Unveiling The Power Of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) In Surveying And Mapping
Unveiling the Power of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) in Surveying and Mapping
Related Articles: Unveiling the Power of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) in Surveying and Mapping
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Power of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) in Surveying and Mapping. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Power of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) in Surveying and Mapping

Geographic Information Systems (GIS) have revolutionized the way we gather, analyze, and visualize spatial data. In the realm of surveying and mapping, GIS has become an indispensable tool, offering a comprehensive and efficient approach to understanding and representing the physical world. This article delves into the intricacies of GIS survey maps, exploring their capabilities, applications, and significance in various fields.
Understanding GIS Survey Maps: A Digital Representation of Reality
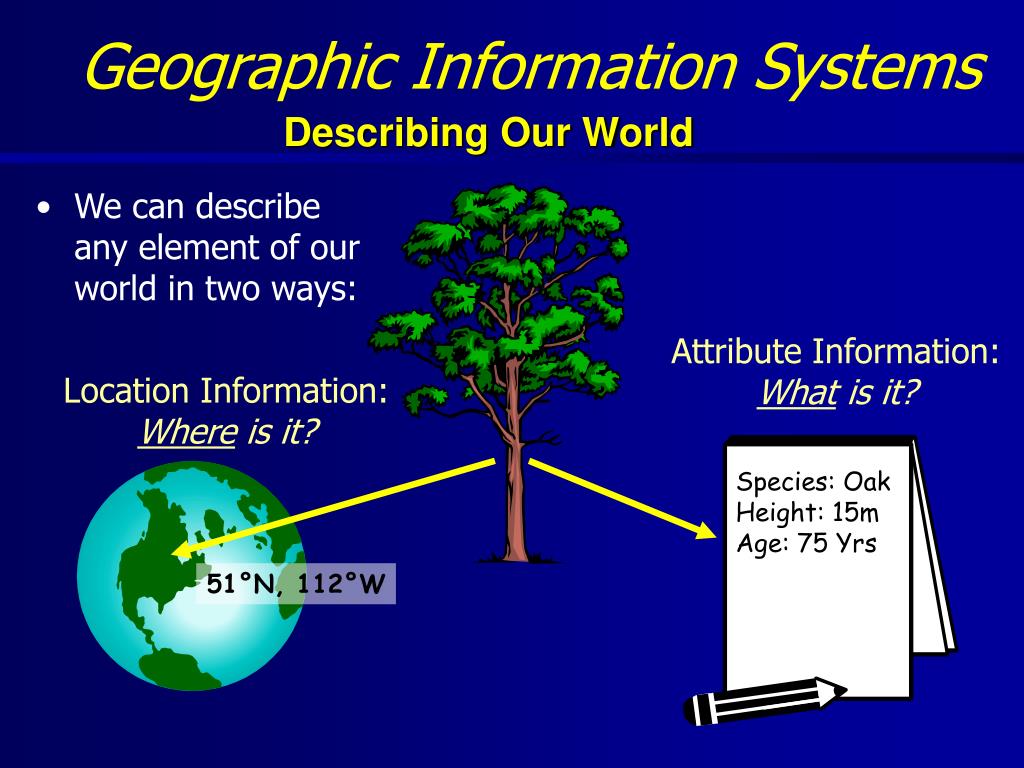
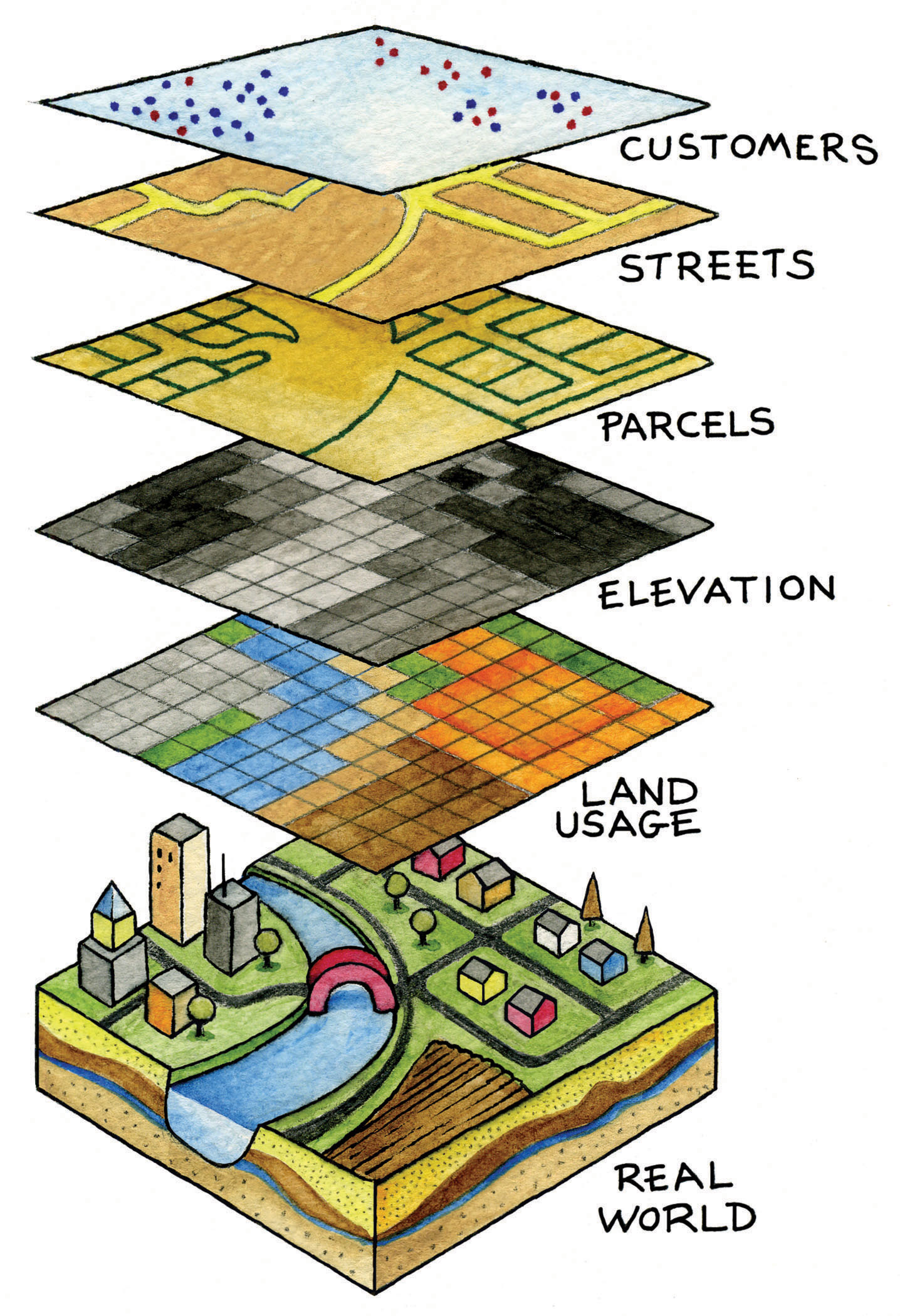
GIS survey maps are digital representations of geographic features, incorporating spatial data collected through surveying techniques. They go beyond traditional paper maps by integrating multiple layers of information, each representing a specific aspect of the surveyed area. These layers can include:
- Topographic Data: Elevations, contours, and terrain features.
- Land Ownership Boundaries: Property lines, easements, and legal designations.
- Infrastructure Data: Roads, utilities, buildings, and other man-made structures.
- Environmental Data: Vegetation, water bodies, soil types, and geological formations.
- Demographic Data: Population density, socioeconomic factors, and other human-related information.
This layered approach allows for a multifaceted understanding of the surveyed area, enabling analysts to identify patterns, relationships, and potential issues that might not be apparent from a single layer of information.
The Advantages of GIS Survey Maps: A Powerful Tool for Decision Making
GIS survey maps offer a multitude of benefits, making them invaluable for various applications:
- Enhanced Accuracy and Precision: GIS utilizes precise surveying techniques and geospatial referencing systems, ensuring accurate representation of geographic features.
- Data Integration and Analysis: Combining multiple data layers within a GIS environment enables comprehensive analysis, revealing hidden relationships and insights.
- Visualization and Communication: GIS maps provide clear and intuitive visualizations, facilitating effective communication of complex spatial information to stakeholders.
- Spatial Modeling and Prediction: GIS tools allow for spatial modeling and prediction, enabling informed decision-making based on projected scenarios and potential impacts.
- Efficient Data Management: GIS provides a centralized platform for storing, managing, and updating spatial data, ensuring consistency and accessibility.
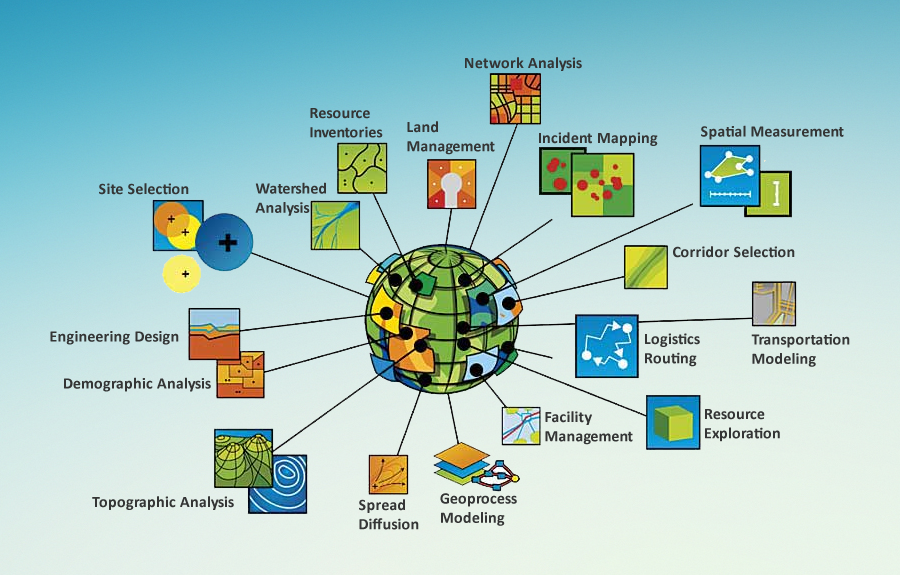
Applications of GIS Survey Maps: From Urban Planning to Environmental Management
GIS survey maps find diverse applications across various industries and disciplines:
- Urban Planning and Development: GIS maps assist in planning new infrastructure, managing urban growth, and optimizing resource allocation.
- Environmental Management: GIS maps aid in monitoring environmental conditions, identifying pollution sources, and managing natural resources.
- Transportation Planning: GIS maps facilitate efficient route planning, traffic management, and transportation network optimization.
- Agriculture and Forestry: GIS maps assist in crop monitoring, soil analysis, and forest resource management.
- Disaster Management: GIS maps play a crucial role in disaster preparedness, response, and recovery efforts.
- Real Estate and Property Management: GIS maps provide valuable insights for property valuation, land acquisition, and property development.
- Archaeology and Cultural Heritage: GIS maps aid in site documentation, mapping archaeological features, and preserving cultural heritage.
FAQs on GIS Survey Maps: Addressing Common Queries
Q1: What are the key components of a GIS survey map?
A: A GIS survey map typically consists of:
- Base Map: A foundation map depicting geographic features such as roads, water bodies, and boundaries.
- Data Layers: Multiple layers of information representing different aspects of the surveyed area, as described earlier.
- Symbols and Legends: Visual representations and explanations of the data layers and their associated attributes.
- Spatial Referencing System: A coordinate system that defines the location of features on the map.
Q2: What software is used to create GIS survey maps?
A: Popular GIS software programs include:
- ArcGIS: A comprehensive suite of GIS tools developed by Esri.
- QGIS: A free and open-source GIS software platform.
- MapInfo Pro: A GIS software package known for its mapping and analysis capabilities.
Q3: What are the challenges associated with GIS survey map creation?
A: Challenges include:
- Data Acquisition and Accuracy: Ensuring the accuracy and completeness of spatial data is crucial for reliable GIS mapping.
- Data Integration and Standardization: Integrating data from different sources and ensuring data consistency can be challenging.
- Software Proficiency: Using GIS software effectively requires specialized knowledge and training.
- Data Security and Privacy: Safeguarding sensitive spatial data is essential, especially in applications involving personal information.
Tips for Effective GIS Survey Map Creation:
- Define Clear Objectives: Establish specific goals and questions to be addressed by the GIS map.
- Utilize High-Quality Data: Ensure the accuracy and reliability of the data used in the map.
- Choose Appropriate Data Layers: Select data layers relevant to the intended purpose of the map.
- Employ Effective Visualization Techniques: Utilize clear and informative symbols, colors, and legends.
- Document and Share the Map: Provide clear documentation and metadata for understanding the map’s content and methodology.
Conclusion: The Future of Surveying and Mapping with GIS
GIS survey maps have emerged as a cornerstone of modern surveying and mapping practices. Their ability to integrate, analyze, and visualize spatial information empowers decision-makers across various sectors. As technology continues to advance, GIS is poised to further revolutionize how we understand and interact with the world around us. Continued investment in GIS research, development, and education will ensure its continued impact on shaping a more informed and sustainable future.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Power of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) in Surveying and Mapping. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Navigating The Digital Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide To AT&T’s Service Map For Internet
- Navigating The Keystone Resort Ski Map: A Comprehensive Guide To Exploring The Mountain
- Navigating The Waters: Understanding Nautical Mile Maps
- Navigating The Rails: A Comprehensive Guide To The RTD Train Map
- Navigating Baltimore County: A Guide To The Zoning Map
- A Comprehensive Guide To Parris Island, South Carolina: Navigating The Cradle Of Marines
- Navigating The Waters Of Smith Lake, Alabama: A Comprehensive Guide
- Navigating Kingsland, Texas: A Comprehensive Guide To The City’s Map
Leave a Reply