The Nile River: A Lifeline Traversing Time And Geography
The Nile River: A Lifeline Traversing Time and Geography
Related Articles: The Nile River: A Lifeline Traversing Time and Geography
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Nile River: A Lifeline Traversing Time and Geography. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Nile River: A Lifeline Traversing Time and Geography
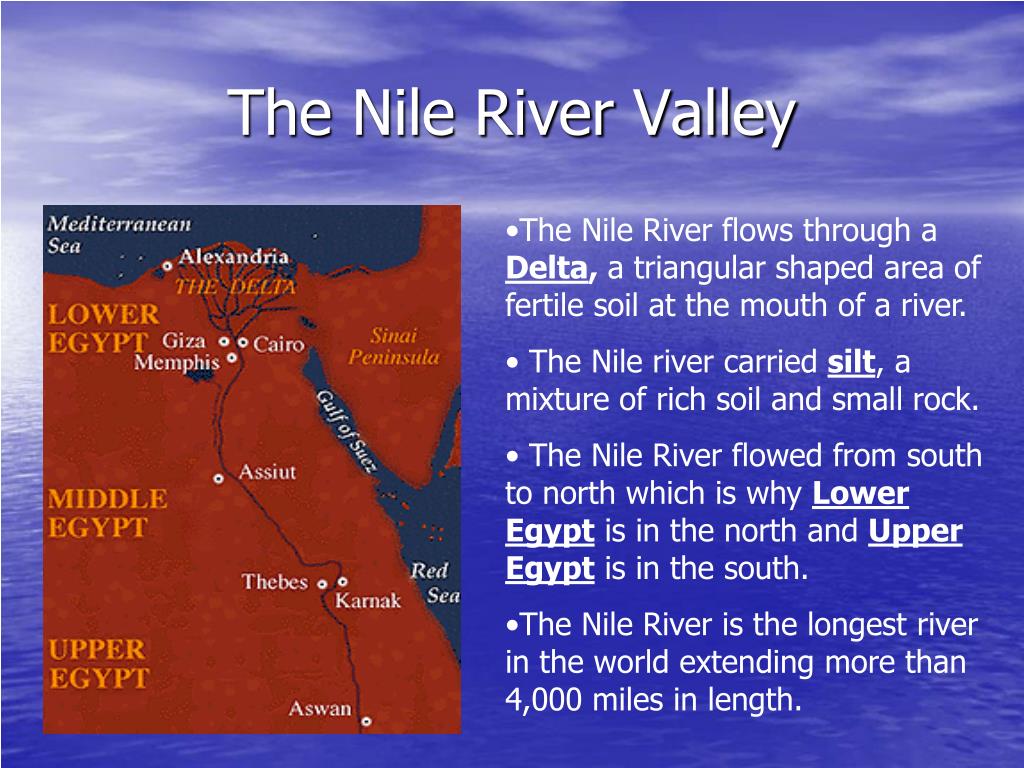
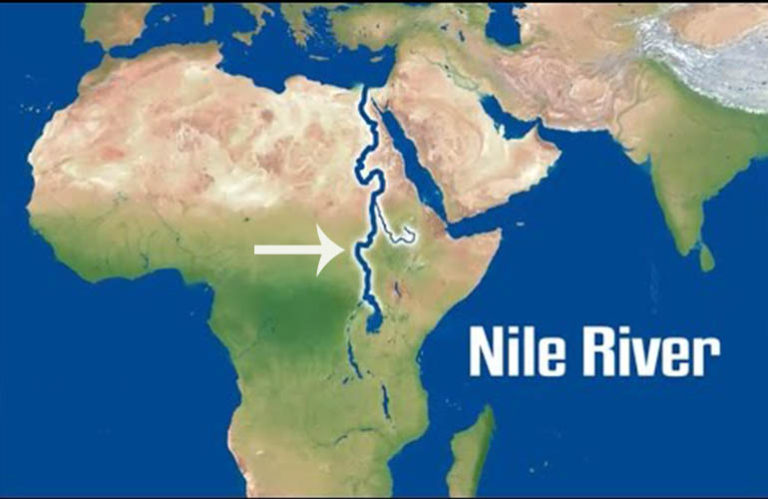
The Nile River, the longest river in the world, is a geographical and historical marvel, a lifeline that has sustained civilizations for millennia. Its journey begins in the heart of Africa and culminates in the Mediterranean Sea, carving a path through diverse landscapes and cultures. Understanding the Nile’s map location reveals its profound impact on the surrounding environment, its role in shaping history, and its enduring significance today.
A River of Origins and Destinations
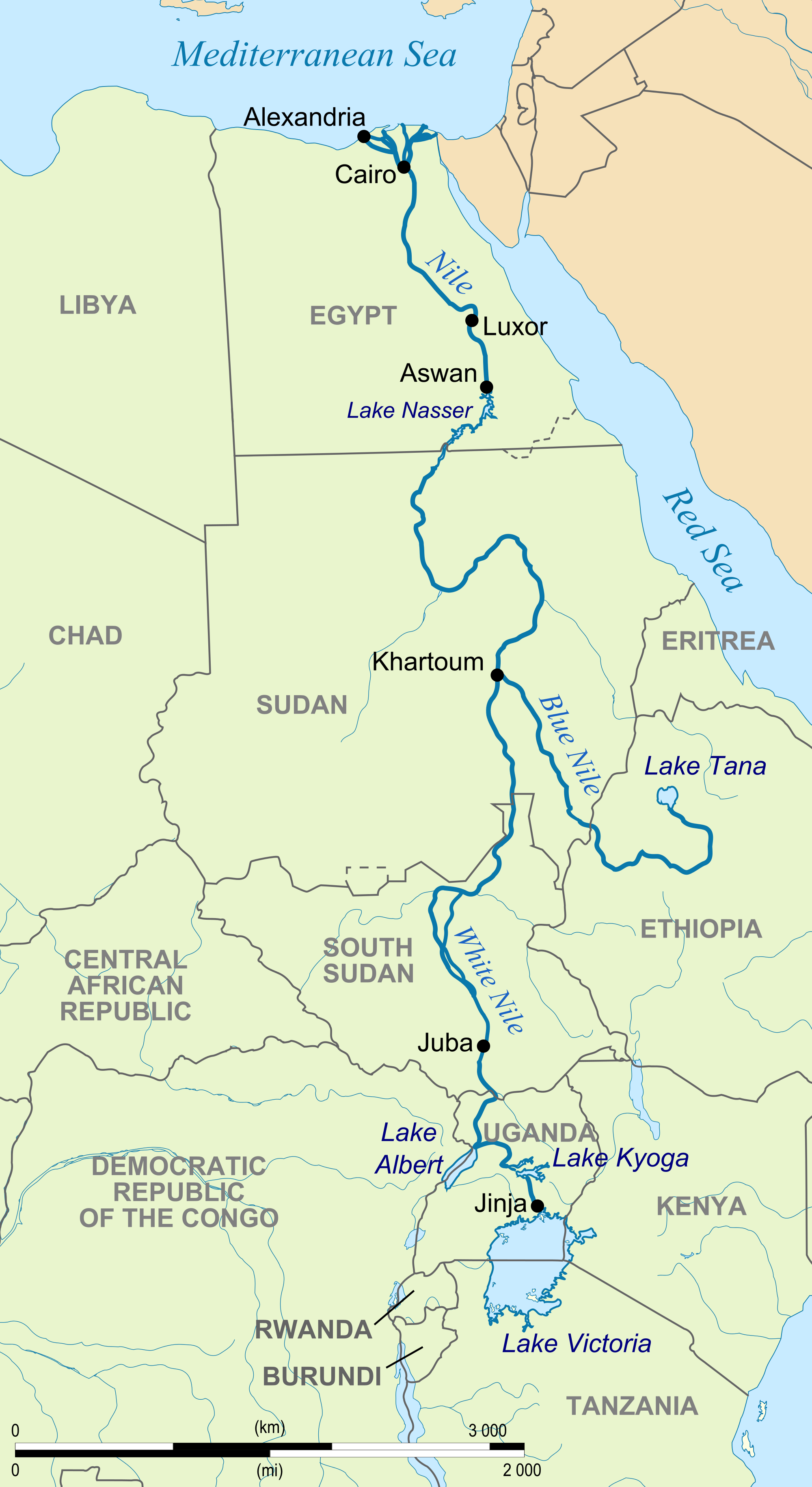
The Nile River’s journey begins in the East African highlands, with its two primary tributaries: the White Nile and the Blue Nile. The White Nile, originating in the Lake Victoria region of Uganda, flows northward through South Sudan and Sudan, gradually gaining volume as it receives contributions from smaller tributaries.
The Blue Nile, originating in the Ethiopian Highlands, carries a greater sediment load, contributing to the Nile’s rich alluvial soil. Its journey is marked by dramatic gorges and waterfalls, culminating in a confluence with the White Nile at Khartoum, Sudan.
From this point, the Nile flows northward as a single, mighty river, traversing the vast expanse of Sudan before entering Egypt. It winds its way through the Egyptian desert, creating a fertile strip known as the Nile Valley, a lifeline for agriculture and civilization. The river’s journey ends at the Mediterranean Sea, where it forms a vast delta, a testament to its immense power and enduring influence.
A Map Unveiling a Rich History
The Nile River’s map location is inextricably linked to the rise and fall of ancient civilizations. The fertile Nile Valley provided the resources and conditions for the development of the ancient Egyptian civilization, one of the most influential in human history. The river’s predictable floods, essential for irrigation and agriculture, facilitated the growth of sophisticated societies, monumental architecture, and vibrant cultural traditions.
The Nile also served as a crucial transportation route, connecting different regions and facilitating trade. This connectivity played a vital role in the spread of ideas, technology, and culture, fostering interactions between diverse communities along its banks. The Nile’s map location, therefore, is not merely a geographical marker but a testament to the enduring power of rivers to shape human history and civilization.
A Modern Lifeline: Challenges and Opportunities
Today, the Nile River continues to be a lifeline for millions of people across eleven countries. It remains a crucial source of water for agriculture, industry, and drinking water, sustaining livelihoods and driving economies. However, the Nile’s map location also presents challenges.
The river’s water resources are increasingly under pressure due to population growth, urbanization, and climate change. The Nile Basin is home to a diverse range of ecosystems, but its water quality is threatened by pollution from industrial and agricultural activities.
Furthermore, the Nile’s map location has led to disputes over water rights and resources, particularly between upstream and downstream countries. These tensions highlight the need for collaborative management and sustainable water resource utilization to ensure the river’s long-term health and the well-being of the populations it sustains.
Exploring the Nile: A Journey of Discovery
The Nile River’s map location invites exploration and discovery. Its diverse ecosystems, from the lush wetlands of the Sudd in South Sudan to the arid desert landscapes of Egypt, offer unique opportunities for wildlife viewing, cultural immersion, and adventure.
Cruises along the Nile offer a captivating journey through time, allowing travelers to witness ancient temples, pharaohs’ tombs, and bustling markets. The Nile’s rich history and vibrant culture are intertwined with its geographical location, offering a glimpse into the past and present of a region that has long been shaped by the river’s flow.
FAQs about the Nile River
Q: How long is the Nile River?
A: The Nile River is approximately 6,650 kilometers (4,132 miles) long, making it the longest river in the world.
Q: Where does the Nile River begin and end?
A: The Nile River begins in the East African highlands, with its two primary tributaries: the White Nile and the Blue Nile. It ends at the Mediterranean Sea, forming a vast delta.
Q: What countries does the Nile River flow through?
A: The Nile River flows through eleven countries: Tanzania, Uganda, Rwanda, Burundi, Democratic Republic of Congo, South Sudan, Ethiopia, Sudan, Egypt, Eritrea, and Kenya.
Q: What are the main tributaries of the Nile River?
A: The two main tributaries of the Nile River are the White Nile and the Blue Nile.
Q: Why is the Nile River so important?
A: The Nile River is vital for agriculture, industry, and drinking water for millions of people across eleven countries. It also serves as a crucial transportation route and plays a significant role in the region’s history and culture.
Tips for Exploring the Nile River
- Plan your trip in advance: The Nile River offers a variety of experiences, from wildlife safaris to historical explorations. Research your interests and plan your itinerary accordingly.
- Choose the right time to travel: The best time to visit the Nile River is during the dry season (October to April) when the weather is pleasant and the water levels are low.
- Consider a Nile cruise: Nile cruises offer a comfortable and immersive way to explore the river and its surrounding attractions.
- Respect local customs and traditions: The Nile River flows through diverse cultures, so it is important to be respectful of local customs and traditions.
- Be environmentally responsible: The Nile River is a precious resource, so it is essential to be environmentally responsible during your travels.
Conclusion
The Nile River’s map location is a testament to the enduring power of nature to shape human history and civilization. Its journey through diverse landscapes and cultures, its role as a lifeline for millions of people, and its rich history make it a captivating and essential subject of study and exploration. Understanding the Nile’s map location allows us to appreciate its profound impact on the environment, its role in shaping societies, and its enduring significance for generations to come.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Nile River: A Lifeline Traversing Time and Geography. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Navigating The Digital Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide To AT&T’s Service Map For Internet
- Navigating The Keystone Resort Ski Map: A Comprehensive Guide To Exploring The Mountain
- Navigating The Waters: Understanding Nautical Mile Maps
- Navigating The Rails: A Comprehensive Guide To The RTD Train Map
- Navigating Baltimore County: A Guide To The Zoning Map
- A Comprehensive Guide To Parris Island, South Carolina: Navigating The Cradle Of Marines
- Navigating The Waters Of Smith Lake, Alabama: A Comprehensive Guide
- Navigating Kingsland, Texas: A Comprehensive Guide To The City’s Map
Leave a Reply