Unraveling The Human Body: A Comprehensive Guide To Muscle Anatomy
Unraveling the Human Body: A Comprehensive Guide to Muscle Anatomy
Related Articles: Unraveling the Human Body: A Comprehensive Guide to Muscle Anatomy
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Human Body: A Comprehensive Guide to Muscle Anatomy. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Human Body: A Comprehensive Guide to Muscle Anatomy

The human body is a marvel of engineering, a complex system of interconnected tissues and organs that work in concert to perform a myriad of functions. One of the most fascinating and intricate aspects of this system is the musculoskeletal system, a network of bones, muscles, tendons, and ligaments that provide structure, support, and movement. Understanding the intricate arrangement and function of muscles is crucial for various fields, including healthcare, sports, and fitness. This comprehensive guide delves into the anatomy of human muscles, exploring their organization, types, functions, and significance.
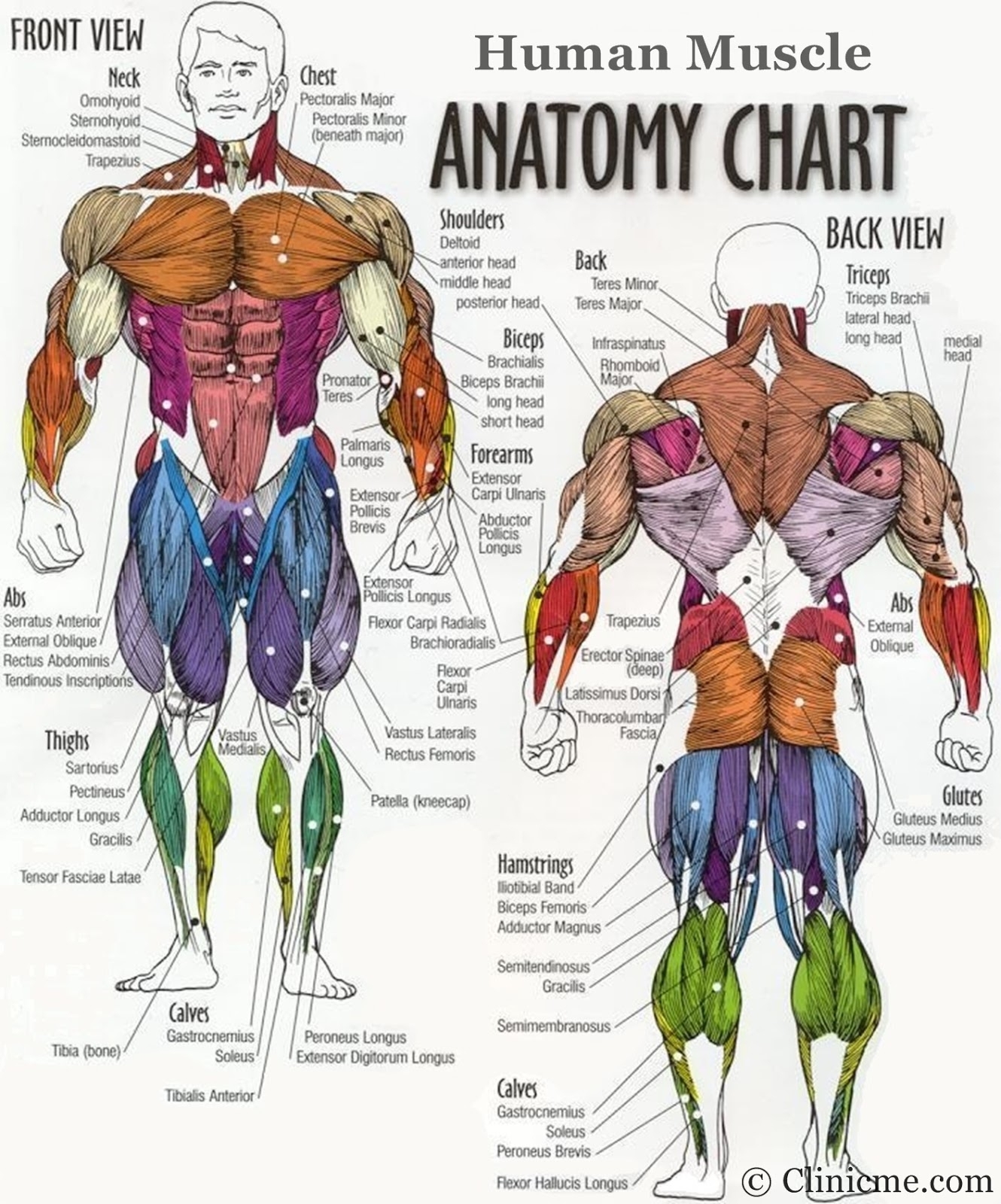
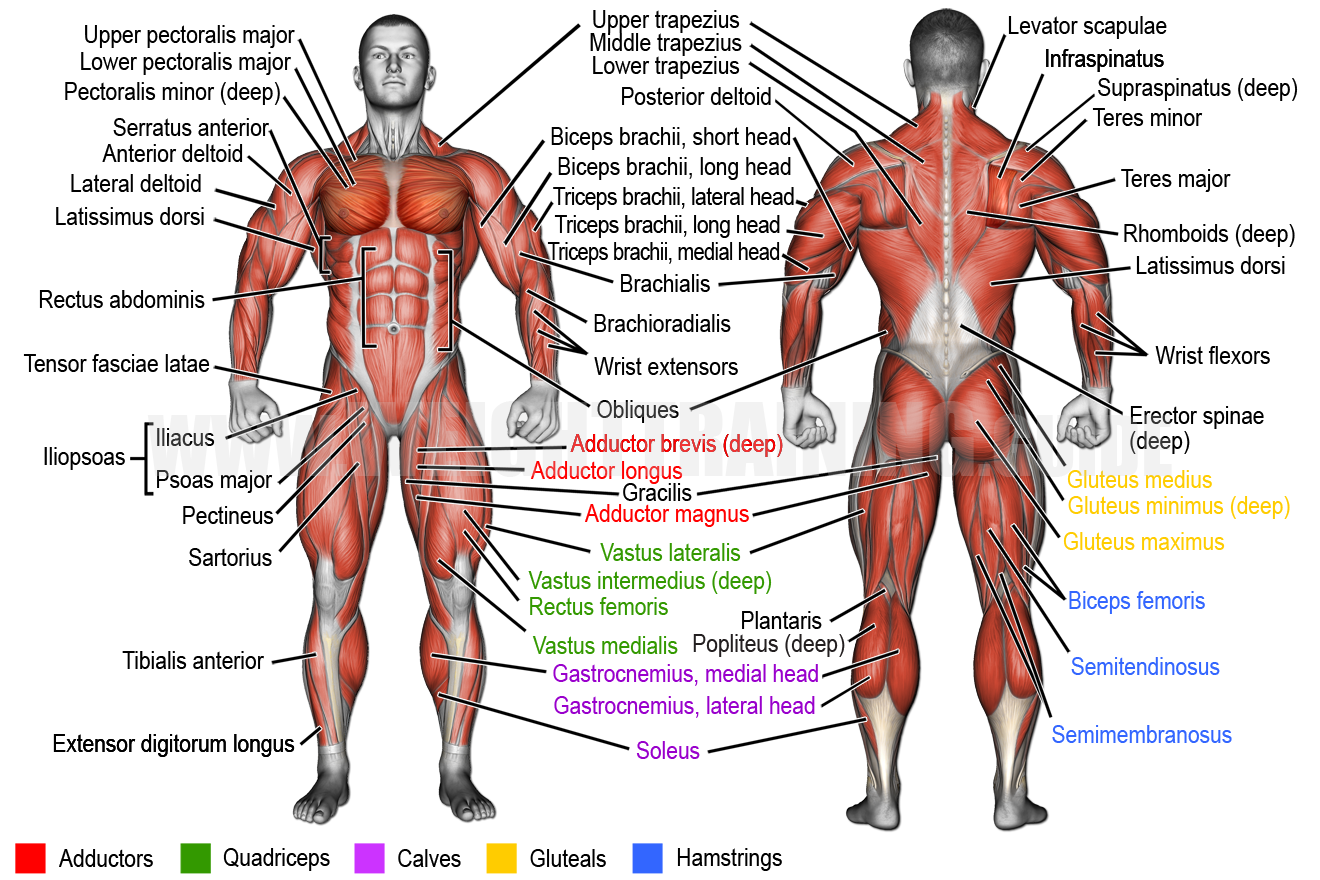
A Visual Journey: The Map of Body Muscles
The human body is a canvas of over 600 muscles, each meticulously placed and interconnected to facilitate movement and support. Visualizing these muscles through anatomical charts, often referred to as "muscle maps," offers a comprehensive understanding of their arrangement and relationships. These maps serve as invaluable tools for healthcare professionals, fitness enthusiasts, and anyone seeking to deepen their knowledge of human anatomy.
Types of Muscles: A Categorical Overview
Muscles are classified based on their structure, function, and location within the body. Understanding these categories provides a foundational understanding of muscle anatomy.
-
Skeletal Muscles: These are the muscles that attach to bones via tendons and are responsible for voluntary movement. They are striated, meaning they have a striped appearance under a microscope, due to the arrangement of protein filaments within their cells. Examples include the biceps brachii (upper arm), quadriceps femoris (thigh), and gastrocnemius (calf).
-
Smooth Muscles: Found in the walls of internal organs, such as the stomach, intestines, and blood vessels, smooth muscles are responsible for involuntary movements, such as digestion and blood flow regulation. They lack the striated appearance of skeletal muscles.
-
Cardiac Muscle: This specialized muscle tissue forms the heart, responsible for pumping blood throughout the body. It exhibits striated appearance but functions involuntarily, controlled by the autonomic nervous system.
Functions of Muscles: A Symphony of Movement and Support
Muscles play a vital role in maintaining human health and function. Their primary functions can be summarized as follows:
-
Movement: Muscles contract and relax, pulling on bones to generate movement. This allows us to walk, run, jump, lift, and perform countless other actions.
-
Support: Muscles provide structural support to the body, maintaining posture and preventing excessive movement.
-
Protection: Muscles act as cushions and shields, protecting vital organs from injury.
-
Heat Production: Muscle contraction generates heat, contributing to the body’s overall temperature regulation.
Exploring Muscle Anatomy: A Regional Approach
To fully appreciate the complexity of the musculoskeletal system, it is helpful to dissect the body into distinct regions and explore the muscles within each.
Head and Neck:
-
Facial Muscles: These muscles are responsible for facial expressions, chewing, and swallowing. Examples include the orbicularis oculi (closes the eyelids), zygomaticus major (raises the corners of the mouth), and masseter (chewing muscle).
-
Neck Muscles: These muscles support the head, facilitate neck movement, and aid in swallowing. Examples include the sternocleidomastoid (rotates and flexes the head), trapezius (elevates and rotates the shoulder), and scalenes (elevate the first rib).
Upper Limb:
-
Shoulder Muscles: These muscles control shoulder movement and support the arm. Examples include the deltoid (abducts the arm), supraspinatus (rotates the arm outward), and pectoralis major (adducts and flexes the arm).
-
Arm Muscles: These muscles control elbow flexion and extension, as well as forearm rotation. Examples include the biceps brachii (flexes the elbow), triceps brachii (extends the elbow), and brachialis (flexes the elbow).
-
Forearm Muscles: These muscles control wrist and finger movements. Examples include the flexor carpi radialis (flexes the wrist), extensor carpi ulnaris (extends the wrist), and flexor digitorum superficialis (flexes the fingers).
Trunk:
-
Back Muscles: These muscles support the spine, maintain posture, and control trunk movements. Examples include the erector spinae (extends the spine), latissimus dorsi (extends and adducts the arm), and trapezius (elevates and rotates the shoulder).
-
Abdominal Muscles: These muscles support the abdominal cavity, protect internal organs, and facilitate trunk movement. Examples include the rectus abdominis (flexes the trunk), external oblique (rotates and flexes the trunk), and internal oblique (rotates and flexes the trunk).
Lower Limb:
-
Hip Muscles: These muscles control hip movement and support the leg. Examples include the iliopsoas (flexes the hip), gluteus maximus (extends the hip), and adductor longus (adducts the hip).
-
Thigh Muscles: These muscles control knee flexion and extension. Examples include the quadriceps femoris (extends the knee), hamstring muscles (flexes the knee), and sartorius (flexes the hip and knee).
-
Leg Muscles: These muscles control ankle and foot movements. Examples include the gastrocnemius (plantar flexes the foot), soleus (plantar flexes the foot), and tibialis anterior (dorsiflexes the foot).
The Significance of Muscle Maps: A Multifaceted Perspective
Muscle maps hold immense value across various fields, contributing to a deeper understanding of human anatomy and its implications.
-
Healthcare: Medical professionals rely on muscle maps for accurate diagnosis and treatment of musculoskeletal disorders. Understanding muscle anatomy is crucial for identifying injuries, performing surgical procedures, and developing rehabilitation plans.
-
Fitness and Exercise: Fitness professionals utilize muscle maps to design effective workout routines, targeting specific muscle groups for strength training, flexibility, and endurance.
-
Sports: Coaches and athletes use muscle maps to analyze movement patterns, identify areas for improvement, and optimize performance.
-
Education: Muscle maps serve as essential visual aids in anatomy and physiology courses, facilitating understanding of complex anatomical structures and their functions.
-
Art and Illustration: Artists and illustrators use muscle maps as references for creating realistic and anatomically accurate depictions of the human body.
Frequently Asked Questions about Muscle Maps
Q: What are the best resources for learning about muscle maps?
A: Numerous resources are available for exploring muscle maps, including anatomical atlases, online databases, and educational websites. Books such as "Gray’s Anatomy" and "Netter’s Atlas of Human Anatomy" offer detailed illustrations and descriptions. Websites like Kenhub and Anatomy.TV provide interactive muscle maps with detailed information and 3D models.
Q: How can I use muscle maps to improve my fitness routine?
A: By studying muscle maps, you can identify the muscle groups involved in specific exercises and tailor your workouts to target specific areas. Understanding muscle anatomy allows you to optimize your training program for maximum effectiveness and minimize the risk of injury.
Q: Are there any specific muscle maps for different sports or activities?
A: Yes, specialized muscle maps exist for various sports and activities, highlighting the muscles most involved in those specific movements. For example, muscle maps for runners emphasize the muscles of the lower limbs, while those for swimmers focus on the muscles of the upper body and core.
Tips for Using Muscle Maps Effectively
-
Start with a basic overview: Begin by studying a general muscle map that shows the major muscle groups and their locations.
-
Focus on specific areas: Once you have a general understanding, delve deeper into specific regions of interest, such as the muscles of the shoulder or the leg.
-
Use interactive resources: Explore online databases and websites that provide interactive muscle maps, allowing you to rotate and zoom in on specific structures.
-
Relate anatomy to function: Don’t just memorize muscle names; try to understand how each muscle contributes to overall movement and function.
-
Practice visualization: Imagine the muscles contracting and relaxing during different movements, helping you to visualize their roles in the body.
Conclusion: A Powerful Tool for Understanding the Human Body
Muscle maps serve as invaluable tools for understanding the intricate workings of the human musculoskeletal system. Whether you are a healthcare professional, fitness enthusiast, or simply curious about the complexities of the human body, these visual representations offer a comprehensive and engaging approach to learning anatomy. By exploring muscle maps, you gain a deeper appreciation for the incredible design and functionality of the human body, paving the way for a greater understanding of health, movement, and well-being.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Human Body: A Comprehensive Guide to Muscle Anatomy. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Navigating The Digital Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide To AT&T’s Service Map For Internet
- Navigating The Keystone Resort Ski Map: A Comprehensive Guide To Exploring The Mountain
- Navigating The Waters: Understanding Nautical Mile Maps
- Navigating The Rails: A Comprehensive Guide To The RTD Train Map
- Navigating Baltimore County: A Guide To The Zoning Map
- A Comprehensive Guide To Parris Island, South Carolina: Navigating The Cradle Of Marines
- Navigating The Waters Of Smith Lake, Alabama: A Comprehensive Guide
- Navigating Kingsland, Texas: A Comprehensive Guide To The City’s Map
Leave a Reply