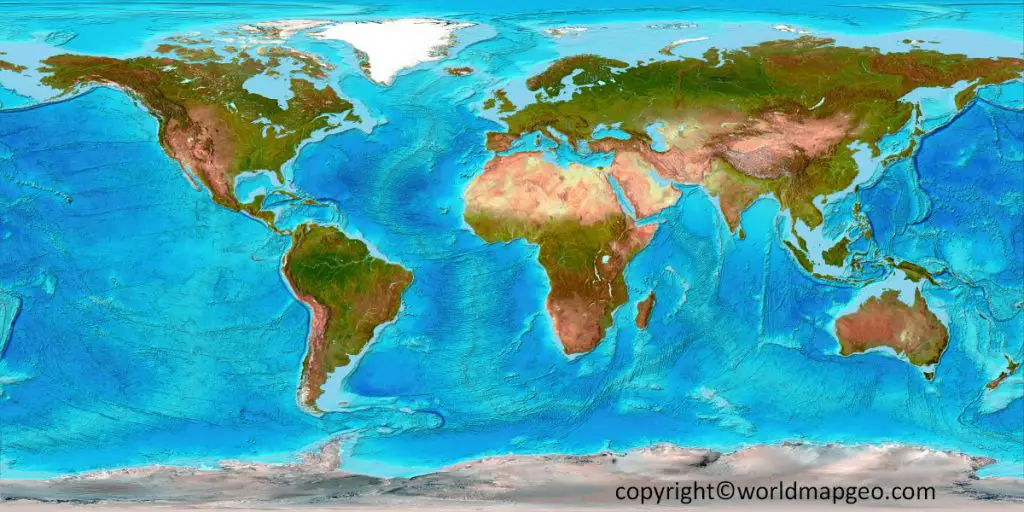
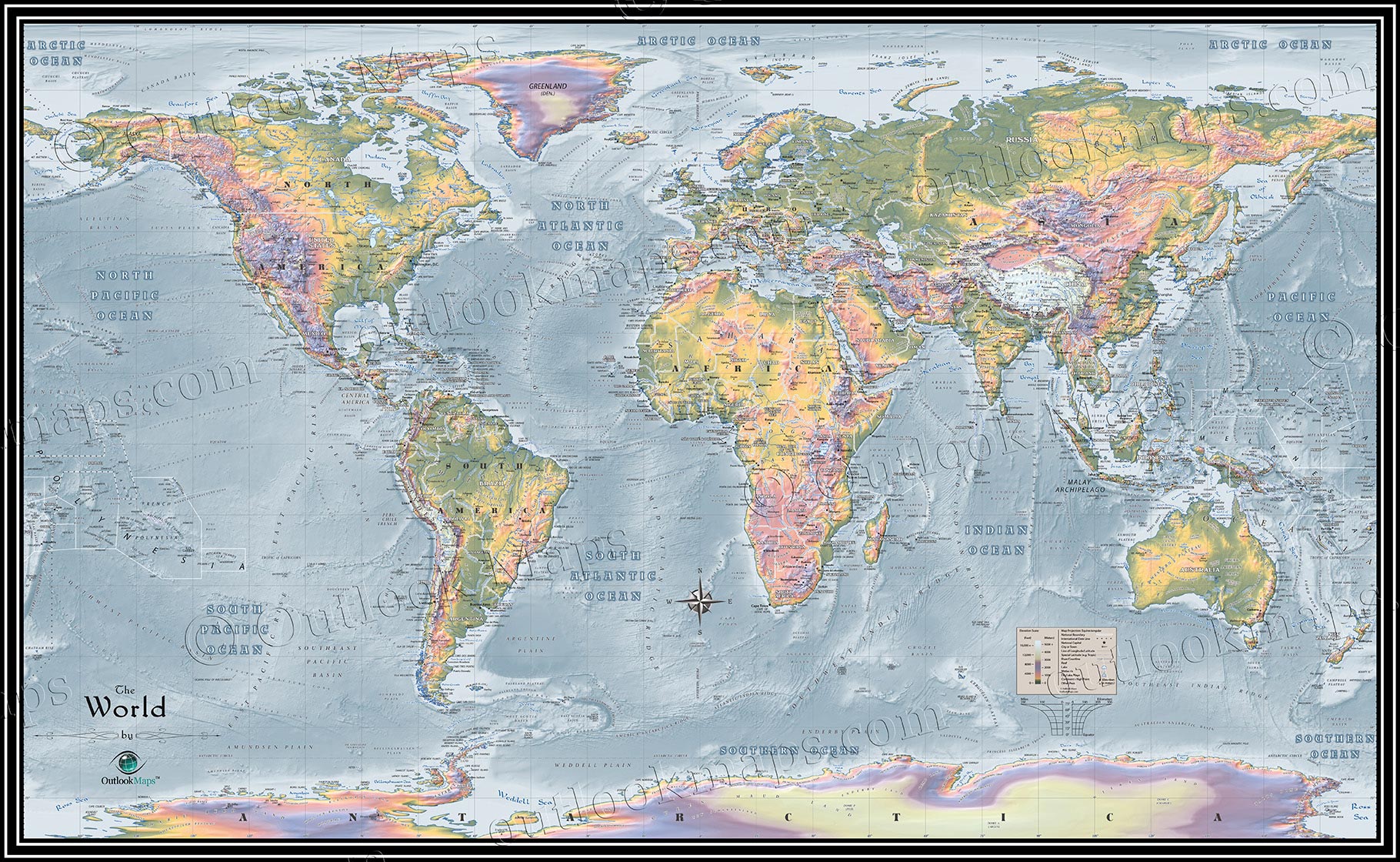
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Earth’s Diverse Topography: A Journey Through World Map Terrain. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Navigating The Digital Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide To AT&T’s Service Map For Internet
- Navigating The Keystone Resort Ski Map: A Comprehensive Guide To Exploring The Mountain
- Navigating The Waters: Understanding Nautical Mile Maps
- Navigating The Rails: A Comprehensive Guide To The RTD Train Map
- Navigating Baltimore County: A Guide To The Zoning Map
- A Comprehensive Guide To Parris Island, South Carolina: Navigating The Cradle Of Marines
- Navigating The Waters Of Smith Lake, Alabama: A Comprehensive Guide
- Navigating Kingsland, Texas: A Comprehensive Guide To The City’s Map
Leave a Reply