Unveiling The Secrets Of The Antarctic Circle: A Geographical And Scientific Exploration
Unveiling the Secrets of the Antarctic Circle: A Geographical and Scientific Exploration
Related Articles: Unveiling the Secrets of the Antarctic Circle: A Geographical and Scientific Exploration
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Secrets of the Antarctic Circle: A Geographical and Scientific Exploration. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Secrets of the Antarctic Circle: A Geographical and Scientific Exploration
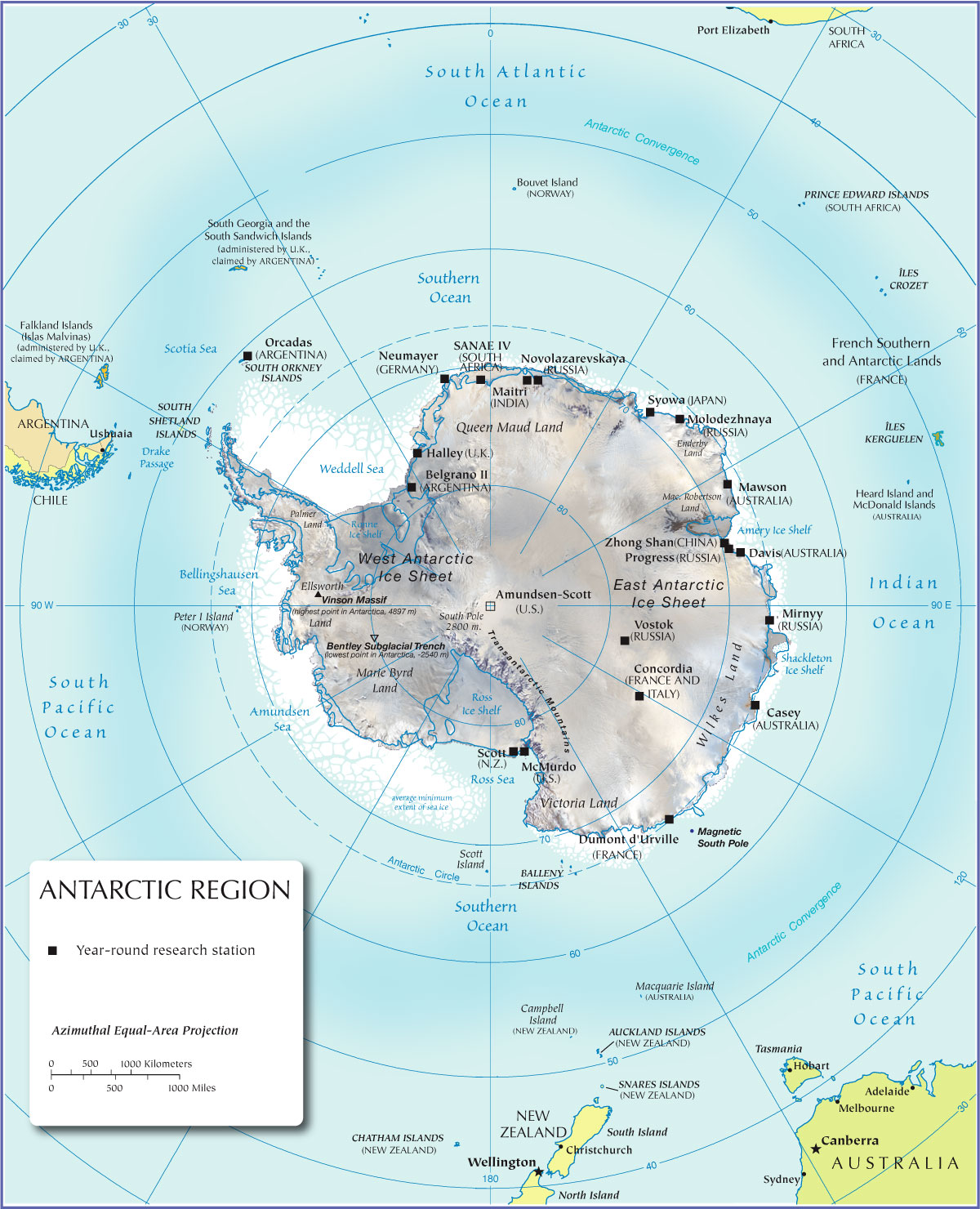
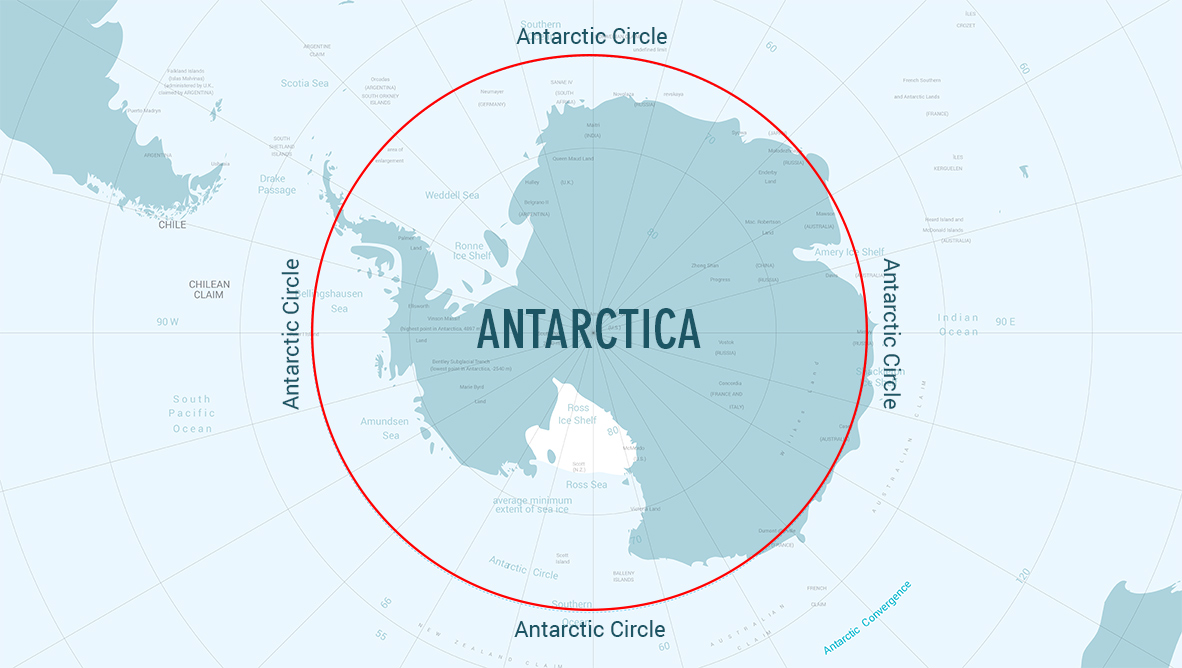
The Antarctic Circle, an invisible line encircling the Earth at 66.5° south latitude, marks a significant boundary in our planet’s geography and climate. It defines the southernmost region where the sun remains continuously above the horizon for at least 24 hours during the summer solstice and below the horizon for at least 24 hours during the winter solstice. This unique phenomenon, known as the midnight sun and polar night respectively, profoundly influences the environment and ecosystems within the Antarctic Circle.
A Journey Through the Antarctic Circle: Exploring its Significance
Beyond its geographical definition, the Antarctic Circle holds immense scientific and ecological importance. It encompasses the vast and icy continent of Antarctica, along with surrounding islands and waters, forming a critical component of the global climate system.
-
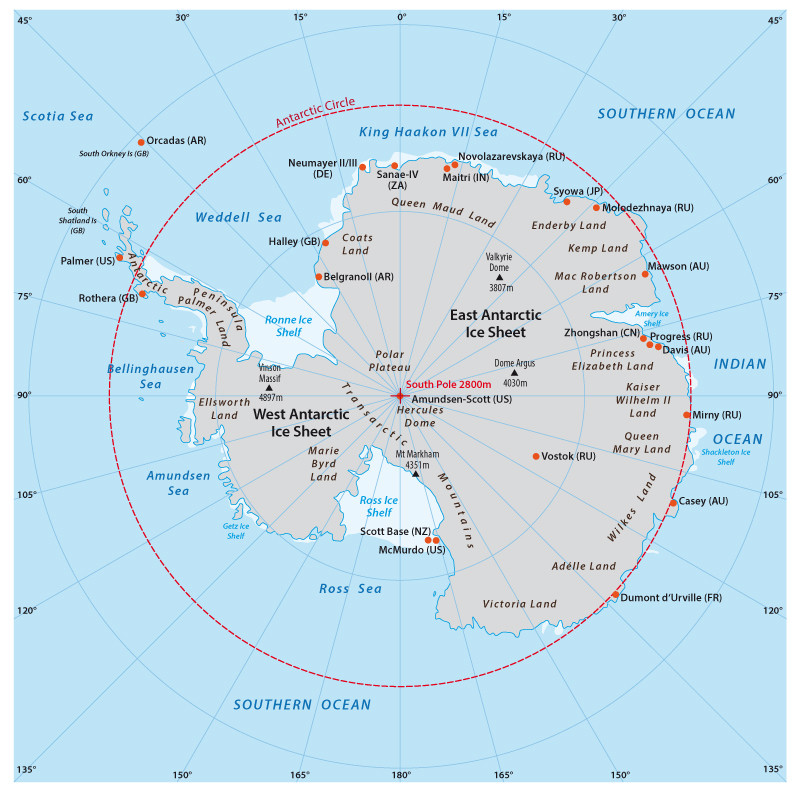
A Cradle of Ice and Cold: The Antarctic Circle is home to the largest ice sheet on Earth, covering an area larger than the United States. This massive ice sheet, along with surrounding glaciers and ice shelves, plays a vital role in regulating global sea levels. Understanding the dynamics of ice formation, melting, and movement within the Antarctic Circle is crucial for predicting future sea level rise and its impact on coastal communities worldwide.
-
A Sanctuary of Biodiversity: Despite its harsh conditions, the Antarctic Circle harbors a unique and diverse range of life forms. From penguins and seals to whales and krill, the region’s ecosystems are intricately interconnected and highly sensitive to environmental changes. Studying these ecosystems provides valuable insights into the resilience and adaptability of life in extreme environments and helps us understand the potential consequences of climate change on biodiversity.
-
A Window to the Past: The ice sheets and sediments of the Antarctic Circle hold a rich archive of past climate and environmental conditions. By studying ice cores, scientists can reconstruct past temperatures, atmospheric composition, and even ancient ecosystems, providing valuable data for understanding long-term climate change and its impacts.
-
A Hub for Scientific Research: The unique and extreme conditions within the Antarctic Circle present a unique laboratory for scientific research. Researchers from across the globe collaborate in conducting studies on a wide range of topics, including climate change, glaciology, oceanography, and astrophysics. The Antarctic Circle serves as a platform for international cooperation and knowledge sharing, contributing to our understanding of the Earth and its interconnected systems.
Navigating the Antarctic Circle: A Look at its Geography and Climate
The Antarctic Circle’s geographical location and its proximity to the South Pole create unique climatic conditions that shape the region’s environment and ecosystems.
-
The Polar Night and Midnight Sun: The most striking feature of the Antarctic Circle is the phenomenon of the polar night and midnight sun. During the winter solstice, the sun remains below the horizon for 24 hours, plunging the region into continuous darkness. Conversely, during the summer solstice, the sun remains above the horizon for 24 hours, bathing the region in continuous daylight. This extreme variation in sunlight influences the behavior and physiology of organisms within the Antarctic Circle.
-
Cold and Icy Conditions: The Antarctic Circle experiences extremely cold temperatures, with average winter temperatures ranging from -10°C to -60°C. The vast ice sheets and glaciers act as giant heat sinks, further cooling the surrounding air and water. These frigid conditions create a unique environment that supports specialized life forms adapted to survive in extreme cold.
-
Strong Winds and Limited Precipitation: The Antarctic Circle experiences strong, persistent winds, primarily due to the Coriolis effect and the large temperature differences between the polar regions and lower latitudes. These winds can reach speeds exceeding 100 kilometers per hour, creating challenging conditions for both human activity and wildlife. Precipitation within the Antarctic Circle is limited, primarily in the form of snow.
Exploring the Antarctic Circle: A Glimpse into Human Activities and Impacts
Despite its harsh environment, the Antarctic Circle has attracted human activity for centuries, driven by exploration, scientific research, and resource extraction.
-
Exploration and Scientific Research: Since the early 19th century, explorers and scientists have been drawn to the Antarctic Circle, seeking to understand its geography, climate, and ecosystems. Numerous expeditions have been launched to map the region, study its wildlife, and collect data on climate change.
-
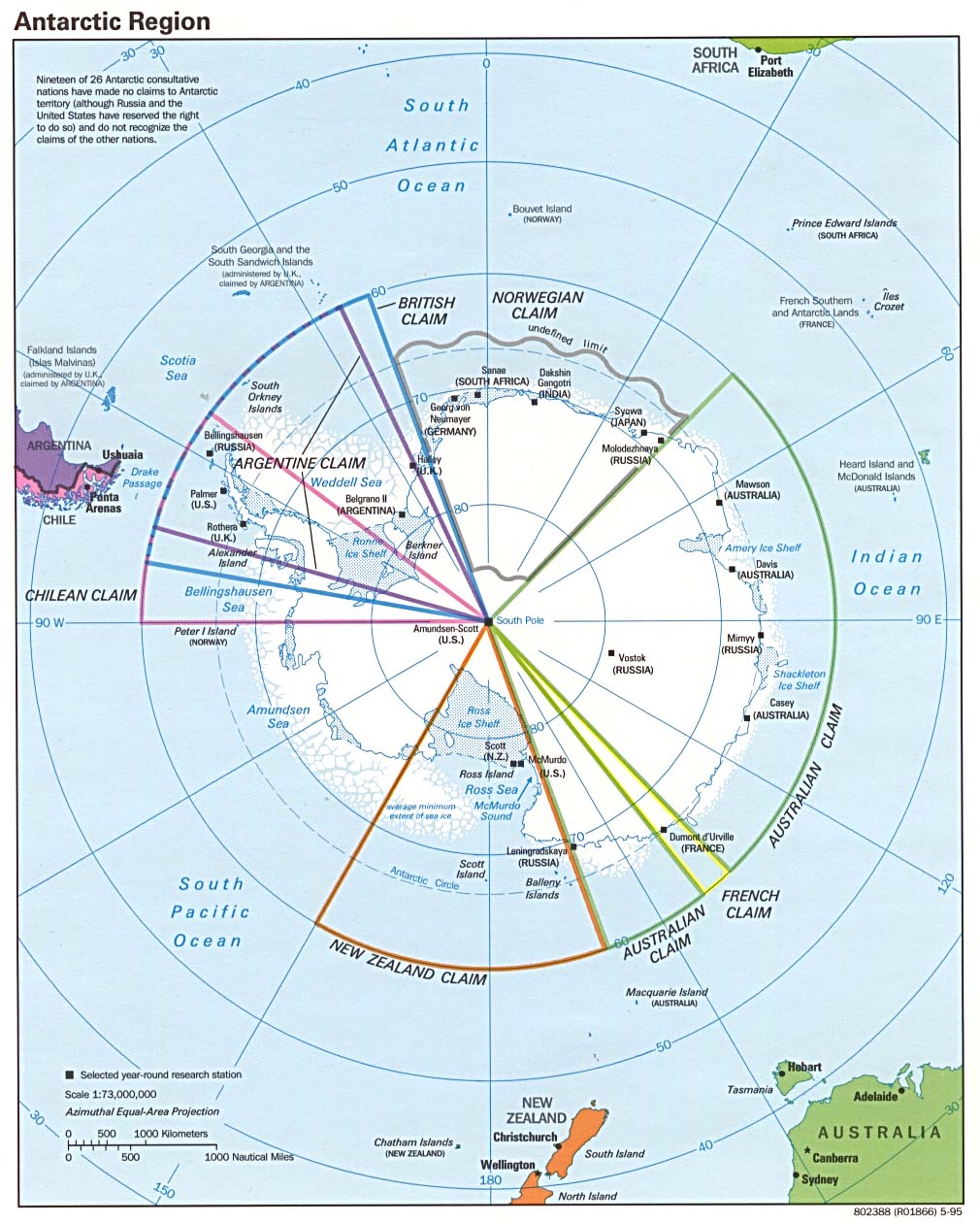
Resource Extraction: The Antarctic Circle holds significant mineral resources, including coal, iron ore, and oil. However, international agreements have been established to limit resource extraction in the region, recognizing its unique environmental value.
-
Tourism: In recent years, tourism to the Antarctic Circle has increased, offering visitors the opportunity to experience the region’s breathtaking landscapes and wildlife. However, tourism activities need to be carefully managed to minimize environmental impacts and ensure the sustainability of the region’s ecosystems.
FAQs about the Antarctic Circle
1. What are the main characteristics of the Antarctic Circle?
The Antarctic Circle is defined by its unique geographical location at 66.5° south latitude, resulting in the phenomenon of the polar night and midnight sun. It is characterized by its vast ice sheets, extreme cold, strong winds, and limited precipitation.
2. Why is the Antarctic Circle important?
The Antarctic Circle holds immense scientific and ecological importance. It plays a vital role in regulating global sea levels, harbors unique and diverse ecosystems, provides valuable data on past climate change, and serves as a hub for international scientific research.
3. What are some of the challenges associated with exploring and researching the Antarctic Circle?
Exploring and researching the Antarctic Circle presents significant challenges, including extreme cold, strong winds, limited access, and the need to minimize environmental impacts.
4. How does the Antarctic Circle impact global climate?
The Antarctic Circle’s ice sheets and glaciers play a crucial role in regulating global sea levels. Changes in ice formation, melting, and movement within the Antarctic Circle can have significant impacts on global climate patterns and sea level rise.
5. What are the future prospects for the Antarctic Circle?
The future of the Antarctic Circle is uncertain, facing challenges from climate change, resource extraction, and tourism. It is essential to prioritize conservation efforts and sustainable management practices to protect this unique and valuable region.
Tips for Understanding the Antarctic Circle
- Visualize the Antarctic Circle: Use maps and globes to visualize the location and extent of the Antarctic Circle.
- Explore the phenomenon of the polar night and midnight sun: Research the causes and effects of these unique phenomena.
- Learn about the Antarctic Treaty System: Understand the international agreements that govern activities within the Antarctic Circle.
- Follow scientific research on the Antarctic Circle: Stay informed about the latest discoveries and insights related to the region.
Conclusion
The Antarctic Circle, a boundary defined by the Earth’s tilt and its journey around the sun, holds a profound significance beyond its geographical location. It serves as a critical component of the global climate system, a sanctuary for unique biodiversity, a window to the past, and a hub for international scientific research. Understanding the Antarctic Circle and its importance is essential for addressing global challenges like climate change, preserving biodiversity, and ensuring the sustainable management of this unique and valuable region. As we continue to explore and research the Antarctic Circle, we gain valuable insights into our planet’s past, present, and future, ultimately enhancing our understanding of the interconnectedness of life on Earth.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Secrets of the Antarctic Circle: A Geographical and Scientific Exploration. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Navigating The Digital Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide To AT&T’s Service Map For Internet
- Navigating The Keystone Resort Ski Map: A Comprehensive Guide To Exploring The Mountain
- Navigating The Waters: Understanding Nautical Mile Maps
- Navigating The Rails: A Comprehensive Guide To The RTD Train Map
- Navigating Baltimore County: A Guide To The Zoning Map
- A Comprehensive Guide To Parris Island, South Carolina: Navigating The Cradle Of Marines
- Navigating The Waters Of Smith Lake, Alabama: A Comprehensive Guide
- Navigating Kingsland, Texas: A Comprehensive Guide To The City’s Map
Leave a Reply