Unveiling The Ice Age: A Map Of North America Transformed
Unveiling the Ice Age: A Map of North America Transformed
Related Articles: Unveiling the Ice Age: A Map of North America Transformed
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Ice Age: A Map of North America Transformed. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Ice Age: A Map of North America Transformed

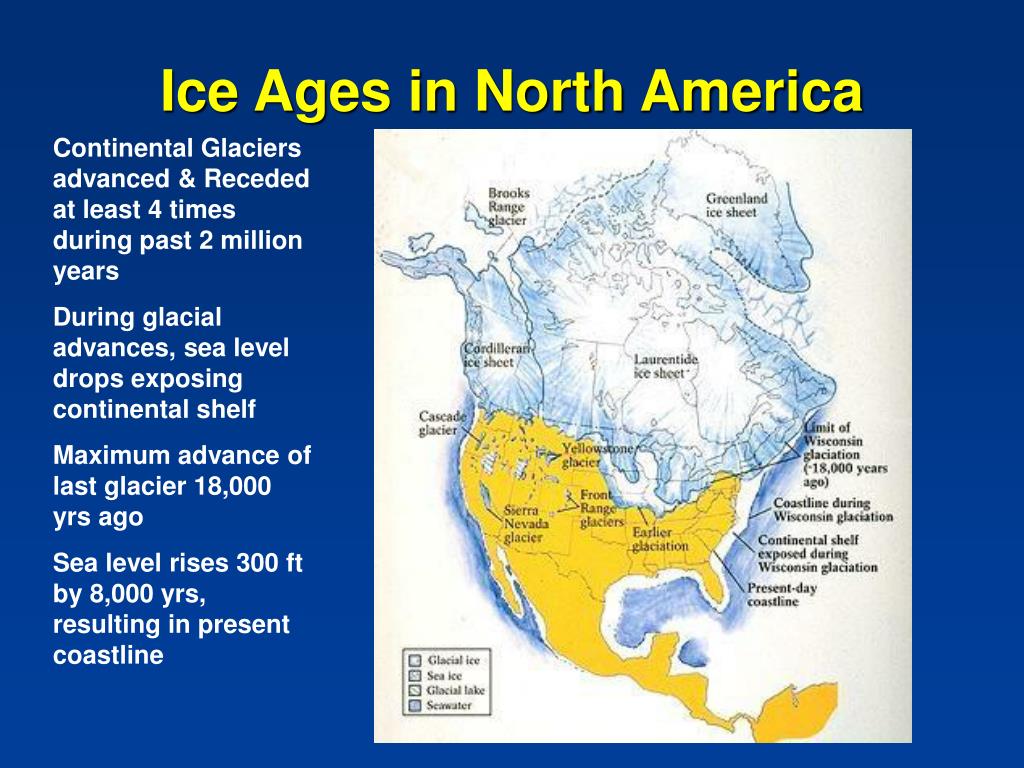
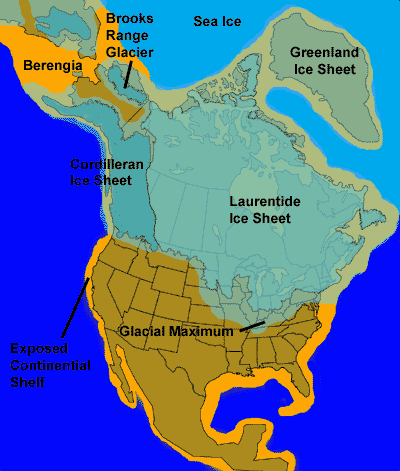
The North America we know today, with its diverse landscapes and ecosystems, is a product of a dramatic and transformative period: the Pleistocene Ice Age. This epoch, spanning from roughly 2.6 million to 11,700 years ago, witnessed the Earth’s climate fluctuate between glacial and interglacial periods. During glacial periods, vast ice sheets, miles thick, blanketed much of the continent, reshaping its geography, influencing its biodiversity, and ultimately laying the foundation for the North America we see today.
Understanding the extent and impact of these ice sheets is crucial for unraveling the continent’s geological history, understanding its present-day ecosystems, and even predicting future climate change scenarios.
Mapping the Ice Age:
Ice age maps of North America provide a visual representation of the extent of glacial coverage during different stages of the Pleistocene. These maps are constructed using a combination of geological evidence, including:
- Landforms: Glacial features like moraines (deposits of rock and sediment left behind by glaciers), drumlins (elongated hills formed by glacial erosion), and eskers (winding ridges of sand and gravel deposited by meltwater streams) provide clues about the movement and extent of glaciers.
- Isotopes: Analyzing the isotopic composition of rocks, sediments, and fossils allows scientists to reconstruct past climates and the presence of ice sheets.
- Paleontological evidence: Fossils of plants and animals adapted to cold climates provide further evidence of glacial presence and the extent of ice sheets.
The Impact of Ice Age Glaciation:
The ice age had a profound impact on North America, leaving a lasting imprint on its landscape, biodiversity, and human history.
1. Shaping the Land:
- Glacial Erosion: The immense weight of ice sheets carved out valleys, lakes, and fjords, sculpting the landscape we see today. The Great Lakes, for example, were formed by glacial erosion and subsequent filling with meltwater.
- Deposition: As glaciers melted, they deposited vast amounts of sediment, creating fertile plains, moraines, and eskers. These landforms, like the Long Island moraine, are vital for agriculture and provide unique habitats for diverse plant and animal life.
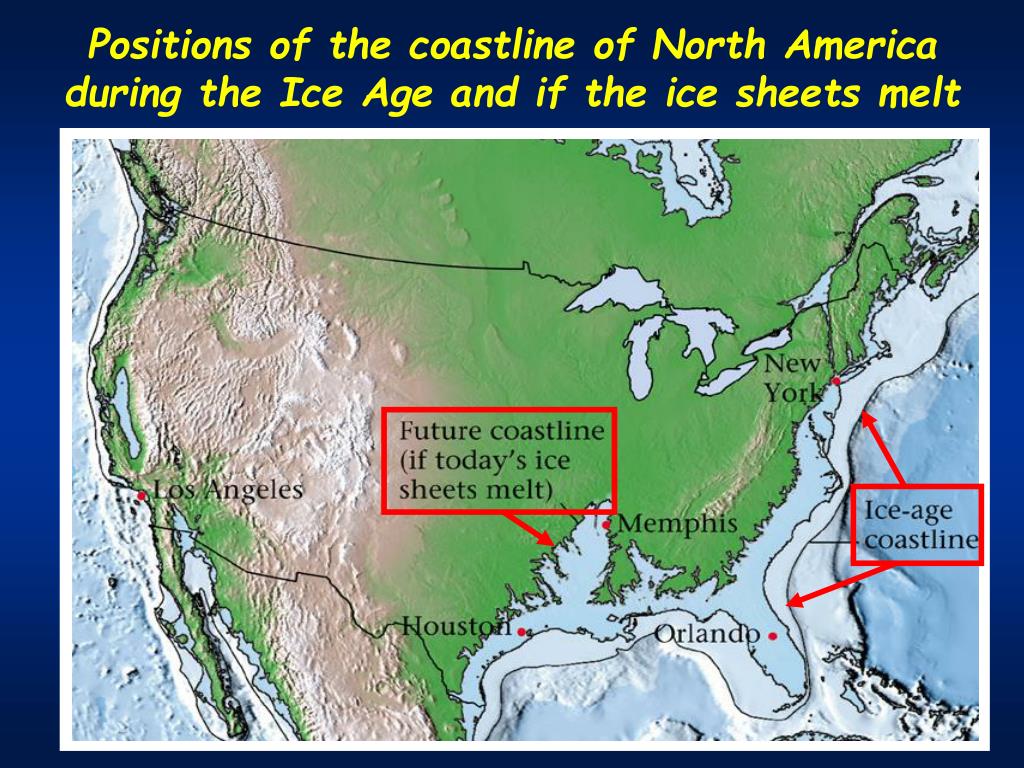
- Sea Level Fluctuations: The massive amount of water locked up in glaciers caused global sea levels to drop significantly. This exposed vast areas of land, connecting continents like Asia and North America through land bridges.
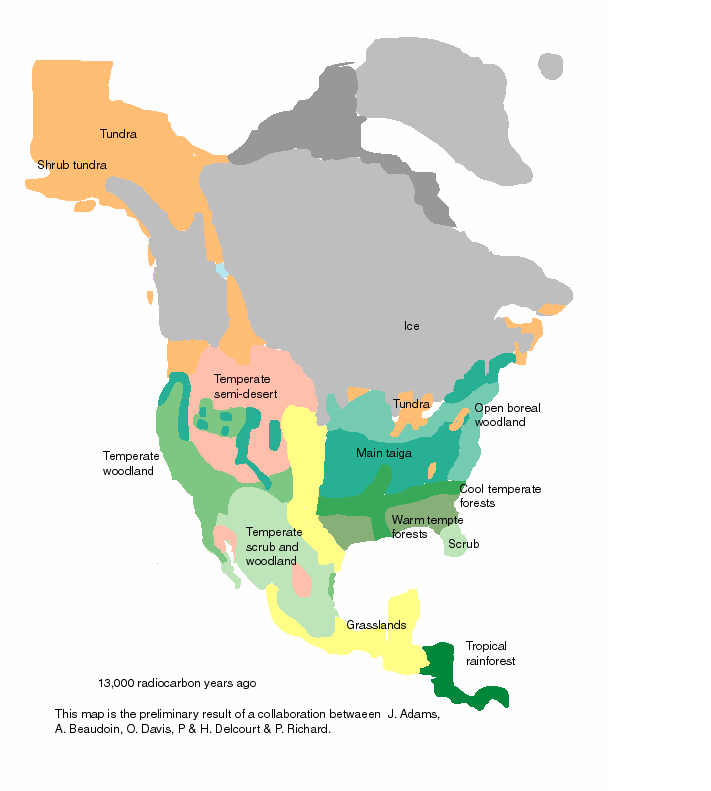
2. Influencing Biodiversity:
- Refugia: As glaciers advanced, they forced plants and animals to retreat to warmer, ice-free areas known as refugia. These refugia acted as pockets of biodiversity, allowing species to survive the harsh conditions and repopulate the continent after the glaciers receded.
- Migration: The ice sheets and associated changes in climate and vegetation forced animals to migrate, leading to the dispersal of species across the continent. The presence of similar species in North America and Eurasia suggests that land bridges allowed for the exchange of fauna between these continents.
- Evolution: The changing environment during the Pleistocene favored adaptations to cold climates, leading to the evolution of unique species like the woolly mammoth, mastodon, and saber-toothed cat.
3. Human History:
- Migration: The Bering Land Bridge, exposed during the glacial periods, facilitated the migration of humans from Asia to North America. This event, known as the Bering Strait Crossing, marks the beginning of human history in the Americas.
- Adaptation: Early humans adapted to the challenging conditions of the ice age, developing hunting and gathering techniques to survive. The presence of tools and weapons associated with hunting large game, like mammoth and bison, provides evidence of human adaptation to this period.
Benefits of Understanding the Ice Age:
- Predicting Future Climate Change: Studying the effects of past climate change helps us understand the potential consequences of future climate change, including rising sea levels, changes in precipitation patterns, and shifts in ecosystems.
- Resource Management: Understanding the geological history of an area helps us manage resources like groundwater, soil, and mineral deposits.
- Conservation: By understanding the impact of past climate change on biodiversity, we can better conserve species and ecosystems that are vulnerable to future climate change.
- Tourism and Recreation: Many popular tourist destinations, including national parks and scenic areas, owe their existence to glacial activity. Understanding the ice age enhances our appreciation of these landscapes and their geological history.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. How do we know about the ice age?
Scientists study various geological evidence, including landforms like moraines and eskers, isotopic analysis of rocks and fossils, and the presence of cold-adapted plant and animal fossils.
2. How long did the ice age last?
The Pleistocene Ice Age lasted from approximately 2.6 million to 11,700 years ago, marked by periods of glacial expansion and retreat.
3. How thick were the ice sheets?
The ice sheets reached thicknesses of several miles, covering vast areas of North America.
4. What was the climate like during the ice age?
The climate was significantly colder than today, with average temperatures several degrees lower.
5. How did the ice age affect sea levels?
The massive amount of water locked up in glaciers caused global sea levels to drop significantly, exposing vast areas of land.
Tips for Understanding Ice Age Maps:
- Pay attention to the legend: The legend will explain the different colors and symbols used on the map, indicating the extent of glacial coverage and different geological features.
- Look for key glacial features: Identify moraines, drumlins, eskers, and other landforms created by glaciers.
- Consider the time period: Maps often depict different stages of the ice age, so pay attention to the time period represented.
- Compare maps to modern geography: Compare the ice age map to a modern map of North America to see how the landscape has changed.
- Connect the dots: Consider how the ice age shaped the landscapes, biodiversity, and human history of North America.
Conclusion:
The ice age was a transformative period in North America’s history, leaving an indelible mark on its landscape, biodiversity, and human history. Understanding the extent and impact of the ice sheets is crucial for appreciating the continent’s geological evolution, managing its resources, and preparing for future climate change. By studying ice age maps and the evidence they reveal, we gain a deeper understanding of the forces that have shaped our planet and the challenges we face in the 21st century.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Ice Age: A Map of North America Transformed. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Navigating The Digital Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide To AT&T’s Service Map For Internet
- Navigating The Keystone Resort Ski Map: A Comprehensive Guide To Exploring The Mountain
- Navigating The Waters: Understanding Nautical Mile Maps
- Navigating The Rails: A Comprehensive Guide To The RTD Train Map
- Navigating Baltimore County: A Guide To The Zoning Map
- A Comprehensive Guide To Parris Island, South Carolina: Navigating The Cradle Of Marines
- Navigating The Waters Of Smith Lake, Alabama: A Comprehensive Guide
- Navigating Kingsland, Texas: A Comprehensive Guide To The City’s Map
Leave a Reply